Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101607-6660
1016076660
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101607-6660
1016076660
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101607-6660
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.25
3.35
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.2
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
57.7
56
59.4
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
13.7
11.6
15.8
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.2)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
57.7
56.7
58.7
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.1
Pump speed
r/min
1450
1450
1450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
72.6
68.6
76.6
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1+0.8
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
59.7
55.7
63.7
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
R1+1.25
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
57.1
53.1
61.1
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_07
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
140
130
150
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1250--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1400
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
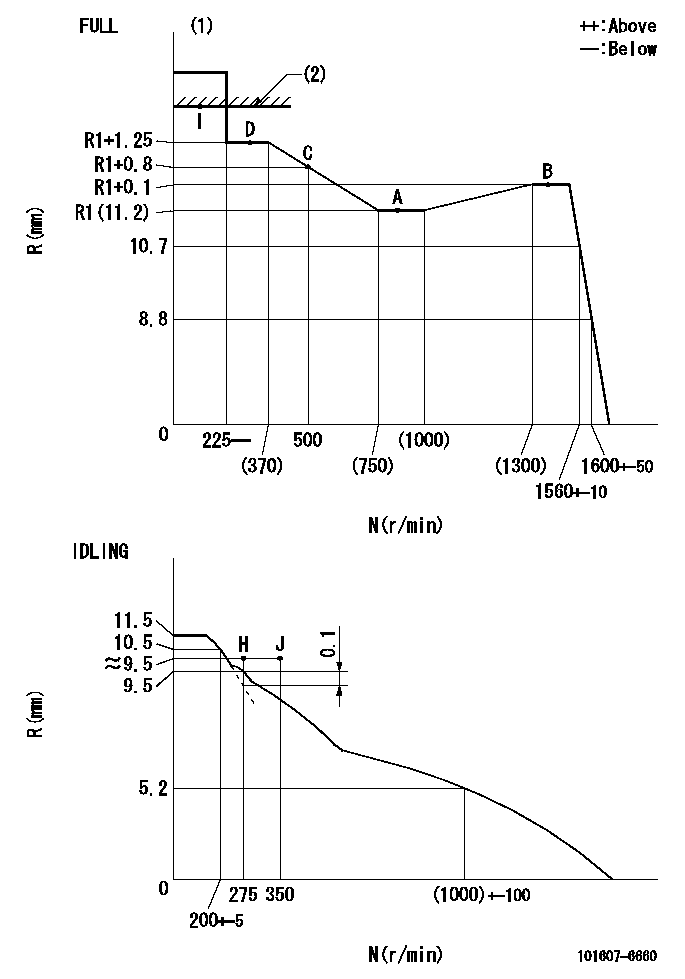
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=F21
----------
----------
T1=F21
----------
Speed control lever angle
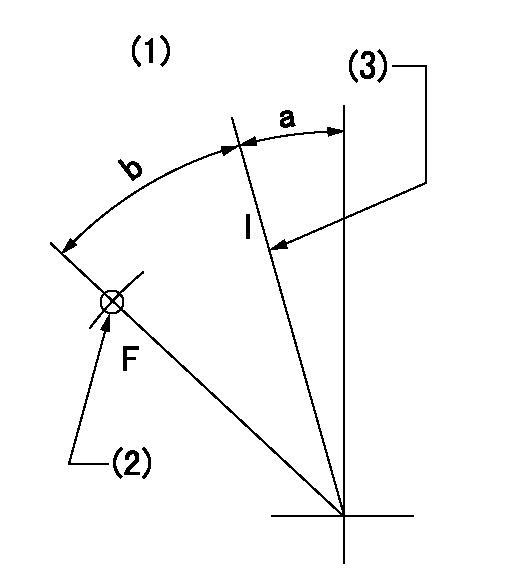
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Accelerator lever
(2)Use the hole at R = aa
(3)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=29mm
----------
a=24deg+-5deg b=41deg+-3deg
----------
aa=29mm
----------
a=24deg+-5deg b=41deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Engine manufacturer's normal use
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Set the stopper bolt at pump speed = aa and rack position = bb (non-injection rack position). Confirm non-injection.
(2)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed = cc. Rack position = actual (non-injection rack position).
(3)Rack position = approximately dd
(4)Free (at delivery)
(5)Use the hole above R = ee
----------
aa=1550r/min bb=7-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(16.8)mm ee=50mm
----------
a=36.5deg+-5deg b=(25deg) c=17deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1550r/min bb=7-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(16.8)mm ee=50mm
----------
a=36.5deg+-5deg b=(25deg) c=17deg+-5deg
0000001501 LEVER
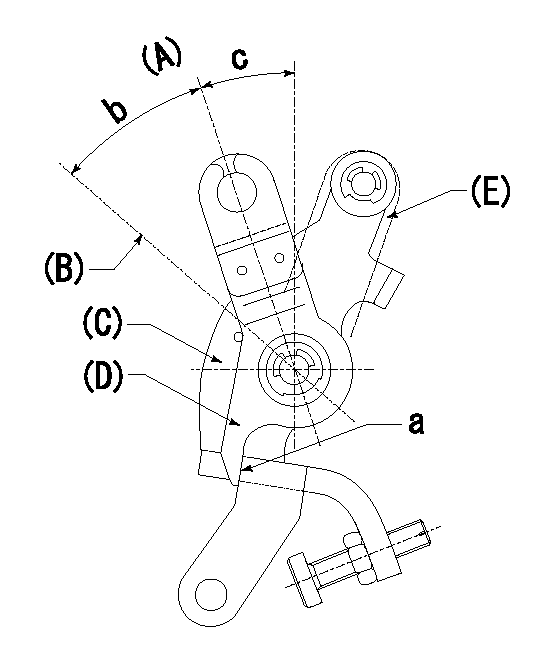
(A) Idle
(B) Full speed
(C) Base lever
(D) Accelerator lever
(E) Accelerator lever delivery position
1. Measure speed lever angle
(1)Measure the angle when the accelerator lever (D) contacted the base lever (C) at a.
----------
----------
b=41deg+-3deg c=24deg+-5deg
----------
----------
b=41deg+-3deg c=24deg+-5deg
0000001601 RACK SENSOR

V1:Supply voltage
V2f:Full side output voltage
V2i:Idle side output voltage
(A) Black
(B) Yellow
(C) Red
(D) Trimmer
(E): Shaft
(F) Nut
(G) Load lever
1. Load sensor adjustment
(1)Connect as shown in the above diagram and apply supply voltage V1.
(2)Hold the load lever (G) against the full side.
(3)Turn the shaft so that the voltage between (A) and (B) is V2.
(4)Hold the load lever (G) against the idle side.
(5)Adjust (D) so that the voltage between (A) and (B) is V2i.
(6)Repeat the above adjustments.
(7)Tighten the nut (F) at the point satisfying the standards.
(8)Hold the load lever against the full side stopper and the idle side stopper.
(9)At this time, confirm that the full side output voltage is V2f and the idle side output voltage is V2i.
----------
V1=3.57+-0.02V V2f=3+0.05V V2i=1+0.1V
----------
----------
V1=3.57+-0.02V V2f=3+0.05V V2i=1+0.1V
----------
0000001701 MICRO SWITCH
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
1. Microswitch adjustment (OPEN type)
Confirm with the lever angle at full.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
2. Idle side microswitch adjustment (OPEN type)
Confirm with the lever angle at idle.
(1)Speed N2
(2)Rack position Rb
----------
N1=1600r/min Ra=8.8+-0.1mm N2=275r/min Rb=9.7+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=1600r/min Ra=8.8+-0.1mm N2=275r/min Rb=9.7+-0.1mm
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=13deg
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
aa=13deg
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
Illustration 2 g01180699
Pour point of fuel mixturesIn order to calculate the amount of lighter fuel that is required to be blended with the heavier fuel, perform the following steps:
Obtain the specification for the cloud point or the pour point of both fuels from your fuel supplier.
Locate the cloud point or the pour point of the heavier fuel on the left side of the table. Mark the point on the table.
Locate the cloud point or the pour point of the lighter fuel on the right side of the table. Mark the point on the table.
Draw a line between the two points that were established. Label this line "A".
Determine the lowest outside temperature for machine operation. Find this point on the left side of the table. Mark this point. Draw a horizontal line from this point. Stop the line at the intersection of line "A". Label this new line "C".
Line "C" and line "A" intersect. Mark this point. Draw a vertical line from this point. Stop the line at the bottom of the table. Label this line "B". The point at the bottom of line "B" reveals the percentage of lighter fuel that is required to modify the cloud point or the pour point.The above example shows that the blending will require a thirty percent mixture of lighter fuel.Additives are a good method to use in order to lower the pour point of a fuel. These additives are known by the following names: pour point depressants, cold flow improvers and wax modifiers. When the additives are used in a low concentration, the fuel will flow through pumps, lines, and hoses.Note: These additives must be thoroughly mixed into the fuel at temperatures that are above the cloud point. The fuel supplier should be consulted in order to blend the fuel with the additives. The blended fuel can be delivered to your fuel tanks.Moisture Content
Problems with fuel filters can occur at any time. The cause of the problem can be water in the fuel or moisture in the fuel. At low temperatures, moisture causes special problems. There are three types of moisture in fuel: dissolved moisture (moisture in solution), free and dispersed moisture in the fuel and free and settled at the bottom of the tank.Most diesel fuels have some dissolved moisture. Just as the moisture in air, the fuel can only contain a specific maximum amount of moisture at any one temperature. The amount of moisture decreases as the temperature is lowered. For example, a fuel could contain 100 ppm (0.010 percent) of water in solution at 18°C (65°F). This same fuel can possibly hold only 30 ppm (0.003 percent) at 4°C (40°F).After the fuel has absorbed the maximum possible amount of water, the additional water will be free and dispersed. Free and dispersed moisture is fine droplets of water that is suspended in the fuel. Since the water is heavier than the fuel, the water will slowly become free and settled at the bottom of the tank. In the above
Have questions with 101607-6660?
Group cross 101607-6660 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
101607-6660
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY