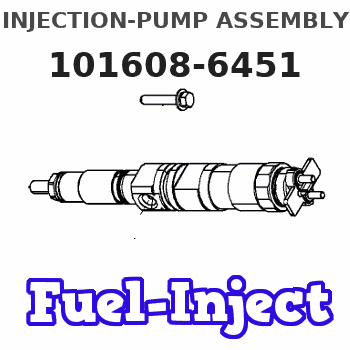
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 613 262
9400613262
ZEXEL
101608-6451
1016086451
Rating:
Service parts 101608-6451 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME440071
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7{180}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101608-6451
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104740-0861
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 613 262
9400613262
ZEXEL
101608-6451
1016086451
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.5
4.45
4.55
Rack position
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11
Pump speed
r/min
1050
1050
1050
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
115
114
116
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
65.3
65.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
490
490
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
7.7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
16.5
15
18
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
11.2++
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
100
100
110
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Rack position
9.1
Boost pressure
kPa
18.7
12
25.4
Boost pressure
mmHg
140
90
190
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
375
375
375
Rack position
10.5
Boost pressure
kPa
56
53.3
58.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
420
400
440
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
(600)
Advance angle
deg.
3
2.5
3.5
Load
0/4
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
720
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Load
0/4
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
(820)
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Load
4/4
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
(1000)
Advance angle
deg.
1.5
1
2
Load
4/4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
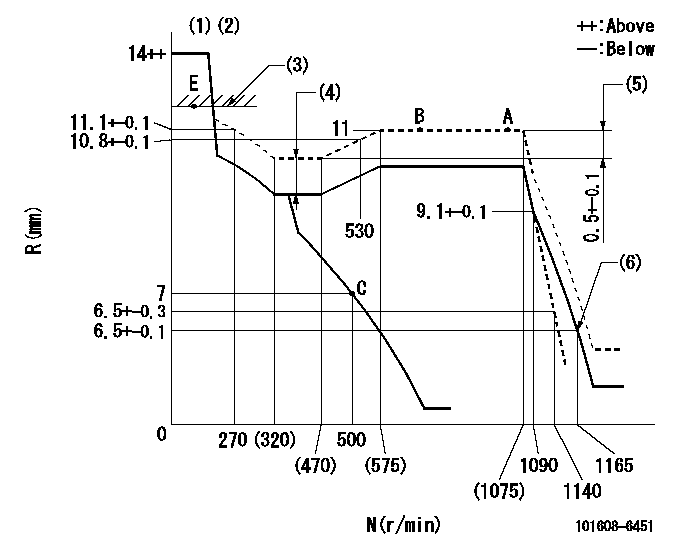
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(5)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
(6)Set idle sub-spring
----------
K=7 BCL=1.4+-0.1mm N1=1050r/min N2=375r/min
----------
----------
K=7 BCL=1.4+-0.1mm N1=1050r/min N2=375r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
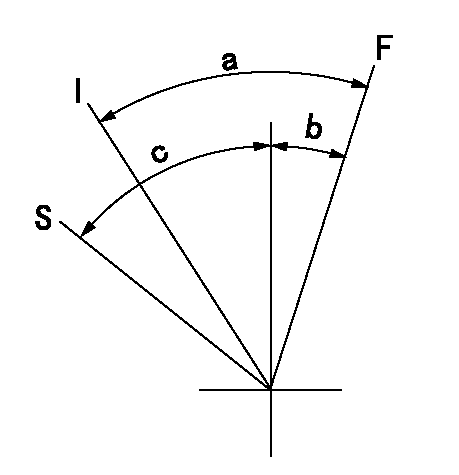
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
----------
----------
a=16deg+-5deg b=2deg+-5deg c=31deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=16deg+-5deg b=2deg+-5deg c=31deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
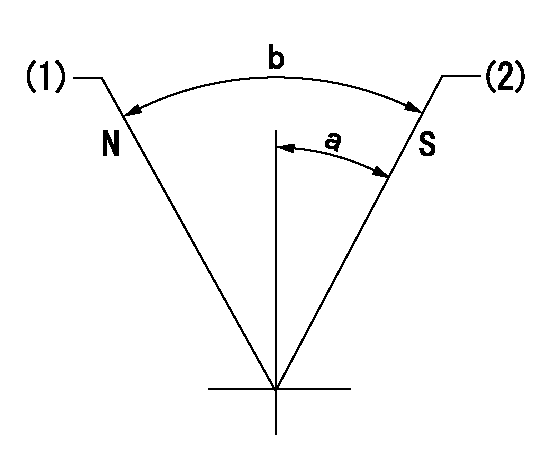
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Normal
(2)Pump speed aa and rack position bb (to be sealed at delivery)
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.5mm
----------
a=35deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.5mm
----------
a=35deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
0000001501 TAMPER PROOF

Tamperproofing-equipped boost compensator cover installation procedure
(A) After adjusting the boost compensator, tighten the bolts to remove the heads.
(1)Before adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten the screw to the specified torque.
(Tightening torque T = T1 maximum)
(2)After adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten to the specified torque to break off the bolt heads.
(Tightening torque T = T2)
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
0000001601 I/P WITH LOAD PLUNGER ADJ
Load plunger-equipped pump adjustment
1. Adjust the variation between cylinders and the injection quantity.
2. At Full point A, adjust the pre-stroke to the specified value.
3. After pre-stroke adjustment, reconfirm that the fuel injection quantity and the variation between cylinders is as specified.
----------
----------
----------
----------
Timing setting
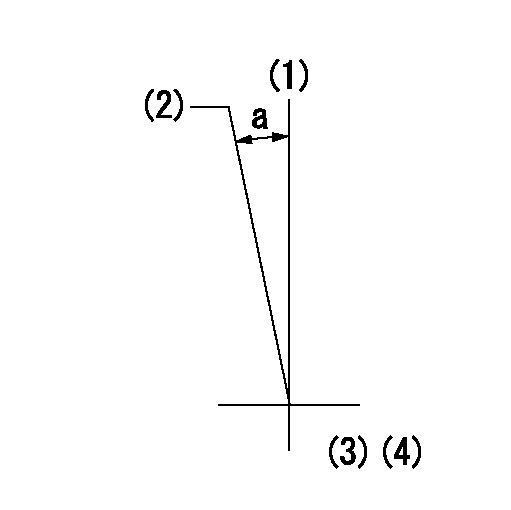
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=8deg
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
aa=8deg
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
1. Disassembly and Assembly of General Parts
1.1 Oil SealsWhen driving oil seals into place, respect the following instructions. Driving Seals into Housing:(a) Orient the seal lip correctly, making sure it is not damaged.(b) Before driving a seal into place, apply a light coat of grease to the periphery of the seal that fits into the housing.(c) Use a driving tool like the one shown in the drawing that is specially designed for the purpose. The tool can properly guide the lip and hold evenly the top of the seal when it is tapped, so it allows the seal to be driven straight down. Do not use hammers on bare seals as seal will be damaged and consequently oil leak will result.
Oil seal driving tool Driving Seals onto Shaft:(a) Coat the seal lip with grease.(b) Use a seal guide like the one shown in the drawing when the shaft has steps, splines, threads or keyways.
Oil seal guide1.2 O-RingsUse a guide when it is necessary to move O-rings over steps, splines, threads or keyways to install them. Apply a light coat of grease to O-rings before fitting them.
O-ring guide1.3 Bearings(1) When driving bearings into place, be sure to tap the race that is being fitted. (If the inner race is being fitted, tap the inner race. Likewise, if it is the outer race that is being fitted, tap the outer race.) Use fitting tools like the one shown in the drawing that are appropriate for inner or outer races.
Bearing fitting tool(2) Bearings are best fitted using a press as shock loads and errors can be minimized.
Fitting bearing using a press1.4 Lock PlatesAlways bend lock plates properly. The drawing on the right shows some of typical lock plates being bent properly and improperly.1.5 Split Pins and Spring PinsAs a rule, all split pins must be replaced with new ones after each removal. It is also important to bend split pins properly. Spring pins must be driven into place completely.
Typical locking plates with good and bad bends
1.1 Oil SealsWhen driving oil seals into place, respect the following instructions. Driving Seals into Housing:(a) Orient the seal lip correctly, making sure it is not damaged.(b) Before driving a seal into place, apply a light coat of grease to the periphery of the seal that fits into the housing.(c) Use a driving tool like the one shown in the drawing that is specially designed for the purpose. The tool can properly guide the lip and hold evenly the top of the seal when it is tapped, so it allows the seal to be driven straight down. Do not use hammers on bare seals as seal will be damaged and consequently oil leak will result.
Oil seal driving tool Driving Seals onto Shaft:(a) Coat the seal lip with grease.(b) Use a seal guide like the one shown in the drawing when the shaft has steps, splines, threads or keyways.
Oil seal guide1.2 O-RingsUse a guide when it is necessary to move O-rings over steps, splines, threads or keyways to install them. Apply a light coat of grease to O-rings before fitting them.
O-ring guide1.3 Bearings(1) When driving bearings into place, be sure to tap the race that is being fitted. (If the inner race is being fitted, tap the inner race. Likewise, if it is the outer race that is being fitted, tap the outer race.) Use fitting tools like the one shown in the drawing that are appropriate for inner or outer races.
Bearing fitting tool(2) Bearings are best fitted using a press as shock loads and errors can be minimized.
Fitting bearing using a press1.4 Lock PlatesAlways bend lock plates properly. The drawing on the right shows some of typical lock plates being bent properly and improperly.1.5 Split Pins and Spring PinsAs a rule, all split pins must be replaced with new ones after each removal. It is also important to bend split pins properly. Spring pins must be driven into place completely.
Typical locking plates with good and bad bends

