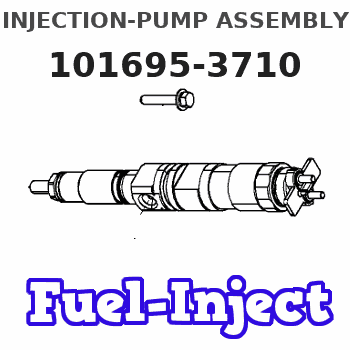
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 616 125
9400616125
ZEXEL
101695-3710
1016953710
KOMATSU
6207711961
6207711961
Rating:
Service parts 101695-3710 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6207-11-3102
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
19.6{200}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 616 125
9400616125
ZEXEL
101695-3710
1016953710
KOMATSU
6207711961
6207711961
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101695-3710
9 400 616 125
6207711961 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S6D95L K
S6D95L K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.4
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
54.7
53.7
55.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
450
450
450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12.5
11.5
13.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
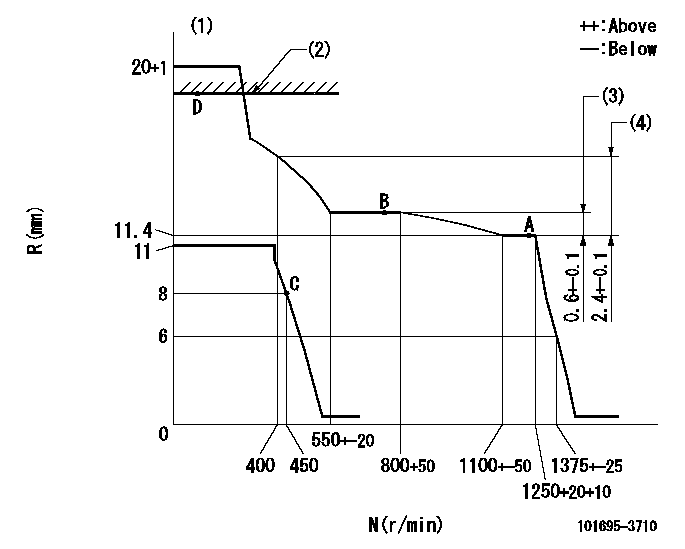
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)RACK LIMIT: RAL
(3)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
(4)Rack difference between N = N3 and N = N4
----------
K=8 RAL=15+0.2mm N1=1250r/min N2=800r/min N3=1250r/min N4=400r/min
----------
----------
K=8 RAL=15+0.2mm N1=1250r/min N2=800r/min N3=1250r/min N4=400r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
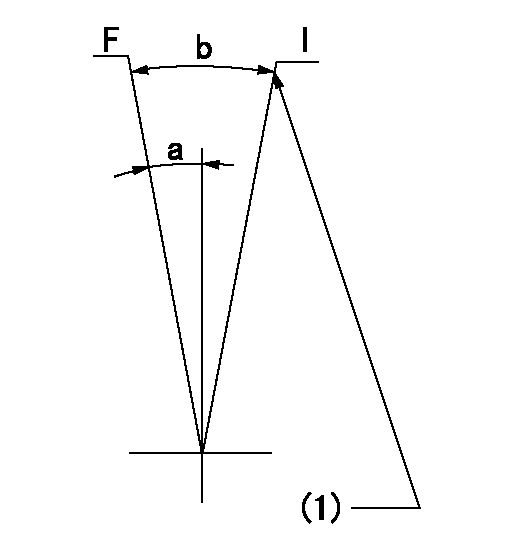
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=29deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=29deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(30deg)
----------
----------
a=(30deg)
Information:
A measurement of fuel consumption is used to check fuel system performance. If fuel consumption of an engine is within the tolerance of specifications shown in the Fuel Setting And Related Information Fiche, the fuel system is performing correctly and no additional time should be spent checking fuel delivery.Fuel consumption - If the specified amount of fuel is being injected into the engine, the fuel delivery specification is being met. Therefore, the basic fuel system (fuel pump and lines, transfer pump, filters and primary fuel pressure) is within functional limits. Additional time spent troubleshooting these components is probably not justified.Fuel system timing - Fuel cannot be burned efficiently if it is not injected into the cylinder at the correct time. Because engines only develop horsepower when they are running, timing must be measured when they are running. The pin timing of the engine is not adequate. Timing must be measured throughout the speed range (this also checks the timing advance operation).Intake manifold pressure - Manifold pressure is an indication of the overall health of the engine. Boost is affected by any one or all of the following: fuel consumption, compression (valve condition, piston ring condition), turbocharger performance, intake restriction (air filters), exhaust restriction (muffler) or timing.Recommended Procedure With Chassis Dynamometer
Possible Causes/Corrections 1. Check Records Used To Determine Fuel ConsumptionMake sure the records are accurate. The minimum period for accurate fuel records is one month or 10,000 miles. Check the tires (air pressure and size), the gap between the tractor and trailer, air deflectors, trailer width, trailer type, engine cooling fan and driver habits. See "Owner/Operator Input" section for more information on the questions that should be asked. 2. Minor Operating FaultsTo help identify a problem before a more involved troubleshooting procedure is started, follow the procedure given in the "Primary Engine Checks" section. 3. Fuel Ratio Control Out Of Adjustment Or DefectiveFollow the procedure in the Testing and Adjusting section of this Service Manual. 4. Check Engine PerformanceDo a Power Analysis Report (PAR), Level II, to check engine performance. Refer to LEBV2810 and SEHS7886 for the tooling and procedures to use. Be sure to make a record of the temperatures for inlet air, fuel (at filter base), lubricating oil and coolant. Also, check for excessive exhaust smoke.At this point, the governor fuel settings should be verified. See the Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual for the correct procedures to use. Also refer back to the information learned earlier (see "Owner Operator Input" section) about truck specifications and application and judge whether or not the engine is performing as expected or customer expectation is realistic. 5. Worn Fuel NozzlesCheck the horsepower on a dynamometer as in Step 4 above. Make a replacement of the fuel injection nozzles and check the horsepower output again. If there is more than 10 hp difference the old nozzles had eroded orifices and were causing high fuel rate.An alternate test is to lower the fuel setting to get the correct hp output.
Possible Causes/Corrections 1. Check Records Used To Determine Fuel ConsumptionMake sure the records are accurate. The minimum period for accurate fuel records is one month or 10,000 miles. Check the tires (air pressure and size), the gap between the tractor and trailer, air deflectors, trailer width, trailer type, engine cooling fan and driver habits. See "Owner/Operator Input" section for more information on the questions that should be asked. 2. Minor Operating FaultsTo help identify a problem before a more involved troubleshooting procedure is started, follow the procedure given in the "Primary Engine Checks" section. 3. Fuel Ratio Control Out Of Adjustment Or DefectiveFollow the procedure in the Testing and Adjusting section of this Service Manual. 4. Check Engine PerformanceDo a Power Analysis Report (PAR), Level II, to check engine performance. Refer to LEBV2810 and SEHS7886 for the tooling and procedures to use. Be sure to make a record of the temperatures for inlet air, fuel (at filter base), lubricating oil and coolant. Also, check for excessive exhaust smoke.At this point, the governor fuel settings should be verified. See the Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual for the correct procedures to use. Also refer back to the information learned earlier (see "Owner Operator Input" section) about truck specifications and application and judge whether or not the engine is performing as expected or customer expectation is realistic. 5. Worn Fuel NozzlesCheck the horsepower on a dynamometer as in Step 4 above. Make a replacement of the fuel injection nozzles and check the horsepower output again. If there is more than 10 hp difference the old nozzles had eroded orifices and were causing high fuel rate.An alternate test is to lower the fuel setting to get the correct hp output.
Have questions with 101695-3710?
Group cross 101695-3710 ZEXEL
Komatsu
101695-3710
9 400 616 125
6207711961
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S6D95L
S6D95L