Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101691-4130
1016914130
ISUZU
1156002480
1156002480

Rating:
Service parts 101691-4130 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
4.
SUPPLY PUMP
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
9-15300-184-2
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
9.8{100}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101691-4130
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104745-8020
as _
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101691-4130
1016914130
ISUZU
1156002480
1156002480
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle holder
105031-2480
Bosch type code
KB69SD273NP6
Opening pressure
MPa
9.8
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
100
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
132424-0620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
2.2
2.15
2.25
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
13
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
117.5
115.2
119.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
13
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
124
120.3
127.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
225
225
225
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
175
172.7
177.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-13
13
Fixing the rack
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
400+-50
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
Advance angle
deg.
0.6
0.1
1.1
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
1.4
0.9
1.9
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1150
Advance angle
deg.
2
1.5
2.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
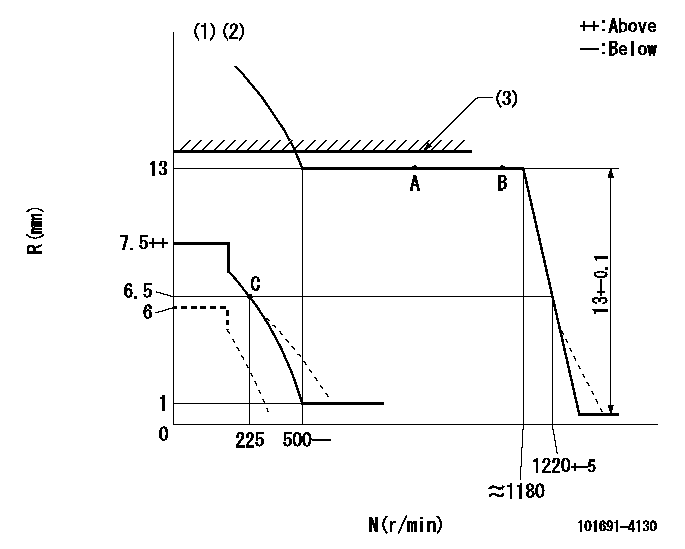
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Beginning of damper spring operation: DL
(2)Set the load lever's stop position so that R = aa (N = 0).
(3)RACK LIMIT: RAL
----------
DL=6-0.2mm aa=6mm RAL=13+0.2mm
----------
----------
DL=6-0.2mm aa=6mm RAL=13+0.2mm
----------
0000000901
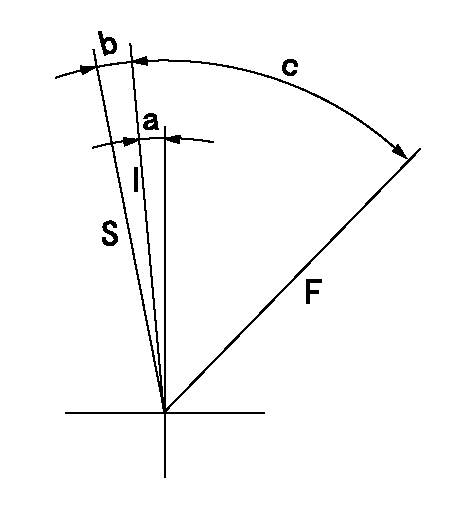
F:Full load
I:Idle
S:Stop
----------
----------
a=6deg+-5deg b=6deg+-5deg c=46deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=6deg+-5deg b=6deg+-5deg c=46deg+-3deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=275r/min Ra=6.5mm
----------
----------
N1=275r/min Ra=6.5mm
----------
Information:
Outside Leaks
Possible Causes/CorrectionsLeaks in Hoses or Connections
Check all hoses and connections for visual signs of leakage. If no leaks are seen, look for damage to hoses or loose clamps.Leaks in the Radiator and/or Expansion Tank
Put pressure to the radiator and/or expansion tank with the 9S8140 Cooling System Pressurizing Pump Group and check for leaks.Leaks in the Heater
Put pressure to the cooling system with the 9S8140 Cooling System Pressurizing Pump Group and check the heater for leaks.Leaks in the Water Pump
Check the water pump for leaks before starting the engine, then start the engine and look for leaks. If there are leaks at the water pump, repair or install a new water pump.Cylinder Head Gasket Leakage
Look for leaks along the surface of the cylinder head gasket. If you see leaks, install a new head gasket.Coolant Leaks At The Overflow Tube
Possible Causes/CorrectionsBad Pressure Cap or Relief Valve
Check the sealing surfaces of the pressure cap and the radiator to be sure the cap is sealing correctly. Check the opening pressure and sealing ability of the pressure cap or relief valve with the 9S8140 Cooling System Pressurizing Pump Group.Engine Runs Too Hot
If coolant temperature is too high, pressure will be high enough to move the cap off of the sealing surface in the radiator and cause coolant loss through the overflow tube. See "Overheating" in Cooling System Troubleshooting section.Expansion Tank Too Small or Installed Wrong
The expansion tank can be either a part of the radiator or it can be installed separately from the radiator. The expansion tank must be large enough to hold the expansion of the coolant as it gets warm or has sudden changes in pressure. Make sure the expansion tank is installed correctly, and the size is according to the recommendations of the truck manufacturer.Cylinder Head Gasket Leakage or Crack(s) in Cylinder Head or Cylinder Block
Remove the radiator cap and, with the engine running, look for air bubbles in the coolant. Bubbles in the coolant are a sign of probable leakage at the head gasket. Remove the cylinder head from the engine. Check cylinder head, cylinder walls and head gasket surface of the cylinder block for cracks. When the head is installed, use a new head gasket, spacer plate gasket, water seals, and O-ring seals.Inside Leakage
Possible Causes/CorrectionsCylinder Head Gasket Leakage
If the cylinder head gasket leaks between a water passage and an opening into the crankcase, coolant will get into the crankcase.Crack(s) in Cylinder Head
Crack(s) in the upper surface of the cylinder head, or an area between a water passage and an opening into the crankcase, can allow coolant to get into the crankcase.Crack(s) in Cylinder Block
Crack(s) in the cylinder block between a water passage and the crankcase will let coolant get into the crankcase.
Possible Causes/CorrectionsLeaks in Hoses or Connections
Check all hoses and connections for visual signs of leakage. If no leaks are seen, look for damage to hoses or loose clamps.Leaks in the Radiator and/or Expansion Tank
Put pressure to the radiator and/or expansion tank with the 9S8140 Cooling System Pressurizing Pump Group and check for leaks.Leaks in the Heater
Put pressure to the cooling system with the 9S8140 Cooling System Pressurizing Pump Group and check the heater for leaks.Leaks in the Water Pump
Check the water pump for leaks before starting the engine, then start the engine and look for leaks. If there are leaks at the water pump, repair or install a new water pump.Cylinder Head Gasket Leakage
Look for leaks along the surface of the cylinder head gasket. If you see leaks, install a new head gasket.Coolant Leaks At The Overflow Tube
Possible Causes/CorrectionsBad Pressure Cap or Relief Valve
Check the sealing surfaces of the pressure cap and the radiator to be sure the cap is sealing correctly. Check the opening pressure and sealing ability of the pressure cap or relief valve with the 9S8140 Cooling System Pressurizing Pump Group.Engine Runs Too Hot
If coolant temperature is too high, pressure will be high enough to move the cap off of the sealing surface in the radiator and cause coolant loss through the overflow tube. See "Overheating" in Cooling System Troubleshooting section.Expansion Tank Too Small or Installed Wrong
The expansion tank can be either a part of the radiator or it can be installed separately from the radiator. The expansion tank must be large enough to hold the expansion of the coolant as it gets warm or has sudden changes in pressure. Make sure the expansion tank is installed correctly, and the size is according to the recommendations of the truck manufacturer.Cylinder Head Gasket Leakage or Crack(s) in Cylinder Head or Cylinder Block
Remove the radiator cap and, with the engine running, look for air bubbles in the coolant. Bubbles in the coolant are a sign of probable leakage at the head gasket. Remove the cylinder head from the engine. Check cylinder head, cylinder walls and head gasket surface of the cylinder block for cracks. When the head is installed, use a new head gasket, spacer plate gasket, water seals, and O-ring seals.Inside Leakage
Possible Causes/CorrectionsCylinder Head Gasket Leakage
If the cylinder head gasket leaks between a water passage and an opening into the crankcase, coolant will get into the crankcase.Crack(s) in Cylinder Head
Crack(s) in the upper surface of the cylinder head, or an area between a water passage and an opening into the crankcase, can allow coolant to get into the crankcase.Crack(s) in Cylinder Block
Crack(s) in the cylinder block between a water passage and the crankcase will let coolant get into the crankcase.
