Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101608-1460
1016081460
Rating:
Service parts 101608-1460 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME075788
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
15.7{160}/21.6{220}
14.
NOZZLE
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101608-1460
1016081460
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101608-1460
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8260
Bosch type code
9 430 610 133
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
18
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
184
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-8420
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.2
3.15
3.25
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.7
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
93.5
90.7
96.3
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
310
310
310
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
10.8
9.2
12.4
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.7)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
93.5
92.5
94.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.3
Pump speed
r/min
1450
1450
1450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
90
86
94
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1-0.35
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
92.5
88.5
96.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
155
155
175
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1150--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1450
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
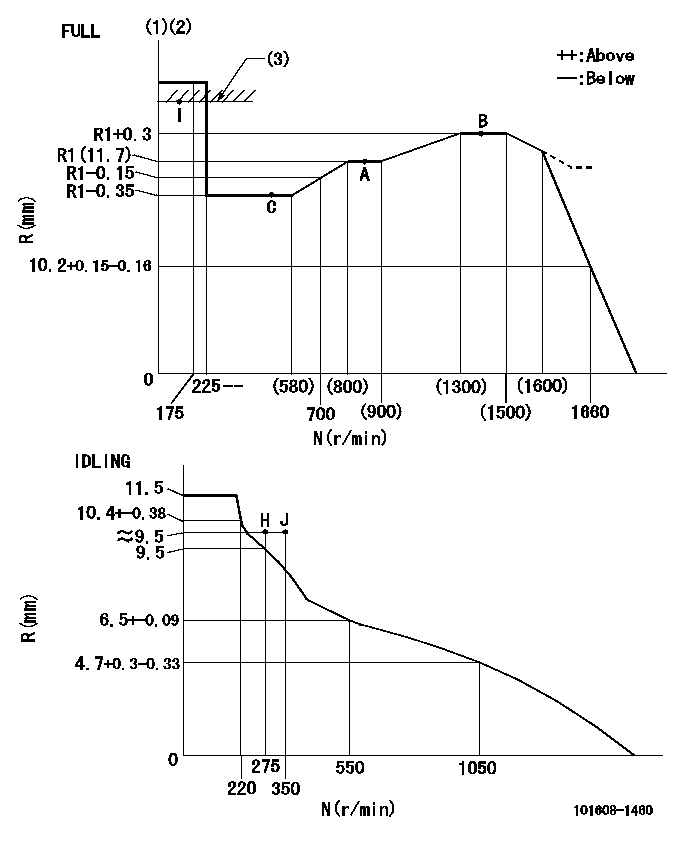
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=L97
----------
----------
T1=L97
----------
Speed control lever angle
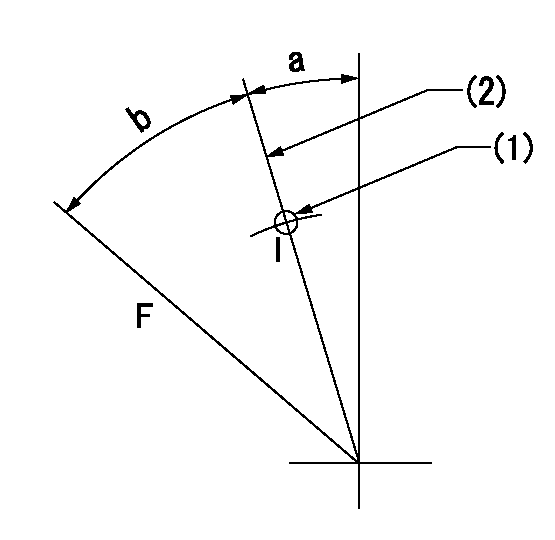
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=40mm
----------
a=18.5deg+-5deg b=(39deg)+-3deg
----------
aa=40mm
----------
a=18.5deg+-5deg b=(39deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle
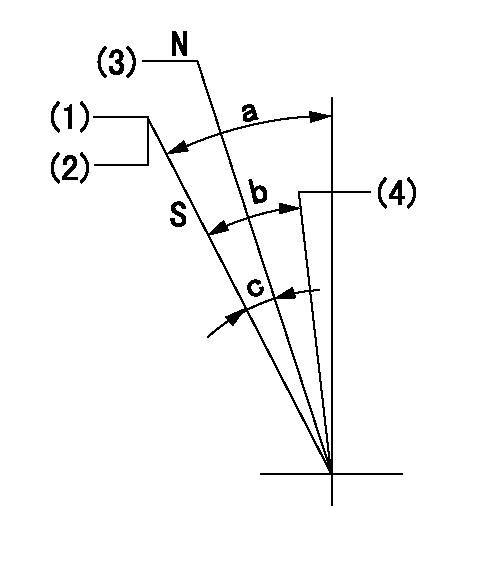
N:Engine manufacturer's normal use
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Set the stopper bolt so that speed = aa and rack position = bb and confirm non-injection.
(2)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed cc. Rack position = dd (non-injection rack position).
(3)Rack position = approximately ee (speed lever full, speed = ff).
(4)Free (at delivery)
----------
aa=1450r/min bb=7.2-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(8.8)mm ee=15mm ff=0r/min
----------
a=36.5deg+-5deg b=(25deg) c=13deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1450r/min bb=7.2-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(8.8)mm ee=15mm ff=0r/min
----------
a=36.5deg+-5deg b=(25deg) c=13deg+-5deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=400r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=400r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm
----------
0000001601 LEVER
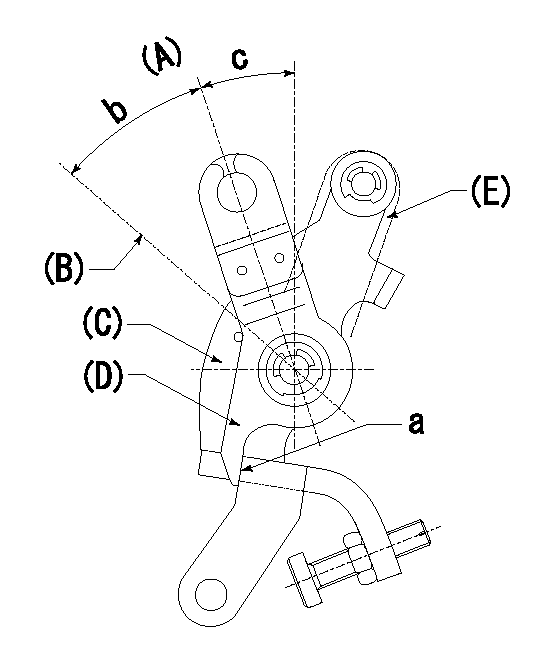
(A) Idle
(B) Full speed
(C) Base lever
(D) Accelerator lever
(E) Accelerator lever delivery position
1. Measure speed lever angle
(1)Measure the angle when the accelerator lever (D) contacted the base lever (C) at a.
----------
----------
b=(39deg)+-3deg c=18.5deg+-5deg
----------
----------
b=(39deg)+-3deg c=18.5deg+-5deg
Timing setting
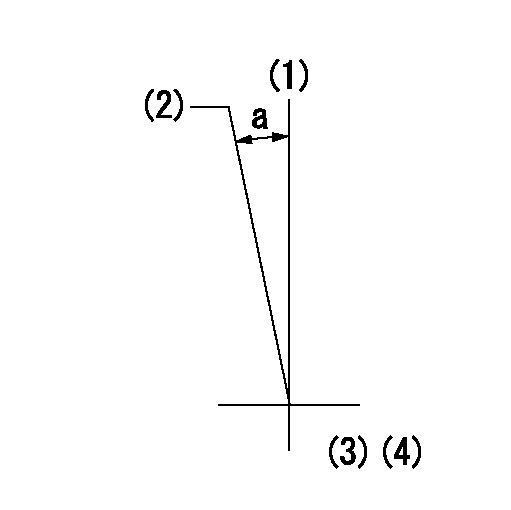
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=12deg
----------
a=(1deg)
----------
aa=12deg
----------
a=(1deg)
Information:
Illustration 9 g06286243
Typical example
Illustration 9 shows the governor plate displaying high wear at the sleeve contact points.
