Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101641-9211
1016419211

Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101641-9211
1016419211
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
2.3
2.25
2.35
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
13.7
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
48.3
47.2
49.4
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9.9+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
360
360
360
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
7.5
6.4
8.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(13.7)
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
48.3
47.2
49.4
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
53.3
53.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
400
400
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1-0.7
Pump speed
r/min
2000
2000
2000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
47.2
45.2
49.2
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
53.3
53.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
400
400
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R2(12.7)
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
34.6
32.6
36.6
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
R2(12.7)
Boost pressure
kPa
15.3
12.6
18
Boost pressure
mmHg
115
95
135
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
R1(13.7)
Boost pressure
kPa
46.7
40
46.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
350
300
350
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
550--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
2.2
1.7
2.7
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1900
Advance angle
deg.
6
5.5
6.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment

N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=74 BCL=1+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=74 BCL=1+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
----------
a=37deg+-5deg b=(38deg)+-3deg
----------
----------
a=37deg+-5deg b=(38deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle
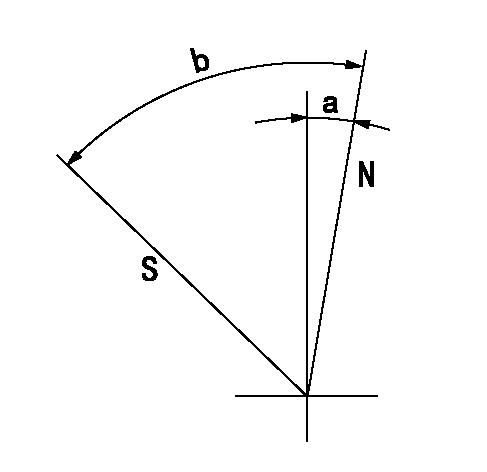
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
Timing setting
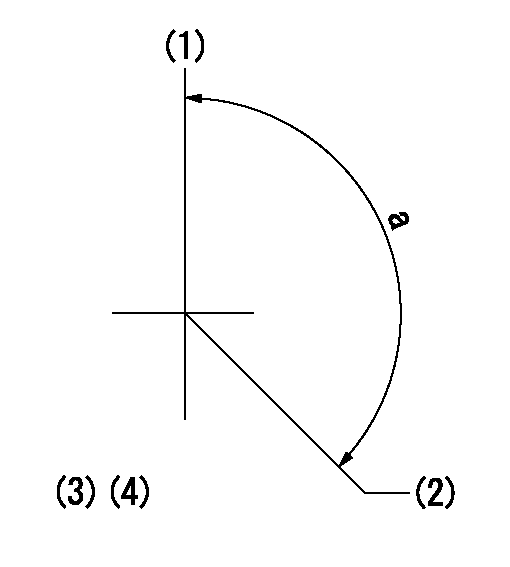
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark 'Y' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=20deg
----------
a=(130deg)
----------
aa=20deg
----------
a=(130deg)
Information:
(3) Check the unit seals installed in the impeller and water pump case for damage and wear. If defects are evident, or when water leaks during operation, replace the unit seals with new ones. Whenever the unit seal is removed, it must be replaced with a new one. (4) Using a gear puller or press, remove the ball bearings. Do not remove the ball bearing except for replacement. (5) When the impeller and flange are removed from the water pump shaft, it may result in insufficient interference. If the interference is below the specification even reassembly is two times or less they must be replaced with new ones.Reassembly
5.3 Thermostat
Removal and installation
Do not remove the thermostat case and front hanger unless they cause water leak or other defects.Inspection
Agitate water in the container with the stirrer to obtain uniform temperature. For the inspection, use the following procedures. (1) Slowly heat water to the thermostat valve opening temperature. Keep this condition for about five minutes and make sure that the valve is open.(2) Raise the water temperature up to 90°C. Keep the condition for five minutes and measure the lift of pellet.(3) Lower temperature down to 65°C or below and ensure that the valve is fully closed. If the thermostat is found defective in any of the above items, replace it with a new one. Support the thermostat so that the heat source will not directly heat the thermostat.5.4 Radiator
Inspection (1) Using a copper wire or similar device, remove dirt, mud, and bugs from the front of radiator core with care to prevent damage to tubings. (2) Connect a hose to one of the radiator ports, cap the other port, and immerse the radiator into water. Using a radiator cap tester, force the compressed air under the specified inspection pressure from the hose end to check for leaks.If there is a leak, resolder the point of leakage or replace the radiator.(3) Inspection of Radiator Cap Check the spring tension and sealing condition of the pressure valve and vent valve. If defective, replace. Check the pressure valve opening pressure, using a radiator cap tester.5.5 Inspection and Adjustment of V-belt Tension
Adjust the belt tension to obtain the specified belt deflection when the center of each belt is pressed with a force of approximately 98 N (10 kgf). 1. A slack belt can be a cause of overheating and undercharge.2. An excessively tight belt may result in damaged bearings and belts.3. When paired belts are to be replaced, be sure to replace both.5.6 Cleaning of Cooling System
If the radiator is used for a long time, rust, scale, mud, etc. are deposited inside, resulting in overheat. Clean the cooling system with city water by using the following procedures.The city water to be used should have the following properties.Required properties of city water 1. Use a cleaning solution if the radiator is seriously obstructed or coolant is seriously contaminated.2. When the cooling system is cleaned or washed with water, make sure that the coolant temperature is
5.3 Thermostat
Removal and installation
Do not remove the thermostat case and front hanger unless they cause water leak or other defects.Inspection
Agitate water in the container with the stirrer to obtain uniform temperature. For the inspection, use the following procedures. (1) Slowly heat water to the thermostat valve opening temperature. Keep this condition for about five minutes and make sure that the valve is open.(2) Raise the water temperature up to 90°C. Keep the condition for five minutes and measure the lift of pellet.(3) Lower temperature down to 65°C or below and ensure that the valve is fully closed. If the thermostat is found defective in any of the above items, replace it with a new one. Support the thermostat so that the heat source will not directly heat the thermostat.5.4 Radiator
Inspection (1) Using a copper wire or similar device, remove dirt, mud, and bugs from the front of radiator core with care to prevent damage to tubings. (2) Connect a hose to one of the radiator ports, cap the other port, and immerse the radiator into water. Using a radiator cap tester, force the compressed air under the specified inspection pressure from the hose end to check for leaks.If there is a leak, resolder the point of leakage or replace the radiator.(3) Inspection of Radiator Cap Check the spring tension and sealing condition of the pressure valve and vent valve. If defective, replace. Check the pressure valve opening pressure, using a radiator cap tester.5.5 Inspection and Adjustment of V-belt Tension
Adjust the belt tension to obtain the specified belt deflection when the center of each belt is pressed with a force of approximately 98 N (10 kgf). 1. A slack belt can be a cause of overheating and undercharge.2. An excessively tight belt may result in damaged bearings and belts.3. When paired belts are to be replaced, be sure to replace both.5.6 Cleaning of Cooling System
If the radiator is used for a long time, rust, scale, mud, etc. are deposited inside, resulting in overheat. Clean the cooling system with city water by using the following procedures.The city water to be used should have the following properties.Required properties of city water 1. Use a cleaning solution if the radiator is seriously obstructed or coolant is seriously contaminated.2. When the cooling system is cleaned or washed with water, make sure that the coolant temperature is