Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
F 019 Z10 371
f019z10371
ZEXEL
101607-6060
1016076060

Rating:
Service parts 101607-6060 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME076953
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
15.7(160)/21.6(220)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
F 019 Z10 371
f019z10371
ZEXEL
101607-6060
1016076060
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-8420
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.2
3.15
3.25
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
12.5
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
113.5
110.1
116.9
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
11.5
9.8
13.2
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(12.5)
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
113.5
112.5
114.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
40
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
300
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+1.2
Pump speed
r/min
1350
1350
1350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
129.8
125.8
133.8
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
40
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
300
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R2(R1-0.
5)
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
92.6
88.6
96.6
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
40
40
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
300
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Rack position
R2-1.15
Boost pressure
kPa
4
2.7
5.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
30
20
40
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Rack position
R2(R1-0.
5)
Boost pressure
kPa
26.7
26.7
26.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
200
200
200
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1180--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1130
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1350
Advance angle
deg.
3.5
3
4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
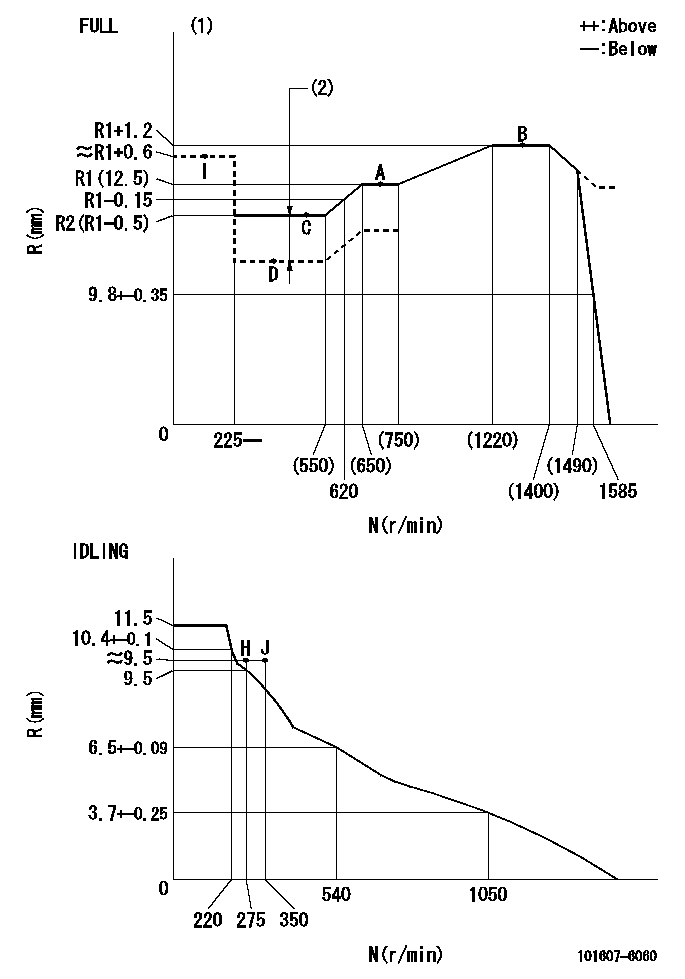
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=H24 BCL=1.15+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=H24 BCL=1.15+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
----------
a=18.5deg+-5deg b=(42deg)+-3deg
----------
----------
a=18.5deg+-5deg b=(42deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle
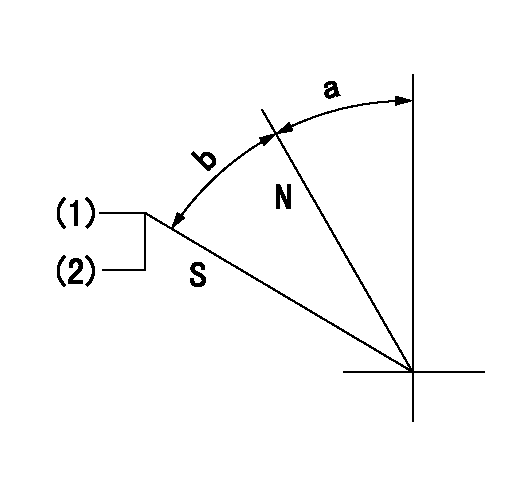
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Set the stopper bolt at pump speed = aa and rack position = bb (non-injection rack position). Confirm non-injection.
(2)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed cc. Rack position = dd (non-injection rack position).
----------
aa=1350r/min bb=7-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(8)mm
----------
a=11.5deg+-5deg b=(28deg)+-5deg
----------
aa=1350r/min bb=7-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(8)mm
----------
a=11.5deg+-5deg b=(28deg)+-5deg
0000001501 LEVER
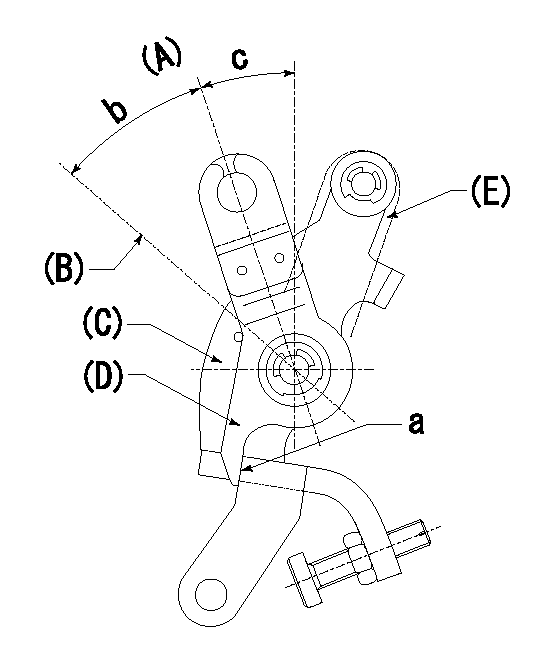
(A) Idle
(B) Full speed
(C) Base lever
(D) Accelerator lever
(E) Accelerator lever delivery position
1. Measure speed lever angle
(1)Measure the angle when the accelerator lever (D) contacted the base lever (C) at a.
----------
----------
b=(42deg)+-3deg c=18.5deg+-5deg
----------
----------
b=(42deg)+-3deg c=18.5deg+-5deg
Timing setting
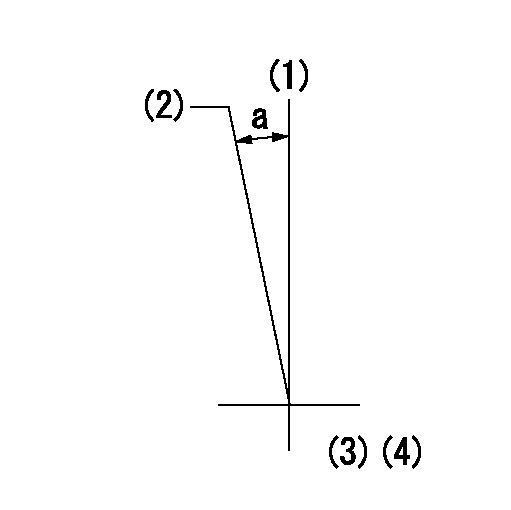
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=11deg
----------
a=(3deg)
----------
aa=11deg
----------
a=(3deg)
Information:
Test Procedure
System Operation
A contactor is a pressure switch or a contactor is a level switch. Contactors can be adjusted in order to operate at a given temperature or pressure.Contactors are set to shutdown setpoints and monitored by the MMS. When a contactor for the shutdown system closes the MMS secures the engine.
Illustration 1 g00563590
Diagram of a contactor
Illustration 2 g00562905
Schematic of the contactorFunctional Test
Check the electrical connectors and check the wiring.
Bodily contact with electrical potential can cause bodily injury or death.To avoid the possibility of injury or death, ensure that the main power supply has been disconnected before performing any maintenance or removing any modules.
Disconnect the power supply.
Check the electrical connectors and check the wiring for damage or bad connections.
Verify that all modules are properly seated.
Verify the status of the LED on the SLC 5/04.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
All of the components are fully installed. All of the components are free of corrosion. All of the components are free of damage. All of the modules are properly seated. Proceed to 2.
The components are not fully installed. The components are not free of corrosion. The components are damaged. All of the modules are not properly seated. Repair the component. Verify that the repair resolves the problem. STOP.
Check for drift.
Apply pressure or apply temperature. Determine when the contact closes.
Measure the continuity between the common terminal and the normally open terminal. Determine when the contact closes.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
The contact closes when the contact is actuated. Proceed to 3.
The contact does not close when the contact is actuated. Replace the contactor. Verify that the repair resolves the problem. Stop.
Check the contactor for chatter.
Verify that the contactor is adjusted to the original setpoint.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
The contactor does not cycle frequently. Stop.
The contactor cycles frequently. Replace the contactor. Verify that the repair resolves the problem. Stop.
System Operation
A contactor is a pressure switch or a contactor is a level switch. Contactors can be adjusted in order to operate at a given temperature or pressure.Contactors are set to shutdown setpoints and monitored by the MMS. When a contactor for the shutdown system closes the MMS secures the engine.
Illustration 1 g00563590
Diagram of a contactor
Illustration 2 g00562905
Schematic of the contactorFunctional Test
Check the electrical connectors and check the wiring.
Bodily contact with electrical potential can cause bodily injury or death.To avoid the possibility of injury or death, ensure that the main power supply has been disconnected before performing any maintenance or removing any modules.
Disconnect the power supply.
Check the electrical connectors and check the wiring for damage or bad connections.
Verify that all modules are properly seated.
Verify the status of the LED on the SLC 5/04.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
All of the components are fully installed. All of the components are free of corrosion. All of the components are free of damage. All of the modules are properly seated. Proceed to 2.
The components are not fully installed. The components are not free of corrosion. The components are damaged. All of the modules are not properly seated. Repair the component. Verify that the repair resolves the problem. STOP.
Check for drift.
Apply pressure or apply temperature. Determine when the contact closes.
Measure the continuity between the common terminal and the normally open terminal. Determine when the contact closes.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
The contact closes when the contact is actuated. Proceed to 3.
The contact does not close when the contact is actuated. Replace the contactor. Verify that the repair resolves the problem. Stop.
Check the contactor for chatter.
Verify that the contactor is adjusted to the original setpoint.The results of the preceding procedure are in the following list:
The contactor does not cycle frequently. Stop.
The contactor cycles frequently. Replace the contactor. Verify that the repair resolves the problem. Stop.