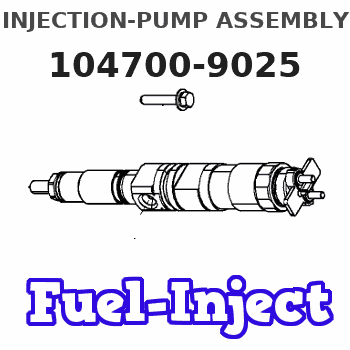
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 460 614 023
9460614023
ZEXEL
104700-9025
1047009025
Rating:
Components :
| 0. | INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY | 104700-9025 |
| 1. | _ | |
| 2. | FUEL INJECTION PUMP | 104600-9025 |
| 3. | NUMBER PLATE | 148643-1100 |
| 4. | _ | |
| 5. | CAPSULE | |
| 6. | ADJUSTING DEVICE | |
| 7. | NOZZLE AND HOLDER ASSY | |
| 8. | Nozzle and Holder | |
| 9. | Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2) | |
| 10. | NOZZLE-HOLDER | |
| 11. | NOZZLE |
Scheme ###:
| 1/6. | [1] | 146601-0700 | PACKING RING |
| 6. | [1] | 146100-0120 | SUPPLY PUMP |
| 9. | [1] | 148103-0400 | COVER |
| 10. | [2] | 139104-0000 | FLAT-HEAD SCREW |
| 12. | [1] | 148200-0520 | DRIVE SHAFT |
| 17. | [1] | 146204-0000 | PLAIN WASHER |
| 20. | [1] | 148210-0120 | ROLLER SET |
| 24. | [1] | 146303-0000 | BEARING PIN |
| 25. | [1] | 146304-0000 | BEARING PIN |
| 26. | [1] | 146305-0000 | CLAMPING BAND |
| 27. | [1] | 146205-0000 | SLOTTED WASHER |
| 29. | [1] | 146220-4320 | CAM PLATE |
| 30. | [1] | 146600-0800 | O-RING |
| 31. | [1] | 146300-1900 | PUMP PLUNGER |
| 32. | [1] | 146301-0000 | SLIDING PIECE |
| 33. | [1] | 146603-1100 | SHIM |
| 34. | [1] | 146306-1800 | COMPRESSION SPRING |
| 34B. | [1] | 146306-2100 | COMPRESSION SPRING |
| 35/1. | [0] | 146603-0700 | SHIM D17.5&7.5T0.60 |
| 35/1. | [0] | 146603-0800 | SHIM D17.5&7.5T0.70 |
| 35/1. | [0] | 146603-0900 | SHIM D17.5&7.5T0.90 |
| 35/1. | [0] | 146603-1000 | SHIM D17.5&7.5T1.00 |
| 35/1. | [0] | 146603-1100 | SHIM D17.5&7.5T1.20 |
| 35/1. | [0] | 146603-3600 | SHIM D17.5&7.5T2.40 |
| 36. | [1] | 146600-0800 | O-RING |
| 37. | [1] | 479765-9121 | TIMER PISTON SENSOR |
| 38. | [2] | 146622-1200 | HEX-SOCKET-HEAD CAP SCREW |
| 39. | [1] | 146310-5600 | COVER |
| 40. | [2] | 146622-1300 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 43. | [1] | 146230-0000 | SHIM |
| 44. | [1] | 146230-0100 | PLAIN WASHER |
| 45. | [1] | 146231-0001 | SLOTTED WASHER |
| 47. | [2] | 146233-0000 | SLOTTED WASHER |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146603-0000 | SHIM D17.0&5.2T0.50 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146603-0100 | SHIM D17.0&5.2T0.80 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146603-0200 | SHIM D17.0&5.2T1.00 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146603-0300 | SHIM D17.0&5.2T1.20 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146603-0400 | SHIM D17.0&5.2T1.50 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146603-0500 | SHIM D17.0&5.2T1.80 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146603-0600 | SHIM D17.0&5.2T2.00 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-1400 | SHIM D17&5.2T0.9 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-1500 | SHIM D17&5.2T1.1 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-1600 | SHIM D17&5.2T1.3 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-1700 | SHIM D17&5.2T1.4 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-1800 | SHIM D17&5.2T1.6 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-1900 | SHIM D17&5.2T1.7 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-5800 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.1 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-5900 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.2 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6000 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.3 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6100 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.4 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6200 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.5 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6300 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.6 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6400 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.7 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6500 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.8 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6600 | SHIM D17&5.2T2.9 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6700 | SHIM D17&5.2T3.0 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6800 | SHIM D17&5.2T3.1 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-6900 | SHIM D17&5.2T3.2 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-7000 | SHIM D17&5.2T3.3 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-7100 | SHIM D17&5.2T3.4 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-7200 | SHIM D17&5.2T0.4 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-7300 | SHIM D17&5.2T0.6 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-7400 | SHIM D17&5.2T0.7 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-7500 | SHIM D17&5.2T1.9 |
| 48/1. | [1] | 146690-7800 | SHIM D17&5.2T0.2 |
| 49. | [2] | 146234-0600 | GUIDE PIN |
| 50. | [1] | 146403-8720 | HYDRAULIC HEAD |
| 50. | [1] | 146403-8720 | HYDRAULIC HEAD |
| 50. | [1] | 146403-8720 | HYDRAULIC HEAD |
| 51. | [1] | 146600-0000 | O-RING |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0000 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.90 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0100 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.92 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0200 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.94 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0300 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.96 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0400 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.98 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0500 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.00 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0600 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.02 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0700 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.04 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0800 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.06 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-0900 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.08 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1000 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.10 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1100 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.12 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1200 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.14 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1300 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.16 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1400 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.18 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1500 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.20 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1600 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.22 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1700 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.24 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1800 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.26 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-1900 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.28 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2000 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.30 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2100 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.32 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2200 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.34 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2300 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.36 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2400 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.38 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2500 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.40 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2600 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.42 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2700 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.44 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2800 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.46 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-2900 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.48 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3000 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.50 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3100 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.52 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3200 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.54 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3300 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.56 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3400 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.58 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3500 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.60 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3600 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.62 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3700 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.64 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3800 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.66 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-3900 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.68 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4000 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.70 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4100 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.72 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4200 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.74 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4300 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.76 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4400 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.78 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4500 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.80 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4600 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.82 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4700 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.84 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4800 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.86 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-4900 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.88 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5000 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T2.90 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5100 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.74 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5200 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.76 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5300 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.78 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5400 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.80 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5500 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.82 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5600 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.84 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5700 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.86 |
| 52/1. | [1] | 146420-5800 | SHIM D9.5&3.0T1.88 |
| 54. | [4] | 146433-0100 | GASKET |
| 55. | [4] | 146430-0320 | DELIVERY-VALVE ASSEMBLY VE4 |
| 56. | [4] | 146432-0801 | COMPRESSION SPRING |
| 58. | [4] | 146440-3120 | FITTING |
| 60. | [3] | 146622-1800 | FLAT-HEAD SCREW |
| 123. | [1] | 146622-0900 | FLAT-HEAD SCREW |
| 130. | [1] | 146421-1920 | CAPSULE |
| 130/2. | [1] | 139508-0200 | GASKET |
| 130/3. | [1] | 146422-0700 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 130/4. | [1] | 146600-0500 | O-RING |
| 133. | [1] | 146600-0600 | O-RING |
| 134. | [1] | 146600-0700 | O-RING |
| 135. | [1] | 146110-3520 | CONTROL VALVE |
| 135/5. | [1] | 146114-0000 | SPRING WASHER |
| 136. | [1] | 148120-0320 | OVER FLOW VALVE |
| 137. | [3] | 139512-0500 | GASKET |
| 138. | [1] | 146669-5821 | INLET UNION |
| 158. | [1] | 146663-5500 | SPACER BUSHING |
| 200. | [1] | 146206-0100 | COILED SPRING |
| 205. | [1] | 029470-4030 | WOODRUFF KEY |
| 230. | [1] | 148613-4721 | BRACKET |
| 236. | [1] | 146622-1400 | HEX-SOCKET-HEAD CAP SCREW |
| 237. | [1] | 146622-1500 | HEX-SOCKET-HEAD CAP SCREW |
| 240. | [1] | 146688-3720 | PULLING ELECTROMAGNET |
| 240/8. | [1] | 146600-1700 | O-RING |
| 243. | [1] | 146621-1000 | UNION NUT |
| 245. | [3] | 139512-0500 | GASKET |
| 246. | [1] | 146125-1000 | EYE BOLT |
| 247. | [1] | 146669-6821 | INLET UNION |
| 248. | [1] | 146663-5600 | SPACER BUSHING |
| 275. | [1] | 148612-1600 | BRACKET |
| 276. | [2] | 146622-1700 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 278. | [2] | 146663-5700 | SPACER BUSHING |
| 282. | [1] | 146622-1900 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-4500 | RESISTER NO. 1 0.18K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-4600 | RESISTER NO. 2 0.30K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-4700 | RESISTER NO. 3 0.43K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-4800 | RESISTER NO. 4 0.62K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-4900 | RESISTER NO. 5 0.82K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-5000 | RESISTER NO. 6 1.10K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-5100 | RESISTER NO. 7 1.50K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-5200 | RESISTER NO. 8 2.00K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-5300 | RESISTER NO. 9 2.70K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-5400 | RESISTER NO.10 3.90K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-5500 | RESISTER NO.11 5.60K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-5600 | RESISTER NO.12 8.20K:OHM |
| 504/1. | [1] | 146649-5700 | RESISTER NO.13 15.00K:OHM |
| 505. | [1] | 148530-3421 | GOVERNOR;ELECTRIC |
| 506. | [3] | 146622-1000 | FLAT-HEAD SCREW |
| 515. | [1] | 106144-1071 | TIMING CONTROL VALVE |
| 515/7. | [1] | 161440-3800 | O-RING |
| 515/8. | [1] | 161440-3700 | O-RING |
| 516. | [2] | 146622-1600 | HEX-SOCKET-HEAD CAP SCREW |
| 530. | [2] | 148650-0000 | BINDER |
| 531. | [1] | 479765-8420 | PULSE GENERATOR |
| 531/6. | [1] | 479773-6500 | O-RING |
| 800S. | [1] | 148009-0620 | PUMP HOUSING |
| 800S/1/6. | [1] | 146601-0700 | PACKING RING |
| 804S. | [1] | 146232-0720 | COMPRESSION SPRING |
| 810S. | [1] | 146600-4620 | REPAIR SET |
| 821S. | [1] | 146210-5720 | ROLLER SET |
| 878S. | [1] | 148600-1300 | SEAL RING |
| 906. | [1] | 148643-1100 | NAMEPLATE |
Include in #2:
104700-9025
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 460 614 023
9460614023
ZEXEL
104700-9025
1047009025
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
104700-9025
9 460 614 023
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4D56T 11CL INJECTION PUMP ASSY COVEC 4 COVEC
4D56T 11CL INJECTION PUMP ASSY COVEC 4 COVEC
9 460 614 023
3310442000 HYUNDAI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4D56T * K 11CL INJECTION PUMP ASSY COVEC 4 COVEC
4D56T * K 11CL INJECTION PUMP ASSY COVEC 4 COVEC
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
1404 Test oil ISO4113orSAEJ967d
Test oil temperature
degC
45
45
50
Nozzle
105780-0060
Bosch type code
NP-DN0SD1510
Nozzle holder
105780-2150
Opening pressure
MPa
13
13
13.3
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
133
133
136
Injection pipe
157805-7320
Injection pipe
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-450
Inside diameter - outside diameter - length (mm) mm 2-6-450
Joint assembly
157641-4720
Tube assembly
157641-4020
Transfer pump pressure
kPa
20
20
20
Transfer pump pressure
kgf/cm2
0.2
0.2
0.2
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Pump chamber pressure
kPa
598
569
627
Pump chamber pressure
kgf/cm2
6.1
5.8
6.4
Basic
*
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Pump chamber pressure
kPa
294
294
Pump chamber pressure
kgf/cm2
3
3
Governor adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Pump chamber pressure
kPa
598
559
637
Pump chamber pressure
kgf/cm2
6.1
5.7
6.5
Governor adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Pump chamber pressure
kPa
735
686
784
Pump chamber pressure
kgf/cm2
7.5
7
8
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Timer stroke
mm
7.7
7.5
7.9
Basic
*
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Timer stroke
mm
1.8
0.3
3.3
Boost compensator adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Timer stroke
mm
5.2
3.1
7.3
Boost compensator adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Timer stroke
mm
7.7
7.4
8
Boost compensator adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
70
70
70
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Timer stroke
mm
4
1.9
6.1
Boost compensator adjustment_06
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Timer stroke
mm
9.75
9.3
10.2
Boost compensator adjustment_07
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
0
0
0
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Timer stroke
mm
0
0
0
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
0
0
0
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Vtps
V
0.51
0.382
0.638
Basic
*
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
0
0
0
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Vtps
V
0.51
0.382
0.638
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Vtps
V
1.925
1.702
2.148
Speed control lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Overflow quantity
cm3/min
550
420
680
0000000901
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
2.73
2.73
2.73
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
63.3
62.8
63.8
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
3.5
Basic
*
_02
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
1.81
1.81
1.81
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
7.3
4.3
10.3
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
2.5
Basic
*
Remarks
Confirmation of difference in delivery
Confirmation of difference in delivery
_03
Pump speed
r/min
2300
2300
2300
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
1.81
1.81
1.81
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
19.4
16.9
21.9
Difference in delivery
mm3/st.
5.5
Basic
*
Remarks
Confirmation of difference in delivery
Confirmation of difference in delivery
_04
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
2.9
2.9
2.9
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
50.3
40.3
60.3
_05
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
1.81
1.81
1.81
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
7.3
4.3
10.3
_06
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
2.59
2.59
2.59
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
51.8
49.3
54.3
_07
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
2.71
2.71
2.71
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60.2
57.7
62.7
_08
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
2.73
2.73
2.73
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
63.3
62.3
64.3
_09
Pump speed
r/min
1900
1900
1900
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
2.56
2.56
2.56
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
53.2
50.7
55.7
_10
Pump speed
r/min
2300
2300
2300
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
1.81
1.81
1.81
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
19.4
16.9
21.9
_11
Pump speed
r/min
2450
2450
2450
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
1
1
1
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
3
Stop lever angle
Pump speed
r/min
1900
1900
1900
U alpha soll + dU alpha soll
V
2.56
2.56
2.56
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
cm3/min
0
0
0
0000001101
Pump speed
r/min
200
200
200
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.7
2.7
2.7
Speed output
N=Measure the actual speed. r/min N+-8
N=Measure the actual speed. r/min N+-8
0000001201
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
TCV duty (%) F TCV 60Hz
%
100
100
100
U alpha soll
V
2.73
2.73
2.73
Temperature output
Measure T = actual output temperature degC T+-5
Measure T = actual output temperature degC T+-5
0000001301
Max. applied voltage
V
8
8
8
Test voltage
V
13
12
14
0000001401
K dimension
mm
3.3
3.2
3.4
KF dimension
mm
5.9
5.8
6
Pre-stroke
mm
0.1
0.08
0.12
Test data Ex:
Injection timing adjustment Comp. resistor/voltage
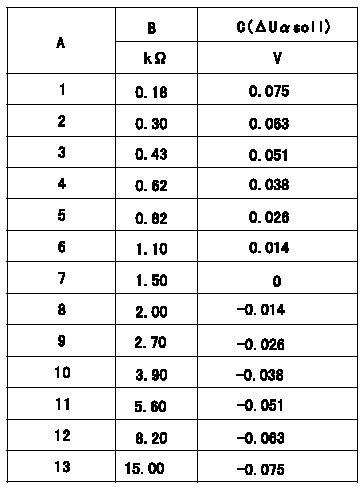
Compensation resistance/compensation voltage comparison
A = Compensation resistor number
B= Compensation resistance
C = Compensation voltage delta U alpha soll
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001601 HARNESS & CONNECTOR
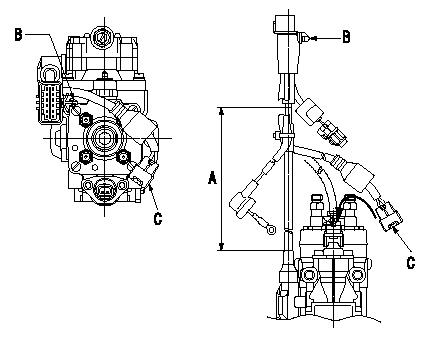
TCV connector assembly specification
(1)Ensure the GE cable is not twisted at section A.