Illustration 10 g06286261
Typical example
Illustration 8 shows the thrust sleeve displaying an excessive wear groove.
Illustration 11 g06286627
Typical example
Illustration 12 g06286629
Typical example
Illustration 11 and Illustration 11 show the weight thrust fingers badly worn.
Illustration 13 g06286630
Typical example
Illustration 13 shows pivot heels showing excessive wear.Fuel Quality
Illustration 14 g06286604
Typical example
Illustration 14 shows that nitrile rubber seals have cracked causing fuel leakage. The cracks in the seals are attributed to fuel attacking the rubber. Ensure that there is no particle contamination in the fuel injection pump.Unmodified Vegetable Oil or Poor Quality FAME
Illustration 15 g06286612
Typical example
Stuck metering valve causing engine overspeed. Top cover of fuel injection pump removed. Black sticky material adhering to all non-alloy surfaces, this is due to the use of unmodified vegetable oil or poor quality FAME. Refer to Illustration 15.High Water Content in Fuel
Illustration 16 g06286613
Typical example
Illustration 17 g06286615
Typical example
Illustration 16 and Illustration 17 show corrosion on component surfaces, due to high water content in fuel.Characteristics Associated with Poor Quality Fuel and Potential Issue
Table 1
Fuel Characteristics Effect Issue
FAMEs in general Causes some elastomers to soften, swell, harden, and crack. Fuel leakage.
Free methanol in FAME Corrodes aluminum and zinc. Low flash point. Corrosion on fuel injection equipment.
FAME process chemicals Potassium and sodium compound. Solid particles. Blocked nozzles.
Dissolved water in FAME Reversion of FAME to a fatty acid. Fuel filter plugging.
Free water in FAME Corrosion. Sustains bacteria. Corrosion on fuel injection equipment. Sludging.
Free glycerine, mono, and
di-glycerines in FAME Corrodes non-ferrous metals.
Sediments on moving parts and lacquering. Fuel filter clogging.
Fuel injector clogging.
Free fatty acid Corrosion of Zinc plating.
Slats of organic acids.
Organic compound formed. Corrosion on fuel injection equipment.
Fuel filter plugging.
Sediment on components
High viscosity at low temperature Generates excessive localized heat.
Higher stressed components. Fuel injection pump seizures.
Early life issues.
Poor nozzle spray.
Corrosive acids Corrodes all metallic parts. Corrosion on fuel injection equipment.
High molecular organic acids Corrosion of Zinc plating.
Slats of organic acids.
Organic compound formed. Corrosion on fuel injection equipment.
Fuel filter plugging.
Sediment on components
Polymerization products Deposits in fuel mixes Fuel filter plugging. Lacquering formation in hot areas. Recommended Procedures
Prime the fuel system to remove any air. Refer to Operation and Maintenance Manual, Fuel System - Prime for the correct procedure.Check the pressure of the fuel system. Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting, Fuel System Pressure - Test for the correct procedure.Check the operation of the fuel injection nozzles. Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjusting, Fuel Injection Nozzle - Test for the correct procedure.To inspect the fuel injection pump, refer to Special Instruction, REHS3767, Inspection of Fuel Injection Pumps on 3054C, C3.3, C4.4 (Mechanical), and C7.1 (Mechanical) Engines for the correct procedure.
Have questions with 101608-1460?
Group cross 101608-1460 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
101608-1460
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY