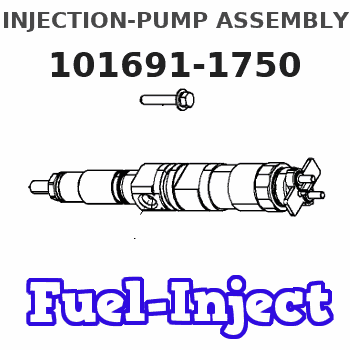
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 615 970
9400615970
ZEXEL
101691-1750
1016911750
MITSUBISHI
3116142031
3116142031
Rating:
Service parts 101691-1750 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
31161-18000
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
11.8{120}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101691-1750
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 615 970
9400615970
ZEXEL
101691-1750
1016911750
MITSUBISHI
3116142031
3116142031
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101691-1750
9 400 615 970
3116142031 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6DC20 * K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
6DC20 * K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-3-4-
5-6
Pre-stroke
mm
2.2
2.15
2.25
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 45 44.5 45.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-4 deg. 165 164.5 165.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 165 164.5 165.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-5 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-6 deg. 285 284.5 285.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 285 284.5 285.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
12.3
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
111
107.5
114.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
10.5
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
87
82.5
91.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-5
5
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
6.3+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
200
200
200
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12
9.4
14.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
1200
1200
1200
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
112
108.5
115.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
14.5++
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
115
115
Fixing the lever
*
Remarks
Excess fuel for starting.
Excess fuel for starting.
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500+-50
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
750
Advance angle
deg.
2
1.4
2.6
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1000
Advance angle
deg.
4
3.4
4.6
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1250
Advance angle
deg.
6.5
5.9
7.1
Timer adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
-
Advance angle
deg.
10
10
10
Remarks
Measure the actual speed, stop
Measure the actual speed, stop
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
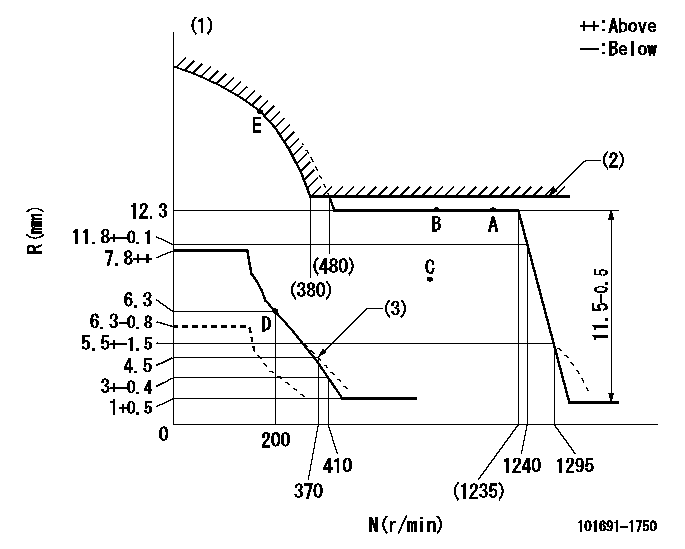
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(2)Rack limit using excess fuel device for starting; RAL (at N = N1).
(3)Damper spring setting
----------
RAL=12.3+0.2mm N1=430r/min
----------
----------
RAL=12.3+0.2mm N1=430r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
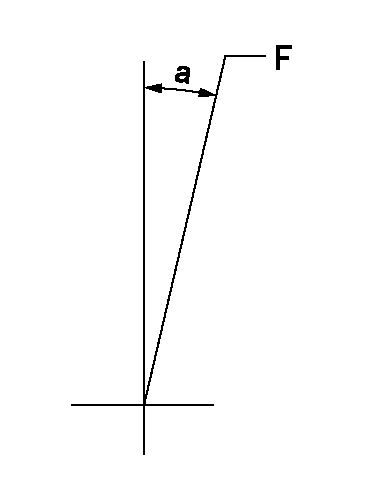
F:Full speed
----------
----------
a=(12.5deg)+-5deg
----------
----------
a=(12.5deg)+-5deg
0000000901
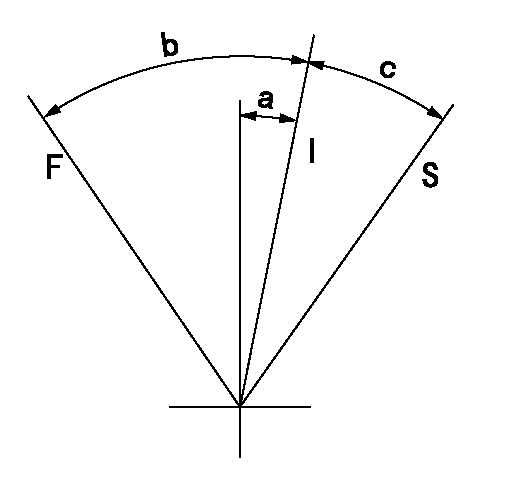
F:Full load
I:Idle
S:Stop
----------
----------
a=11deg+-5deg b=41deg+-3deg c=10deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=11deg+-5deg b=41deg+-3deg c=10deg+-3deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=325r/min Ra=6.3+0.2mm
----------
----------
N1=325r/min Ra=6.3+0.2mm
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(10deg)
----------
----------
a=(10deg)
Information:
Illustration 13 g02915447
Plugged DOC
The DOC utilizes a “pass-through” technology, which is different from the “wall flow” design of a DPF. When a light is shined through the DOC, a visible light should be able to pass through. Utilize a flashlight to check for a plugged DOC face. Aim the flashlight into the DOC inlet, visible light should be seen through the DOC. A plugged DOC can be caused by high oil consumption, not recommended fuel additives, or wrong engine oil types. Refer to the Operation and Maintenance Manual for recommended fluids to use. If light cannot be seen on the outlet of the DOC, then replace the DOC.CRS Bodies
Illustration 14 g06342815
Combustion Group
(1) Head Group - Combustion
(2) Gasket
(3) Tube
(4) Body Assembly - Exhaust CombustionCRS Combustion Body (4) contains the flame necessary for CRS Regeneration. There are two combustion stages that occur within the CRS Body: the primary and secondary combustion. The primary combustion of air and fuel occur within Tube (3) to create the CRS flame immediately following Head Group (1). The secondary combustion of the CRS flame and exhaust gas from the turbocharger occur within Body Assembly (4).The body assembly is the only salvageable part of the combustion group. The body assembly must be cleaned, inspected, and pressure tested prior to reuse.Cleaning
Start by isolating the CRS body from all other CRS exhaust components. Remove the head group, the mounting studs, the tube, and the two gaskets.The gasket area and the bellows joints are the two areas of the CRS body that must be cleaned thoroughly to make a proper seal.Cleaning the remainder of the CRS body is not required. If cleaning the CRS body is desired, then first perform the visual inspection, vacuum inspection, and welding procedures prior to washing the CRS body. This step is to ensure that the CRS body is salvageable, not cracked, and to keep water from getting trapped behind the heat shield.If washing is preferred, then use soap and water as a cleaning solution. Do not submerge the CRS body to prevent water from becoming trapped between the heat shield and the CRS body. A cylinder washing brush, a wire brush with handle, and a greenScotch Brite pads are all acceptable cleaning equipment. Removal of all diesel particulates is not required for inspection.
Do not use any combustible solvents to clean the CRS body.
Visual Inspection
A visual inspection of the CRS body must be completed, special equipment or crack detecting solution is not required. Visually inspect the exterior of the CRS body. Small cracks and/or punctures found on the stainless steel heat shield is normal and should be expected. Inspect the bellows sealing joints and the CRS head mating surface for visual damage.Light surface rust is typically not a problem unless rust is found on a bellows joint or the CRS gasket mating surface. Light rust in these two areas must be removed using a Scotch Brite pad.Serviceability
All bolts, studs, and clamps are not reusable and must be replaced with new components.Any thread damage in the mounting
Have questions with 101691-1750?
Group cross 101691-1750 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
101691-1750
9 400 615 970
3116142031
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6DC20
6DC20