(2)Refer to the figure for the direction of connector clip B.
(3)Route the TCV harness in the direction indicated by the arrows in the figure and install the connector C.
----------
----------
----------
----------
0000001701 HARNESS & CONNECTOR
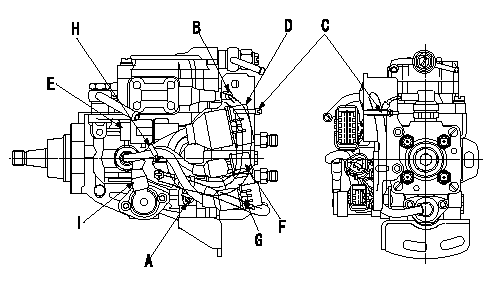
Connector and binder assembly specification
(1)Assemble the connectors and clips in the order A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H.
(2)Fix the GE cable and the FCV cable using the binder C.
(3)Clip the GE cable, the TPS and the P/U harness using clip H. At this time, clip so that the TPS cover is not loose.
(4)Where each connector and sensor harness comes out, ensure that the lead wires are not exposed or visible.
A:Push type clip
B:F.C.V. harness
C:Clip (be careful of installation direction)
D:G.E. Connector
E:Q adjustment connector
F:T.P.S. Connector
G:P/U Connector
H:Clip (be careful of installation direction)
I:T.P.S. Cover
----------
----------
----------
----------
Information:
Introduction
This document provides information about fuel degradation, which can cause a flow restriction of fuel through the fuel system and premature plugging of the filters. These guidelines should be used to guide service personnel in the use of fuels within diesel engines and covers recognized tests in identifying degredated fuels and best practices in storing fuels.This document can be used as a guide, but it does not provide all the information on all practices and procedures for degraded fuels. This document does not provide all the information for best practices for storing and handling fuels. Refer to Caterpillar Commercial Diesel Engine Fluids Recommendations, SEBU6251 for more information.The Thermal Stability and Oxidation Stability of Fuel
Diesel fuels can deteriorate rapidly for a variety of reasons. When the fuel is stressed and stored for long intervals, degradation and oxidation can occur. Degradation and oxidation are complex chemical changes. These changes lead to deposits or sediment from certain hydrocarbons and traces of naturally occurring nitrogen and sulfur containing compounds in the fuel. Fuel composition and environmental factors influences the process.Diesel fuel is being used as a coolant for high pressure fuel injection systems with high temperature fuel wetted walls. This can stress the fuel in the fuel system. The thermal stress and an increase in recirculation fuel temperature is often responsible for fuel degradation and the formation of gums, resins and sediment, which can cause fuel flow restriction through fuel filters and fuel injection systems.Certain products are often left with the fuel in the fuel system for long periods. This exposes the fuel to oxygen. Complex reactions between the oxygen and the fuel components can generate fuel particulates. The particulates in the fuel system can turn into the sludge that is found in fuel tanks, fuel lines and the fuel filters. This will deteriorate the performance of the fuel system. Degradation also leads to a plugged fuel filter, a restriction to the fuel line and deposit formation in the fuel injection nozzle.Biodiesel and blends of biodiesel have poor thermal stability and oxidation stability compared to petroleum distillate diesel fuels. The use of these biodiesels and blends of biodiesel can accelerate the problems that are addressed in this Special Instruction. Using biodiesel blends above the maximum level approved for the engine is not recommended.Thermal and oxidative degradation of diesel fuel can result in a darkening of fuel color. Fuel color is not necessarily an indication of excessive degradation that will lead to the problems outlined in thisSpecial Instruction, but can be an indicator or degradation If concerns arise about the stability of darkened fuel, the thermal oxidation and oxidative stability tests should be run to confirm actual degradation.Thermal Oxidation Stability
