Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 613 384
9400613384
ZEXEL
101608-6520
1016086520
Rating:
Service parts 101608-6520 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME440837
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101608-6520
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104700-0510
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 613 384
9400613384
ZEXEL
101608-6520
1016086520
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.2
3.15
3.25
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
8.7
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
94.5
93.5
95.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
90.6
90.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
680
680
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
515
515
515
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8
6.7
9.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
8.9++
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
65
65
70
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Rack position
R1-1
Boost pressure
kPa
32
25.3
38.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
240
190
290
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Rack position
R1(8.7)
Boost pressure
kPa
81.3
78.6
84
Boost pressure
mmHg
610
590
630
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
0
Advance angle
deg.
3
2
3
Load
0/4
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
650+-25
Advance angle
deg.
3
2
3
Load
0/4
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
750+-25
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Load
0/4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
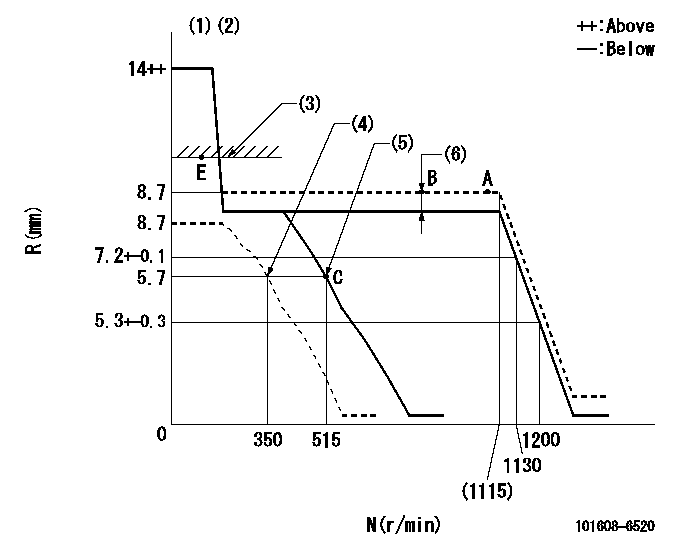
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Set idle sub-spring
(5)Main spring setting
(6)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
K=14 BCL=1+-0.1mm
----------
----------
K=14 BCL=1+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
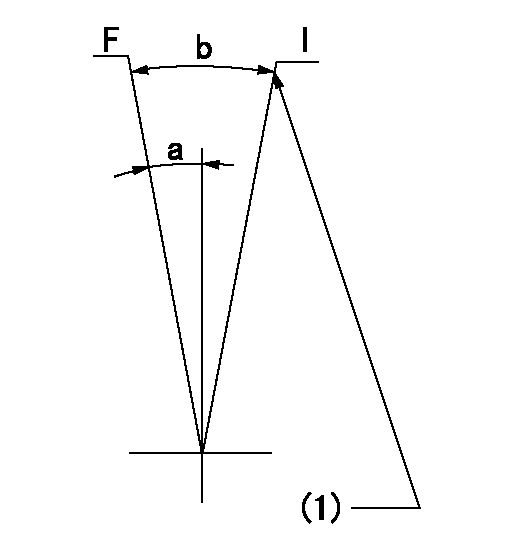
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=6.5deg+-5deg b=19deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=6.5deg+-5deg b=19deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Pump speed aa and rack position bb (to be sealed at delivery)
(2)Normal
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.5mm
----------
a=21deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.5mm
----------
a=21deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark '3' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(130deg)
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(130deg)
Information:
Determination Of Overhaul Timing
Generally, the engine needs an overhaul when the compression pressure of the engine becomes low, and the amounts of engine oil consumption and blow-by gas increase.Reduced power output, increased fuel consumption, low oil pressure, difficult in starting, and increased operating noise are also signs that suggest the need for an overhaul; however, since these problems can be caused by various factors, they do not serve as reliable criteria for determining the need for an overhaul.Reduced compression pressure manifests a variety of symptoms, thus making it difficult to accurately determine when the engine needs an overhaul. The following shows typical problems caused by reduced compression pressure.(1) Decreased output power(2) Increased fuel consumption(3) Increased engine oil consumption(4) Increased blow-by gas from breather due to leakage of combustion gas through worn cylinder liners and piston rings(5) Increased gas leakage due to poor seating of inlet and exhaust valves(6) Difficulty in starting(7) Increased noise from engine parts(8) Abnormal exhaust color after warm-up operationThe engine can exhibit these conditions in various combinations.Some of these problems are directly caused by worn engine parts, while others are not.Phenomena described in (2) and (6) can also result from improper injection volume, incorrect fuel injection timing, worn plungers, defective nozzles, and faulty conditions of electrical devices such as battery, starter and alternator.The most valid reason to overhaul an engine is a decrease in the compression pressure due to worn cylinder liners and pistons, as described in (4), and once this is determined, other symptoms should be taken into consideration in order to make the final judgement of whether the engine needs an overhaul.Measurement of Compression Pressure
Measurement of compression pressurePreparation For Inspection
Check the following before inspection.(1) Make sure that the engine oil, air cleaner, starter, battery, etc. are in normal operating condition.Inspection
(1) Move the control lever to the Stop position.(2) Remove the glow plugs from all cylinders, and attach the gage adapter and compression gage to the cylinder to be tested.(3) Crank the engine with the starter, and read the compression gage indication when the indication stabilizes.(4) If the measured compression pressure is lower than the limit, consider overhauling the engine.
(a) Measure the compression pressure in all cylinders.(b) As compression pressure varies with the engine speed, measure the engine speed at the same time.
Measure the compression pressure while the engine is running at 150 to 200 min-1. The oil and coolant temperatures should be between 20 and 30 °C [68 and 86°F].
It is important to regularly check the compression pressure so that you can tell the difference. * New or overhauled engines have slightly higher compression pressure.* The compression pressure settles to the standard value as the piston rings and valve seats fit in.* As wear progresses further, the compression pressure drops.
Generally, the engine needs an overhaul when the compression pressure of the engine becomes low, and the amounts of engine oil consumption and blow-by gas increase.Reduced power output, increased fuel consumption, low oil pressure, difficult in starting, and increased operating noise are also signs that suggest the need for an overhaul; however, since these problems can be caused by various factors, they do not serve as reliable criteria for determining the need for an overhaul.Reduced compression pressure manifests a variety of symptoms, thus making it difficult to accurately determine when the engine needs an overhaul. The following shows typical problems caused by reduced compression pressure.(1) Decreased output power(2) Increased fuel consumption(3) Increased engine oil consumption(4) Increased blow-by gas from breather due to leakage of combustion gas through worn cylinder liners and piston rings(5) Increased gas leakage due to poor seating of inlet and exhaust valves(6) Difficulty in starting(7) Increased noise from engine parts(8) Abnormal exhaust color after warm-up operationThe engine can exhibit these conditions in various combinations.Some of these problems are directly caused by worn engine parts, while others are not.Phenomena described in (2) and (6) can also result from improper injection volume, incorrect fuel injection timing, worn plungers, defective nozzles, and faulty conditions of electrical devices such as battery, starter and alternator.The most valid reason to overhaul an engine is a decrease in the compression pressure due to worn cylinder liners and pistons, as described in (4), and once this is determined, other symptoms should be taken into consideration in order to make the final judgement of whether the engine needs an overhaul.Measurement of Compression Pressure
Measurement of compression pressurePreparation For Inspection
Check the following before inspection.(1) Make sure that the engine oil, air cleaner, starter, battery, etc. are in normal operating condition.Inspection
(1) Move the control lever to the Stop position.(2) Remove the glow plugs from all cylinders, and attach the gage adapter and compression gage to the cylinder to be tested.(3) Crank the engine with the starter, and read the compression gage indication when the indication stabilizes.(4) If the measured compression pressure is lower than the limit, consider overhauling the engine.
(a) Measure the compression pressure in all cylinders.(b) As compression pressure varies with the engine speed, measure the engine speed at the same time.
Measure the compression pressure while the engine is running at 150 to 200 min-1. The oil and coolant temperatures should be between 20 and 30 °C [68 and 86°F].
It is important to regularly check the compression pressure so that you can tell the difference. * New or overhauled engines have slightly higher compression pressure.* The compression pressure settles to the standard value as the piston rings and valve seats fit in.* As wear progresses further, the compression pressure drops.

