Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 610 818
9400610818
ZEXEL
101696-9751
1016969751
Rating:
Service parts 101696-9751 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
16600-Z5607
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
19.6{200}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 610 818
9400610818
ZEXEL
101696-9751
1016969751
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
134424-1520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
162
147
177
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.65
1.5
1.8
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
3.9
3.85
3.95
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
13.6
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
92.5
90.5
94.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3.5
3.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
17
15.2
18.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(13.6)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
92.5
91.5
93.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
28.7
28.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
215
215
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
(R1+0.3)
+0.05-0.
15
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
99.5
96.3
102.7
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
28.7
28.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
215
215
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R2(R1-0.
2)
Pump speed
r/min
420
420
420
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
80
76.8
83.2
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
28.7
28.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
215
215
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
R2-1.15
Pump speed
r/min
420
420
420
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
56.5
54.5
58.5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_07
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
105
105
125
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
420
420
420
Rack position
R2-1.15
Boost pressure
kPa
6.7
5.4
8
Boost pressure
mmHg
50
40
60
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
420
420
420
Rack position
R2(R1-0.
2)
Boost pressure
kPa
15.3
15.3
15.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
115
115
115
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1170--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1120
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1400
Advance angle
deg.
3
2.5
3.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
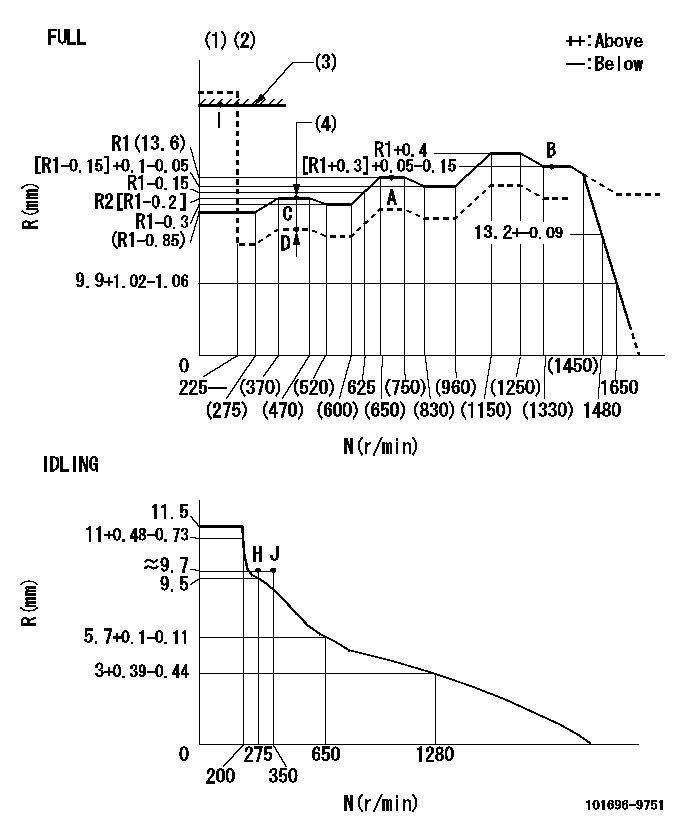
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=M68 BCL=1.15+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=M68 BCL=1.15+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=36mm
----------
a=26deg+-5deg b=39deg+-3deg
----------
aa=36mm
----------
a=26deg+-5deg b=39deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
----------
aa=42mm
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=27deg+-5deg
----------
aa=42mm
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=27deg+-5deg
Timing setting
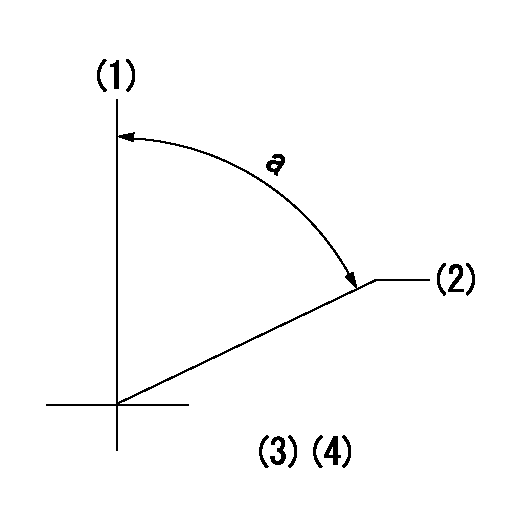
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's threaded hole at the No. 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
Information:
Operating with fuels that do not meet Caterpillar's recommendations can cause the following effects: starting difficulty, poor combustion, deposits in the fuel injectors, reduced service life of the fuel system, deposits in the combustion chamber and reduced service life of the engine.
Cold-soaked starts occur when the engine has not been operated for a time, allowing the crankcase oil and the fuel to become more viscous due to cooler ambient temperatures. Consult the factory if the viscosity of the cold-soaked fuel in the fuel system will be above 20 cSt.
If a particular crude oil exceeds the limits that are listed in Table 1, 3600 Series diesel engines that are configured to use heavy fuel oil may be utilized. Consult your Cat dealer or Customer Service for information about fuel that exceeds the limits that are listed in Table 1.Note: The Crude Oil Specification for Cat 3600 and C280 Series Diesel Engines is applicable to 3500 Series Diesel Engines. Consult your Cat dealer for guidance.
Use of permissible fuels, such as some crude oils, some blends of crude oil with distillate fuel, some biodiesel, and some marine diesel fuel, can result in higher maintenance costs and reduced engine life.