Caterpillar recommends the use of the Accelerated Fuel Oil Stability Test (ASTM D6468). This is a test method that determines the instability of a fuel subjected to a thermal degradation process. This test exposes the fuel to actual operating conditions when the fuel cools the injectors during the engine operation.The test is performed by
This document provides information about fuel degradation, which can cause a flow restriction of fuel through the fuel system and premature plugging of the filters. These guidelines should be used to guide service personnel in the use of fuels within diesel engines and covers recognized tests in identifying degredated fuels and best practices in storing fuels.This document can be used as a guide, but it does not provide all the information on all practices and procedures for degraded fuels. This document does not provide all the information for best practices for storing and handling fuels. Refer to Caterpillar Commercial Diesel Engine Fluids Recommendations, SEBU6251 for more information.The Thermal Stability and Oxidation Stability of Fuel
Diesel fuels can deteriorate rapidly for a variety of reasons. When the fuel is stressed and stored for long intervals, degradation and oxidation can occur. Degradation and oxidation are complex chemical changes. These changes lead to deposits or sediment from certain hydrocarbons and traces of naturally occurring nitrogen and sulfur containing compounds in the fuel. Fuel composition and environmental factors influences the process.Diesel fuel is being used as a coolant for high pressure fuel injection systems with high temperature fuel wetted walls. This can stress the fuel in the fuel system. The thermal stress and an increase in recirculation fuel temperature is often responsible for fuel degradation and the formation of gums, resins and sediment, which can cause fuel flow restriction through fuel filters and fuel injection systems.Certain products are often left with the fuel in the fuel system for long periods. This exposes the fuel to oxygen. Complex reactions between the oxygen and the fuel components can generate fuel particulates. The particulates in the fuel system can turn into the sludge that is found in fuel tanks, fuel lines and the fuel filters. This will deteriorate the performance of the fuel system. Degradation also leads to a plugged fuel filter, a restriction to the fuel line and deposit formation in the fuel injection nozzle.Biodiesel and blends of biodiesel have poor thermal stability and oxidation stability compared to petroleum distillate diesel fuels. The use of these biodiesels and blends of biodiesel can accelerate the problems that are addressed in this Special Instruction. Using biodiesel blends above the maximum level approved for the engine is not recommended.Thermal and oxidative degradation of diesel fuel can result in a darkening of fuel color. Fuel color is not necessarily an indication of excessive degradation that will lead to the problems outlined in thisSpecial Instruction, but can be an indicator or degradation If concerns arise about the stability of darkened fuel, the thermal oxidation and oxidative stability tests should be run to confirm actual degradation.Thermal Oxidation Stability
Caterpillar recommends the use of the Accelerated Fuel Oil Stability Test (ASTM D6468). This is a test method that determines the instability of a fuel subjected to a thermal degradation process. This test exposes the fuel to actual operating conditions when the fuel cools the injectors during the engine operation.The test is performed by
Have questions with 104700-9025?
Group cross 104700-9025 ZEXEL
Hyundai
104700-9025
9 460 614 023
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4D56T
4D56T
