Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101607-6430
1016076430
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101607-6430
1016076430
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101607-6430
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-8420
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.2
3.15
3.25
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.7
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
77.4
75.1
79.7
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
10.8
9.2
12.4
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.7)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
77.4
76.4
78.4
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.55
Pump speed
r/min
1450
1450
1450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
87.7
83.7
91.7
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1-0.4
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
56
52
60
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
(R1+0.5)
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
87.6
83.6
91.6
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_07
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
91
81
101
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1150--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1100
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1450
Advance angle
deg.
6
5.5
6.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
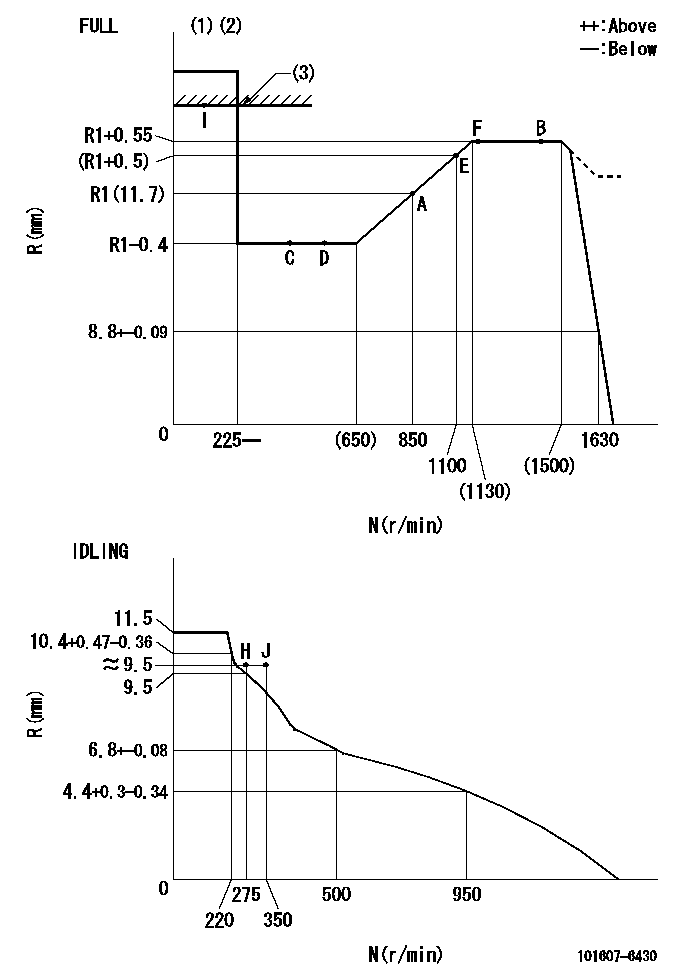
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=H51
----------
----------
T1=H51
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
----------
a=24deg+-5deg b=(46deg)+-3deg
----------
----------
a=24deg+-5deg b=(46deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle
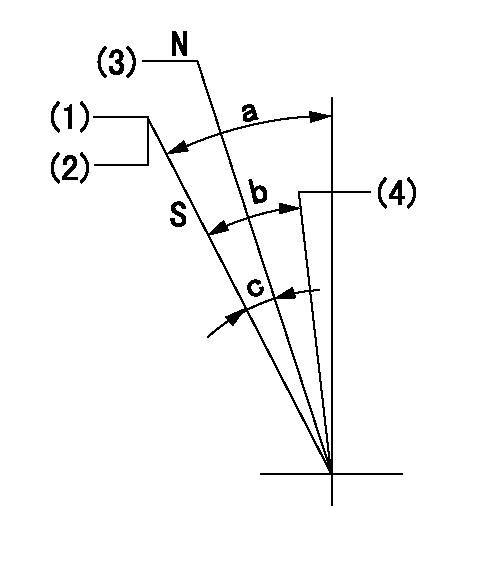
N:Engine manufacturer's normal use
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Set the stopper bolt at pump speed = aa and rack position = bb (non-injection rack position). Confirm non-injection.
(2)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed cc. Rack position = dd (non-injection rack position).
(3)Rack position = approximately ee.
(4)Free (at delivery)
----------
aa=1450r/min bb=7.2-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(8.8)mm ee=15mm
----------
a=36.5deg+-5deg b=(25deg) c=13deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1450r/min bb=7.2-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(8.8)mm ee=15mm
----------
a=36.5deg+-5deg b=(25deg) c=13deg+-5deg
0000001501 LEVER
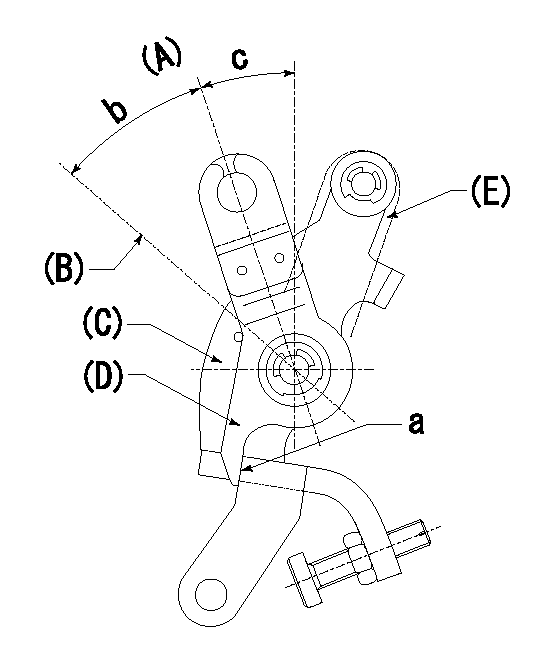
(A) Idle
(B) Full speed
(C) Base lever
(D) Accelerator lever
(E) Accelerator lever delivery position
1. Measure speed lever angle
(1)Measure the angle when the accelerator lever (D) contacted the base lever (C) at a.
----------
----------
b=(46deg)+-3deg c=24deg+-5deg
----------
----------
b=(46deg)+-3deg c=24deg+-5deg
0000001601 RACK SENSOR

V1:Supply voltage
V2f:Full side output voltage
V2i:Idle side output voltage
(A) Black
(B) Yellow
(C) Red
(D) Trimmer
(E): Shaft
(F) Nut
(G) Load lever
1. Load sensor adjustment
(1)Connect as shown in the above diagram and apply supply voltage V1.
(2)Hold the load lever (G) against the full side.
(3)Turn the shaft so that the voltage between (A) and (B) is V2.
(4)Hold the load lever (G) against the idle side.
(5)Adjust (D) so that the voltage between (A) and (B) is V2i.
(6)Repeat the above adjustments.
(7)Tighten the nut (F) at the point satisfying the standards.
(8)Hold the load lever against the full side stopper and the idle side stopper.
(9)At this time, confirm that the full side output voltage is V2f and the idle side output voltage is V2i.
----------
V1=3.57+-0.02V V2f=3+0.05V V2i=1+0.1V
----------
----------
V1=3.57+-0.02V V2f=3+0.05V V2i=1+0.1V
----------
0000001701 MICRO SWITCH
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is OFF.
1. Microswitch adjustment (OPEN type)
Confirm with the lever angle at full.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=1630r/min Ra=8.8+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=1630r/min Ra=8.8+-0.1mm
----------
Timing setting
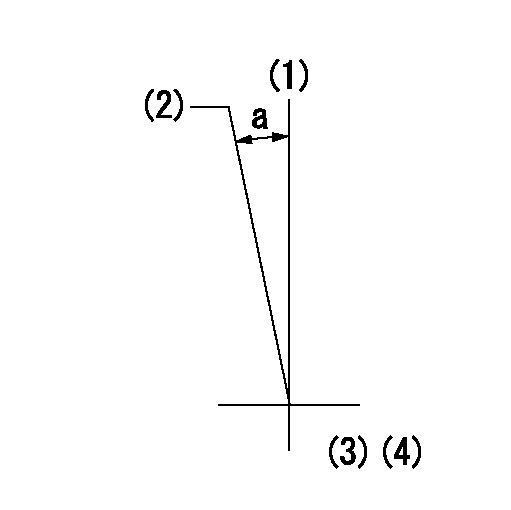
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(2deg)
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(2deg)
Information:
Batteries
Install batteries that will provide adequate cold cranking amps (CCA) in order to start the engine and operate the engine at the coldest expected temperatures. Maintain proper battery electrolyte level. Keep all batteries fully charged to a corrected specific gravity of 1.250 or above and keep the batteries warm. Heating of the battery compartment or storage in a warm location will maximize the cranking power of the battery. The temperature of the batteries has a considerable effect on the available power. The batteries will not have enough power for cranking the engine and starting the engine if the batteries are too cold, even with a warm engine. Batteries typically have only fifty percent of the capability at −10 °C (14 °F) versus 27 °C (81 °F). Only ten percent of the original power is available at a temperature of −35 °C (−31 °F). Check the condition of the batteries and the electrolyte level in each battery cell except for maintenance free batteries. Remove the battery filler caps. Maintain the electrolyte level to the bottom of the openings for the battery filler caps with distilled water. If distilled water is not available, use clean water, that is low in minerals. Do not use artificially softened water or drinking water. The salt in artificially softened water will damage the efficiency of your batteries. At the proper charging rate in a moderate climate, a battery should not require more than 30 cc (1 oz) of water per cell per week. Check the cells weekly in arctic temperatures. The cell water usage could be higher.Block Heaters
A cylinder block coolant heater can improve the startability and a cylinder block coolant heater can reduce the warm-up time by heating the coolant that surrounds the combustion chambers. A cylinder block coolant heater that is powered by electricity can be activated immediately after the engine is stopped. A cylinder block coolant heater will reduce the temperature that will require ether for starting the engine. An effective block heater is a 1250 watt to 1500 watt unit. Contact your truck dealer for more information.Air Inlet Heaters and Ether Starting Systems
If equipped with an air inlet heater (AIH) for cold weather starting, do not use types of starting aids such as ether. Such use could result in an explosion and injury.
When starting the engine with ether, follow these starting procedure instructions carefully. Use ether sparingly and spray it ONLY WHILE CRANKING THE ENGINE. Excessive ether use can cause piston and ring damage. Ether should be used only for cold weather starting.
As temperatures drop below 0 °C (32 °F), starting a cold engine may require assistance in the form of ether starting aids or air inlet heaters. An automatic metered ether injection system is preferred over a manual system. An automatic system reduces the risk of engine damage by minimizing the operator's responsibility in order to correctly determine the quantity of ether that is required. Excessive ether will damage the engine and excessive ether will void the manufacturer's
Install batteries that will provide adequate cold cranking amps (CCA) in order to start the engine and operate the engine at the coldest expected temperatures. Maintain proper battery electrolyte level. Keep all batteries fully charged to a corrected specific gravity of 1.250 or above and keep the batteries warm. Heating of the battery compartment or storage in a warm location will maximize the cranking power of the battery. The temperature of the batteries has a considerable effect on the available power. The batteries will not have enough power for cranking the engine and starting the engine if the batteries are too cold, even with a warm engine. Batteries typically have only fifty percent of the capability at −10 °C (14 °F) versus 27 °C (81 °F). Only ten percent of the original power is available at a temperature of −35 °C (−31 °F). Check the condition of the batteries and the electrolyte level in each battery cell except for maintenance free batteries. Remove the battery filler caps. Maintain the electrolyte level to the bottom of the openings for the battery filler caps with distilled water. If distilled water is not available, use clean water, that is low in minerals. Do not use artificially softened water or drinking water. The salt in artificially softened water will damage the efficiency of your batteries. At the proper charging rate in a moderate climate, a battery should not require more than 30 cc (1 oz) of water per cell per week. Check the cells weekly in arctic temperatures. The cell water usage could be higher.Block Heaters
A cylinder block coolant heater can improve the startability and a cylinder block coolant heater can reduce the warm-up time by heating the coolant that surrounds the combustion chambers. A cylinder block coolant heater that is powered by electricity can be activated immediately after the engine is stopped. A cylinder block coolant heater will reduce the temperature that will require ether for starting the engine. An effective block heater is a 1250 watt to 1500 watt unit. Contact your truck dealer for more information.Air Inlet Heaters and Ether Starting Systems
If equipped with an air inlet heater (AIH) for cold weather starting, do not use types of starting aids such as ether. Such use could result in an explosion and injury.
When starting the engine with ether, follow these starting procedure instructions carefully. Use ether sparingly and spray it ONLY WHILE CRANKING THE ENGINE. Excessive ether use can cause piston and ring damage. Ether should be used only for cold weather starting.
As temperatures drop below 0 °C (32 °F), starting a cold engine may require assistance in the form of ether starting aids or air inlet heaters. An automatic metered ether injection system is preferred over a manual system. An automatic system reduces the risk of engine damage by minimizing the operator's responsibility in order to correctly determine the quantity of ether that is required. Excessive ether will damage the engine and excessive ether will void the manufacturer's
Have questions with 101607-6430?
Group cross 101607-6430 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
101607-6430
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY