Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 615 660
9400615660
ZEXEL
101607-1990
1016071990
MITSUBISHI
ME076886
me076886
Rating:
Service parts 101607-1990 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
10.
NOZZLE AND HOLDER ASSY
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
13.
NOZZLE-HOLDER
14.
NOZZLE
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 615 660
9400615660
ZEXEL
101607-1990
1016071990
MITSUBISHI
ME076886
me076886
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101607-1990
9 400 615 660
ME076886 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D14 * K
6D14 * K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.25
3.35
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
10.9
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
57.5
55.5
59.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
9
7.5
10.5
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(10.9)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
57.5
56.5
58.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1-0.2
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60.5
56.5
64.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1+0.4
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
49
45
53
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
90
80
100
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
900--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
850
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
0.8
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
2.6
2.1
3.1
Timer adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
5.5
5
6
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
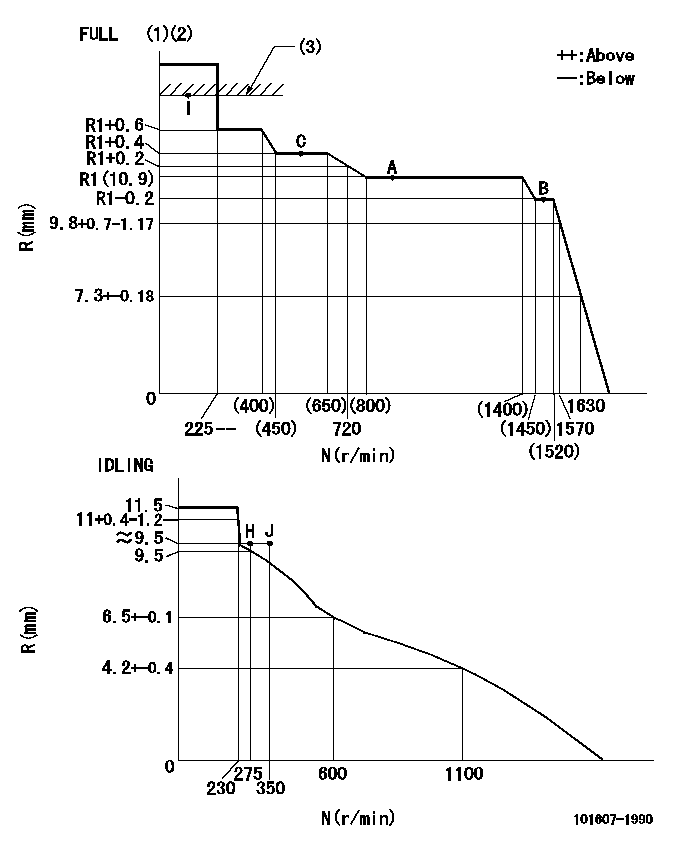
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=G92
----------
----------
T1=G92
----------
Speed control lever angle
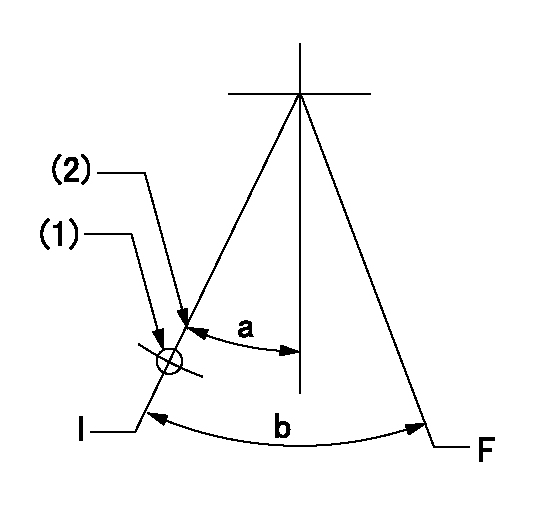
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=33deg+-5deg b=41.5deg+-3deg
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=33deg+-5deg b=41.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Set the stopper bolt at speed = aa and rack position = bb. Confirm non-injection.
(2)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed = cc, rack position = dd. (After setting, apply red paint.)
(3)Rack position = approximately ee (speed lever full, speed = ff).
(4)Free (at delivery)
----------
aa=1500r/min bb=5.4-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(7.4)mm ee=17.4mm ff=0r/min
----------
a=17deg+-5deg b=2deg+-5deg cc=(27deg)
----------
aa=1500r/min bb=5.4-0.5mm cc=275r/min dd=(7.4)mm ee=17.4mm ff=0r/min
----------
a=17deg+-5deg b=2deg+-5deg cc=(27deg)
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=400r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=400r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=16deg
----------
a=(1deg)
----------
aa=16deg
----------
a=(1deg)
Information:
Self-Diagnostics
The electronic system has self-diagnostic capabilities. When a problem is detected, a fault indicator is illuminated on the front of the module. A panel of indicators is also located on the MECP.Module Fault Indicators
A fault should be immediately serviced. A fault indicator is illuminated when a problem exists. When the PLC has an active fault, find the appropriate procedure in the troubleshooting section.Operating Information that is Stored in the Programmable Logic Controller
The SLC 5/04 uses a battery in order to provide backup power to the C-MOS RAM.Programmable Logic Controller Chassis or Rack
The PLC chassis contains the following components:
Power Supply
CPU Module
Input Modules
Output Modules
User Defined ModulesThe system uses the Allen-Bradley SLC 500 series of PLC.Central Processing Unit
Illustration 1 g00562937
The SLC 5/04 processor includes a three-position keyswitch on the front panel. The key switches the system from the following three modes of operation: RUN, PROGRAM and REMOTEThe key can be removed in each of the three positions. The mode changes when the position of the key is switched from the RUN position. Do not substitute the keyswitch for a master control relay. Do not substitute the keyswitch for an emergency stop switch.RUN Position
The RUN position places the processor in the run mode. The processor conducts the following functions:
The processor scans the ladder program.
The processor executes the ladder program.
The processor monitors input devices.
The processor energizes the output devices.
The processor acts on the enabled I/O forces.You can only change the processor's mode with the keyswitch. Revising of the program cannot be performed when you are on-line."PROG" Position
The Program position places the processor in the program mode. The processor does not scan the program and the processor does not execute the program. The controller's outputs are de-energized.You can only change the processor's mode with the keyswitch. Revising of the program can be performed when you are on-line.When the keyswitch is in the program position, a qualified technician can use the programmer interface device in order to change the processor's mode.Remote Position
The remote position places the processor in the remote mode. You can only change the processor's mode with the keyswitch. Revising of the program can be performed when you are on-line.When the keyswitch is in the remote position, a qualified technician can use the programmer interface device in order to change the processor's mode.Processor's Fault Indicators
A fault should be immediately serviced. A fault indicator is illuminated when a problem exists. When the PLC has an active fault, find the appropriate procedure in the troubleshooting section.The Processor's Indicators
Six LED indicators are on the front of the CPU module. The indicators show the operating status of your processor. The indicators have the labels that are in the following list:"RUN", "FLT", "BATT", "FORCE", "DH+" and "RS232"Thermocouple Module
The thermocouple module contains diagnostic features that can identify sources of problems. The problems may occur during power up. The problems may occur during normal operation. Each channel can receive a signal from the sensors or from the analog input devices.
Illustration 2 g00562940
LED indicatorsResistance Temperature Detector Module
The RTD module contains diagnostic features that
The electronic system has self-diagnostic capabilities. When a problem is detected, a fault indicator is illuminated on the front of the module. A panel of indicators is also located on the MECP.Module Fault Indicators
A fault should be immediately serviced. A fault indicator is illuminated when a problem exists. When the PLC has an active fault, find the appropriate procedure in the troubleshooting section.Operating Information that is Stored in the Programmable Logic Controller
The SLC 5/04 uses a battery in order to provide backup power to the C-MOS RAM.Programmable Logic Controller Chassis or Rack
The PLC chassis contains the following components:
Power Supply
CPU Module
Input Modules
Output Modules
User Defined ModulesThe system uses the Allen-Bradley SLC 500 series of PLC.Central Processing Unit
Illustration 1 g00562937
The SLC 5/04 processor includes a three-position keyswitch on the front panel. The key switches the system from the following three modes of operation: RUN, PROGRAM and REMOTEThe key can be removed in each of the three positions. The mode changes when the position of the key is switched from the RUN position. Do not substitute the keyswitch for a master control relay. Do not substitute the keyswitch for an emergency stop switch.RUN Position
The RUN position places the processor in the run mode. The processor conducts the following functions:
The processor scans the ladder program.
The processor executes the ladder program.
The processor monitors input devices.
The processor energizes the output devices.
The processor acts on the enabled I/O forces.You can only change the processor's mode with the keyswitch. Revising of the program cannot be performed when you are on-line."PROG" Position
The Program position places the processor in the program mode. The processor does not scan the program and the processor does not execute the program. The controller's outputs are de-energized.You can only change the processor's mode with the keyswitch. Revising of the program can be performed when you are on-line.When the keyswitch is in the program position, a qualified technician can use the programmer interface device in order to change the processor's mode.Remote Position
The remote position places the processor in the remote mode. You can only change the processor's mode with the keyswitch. Revising of the program can be performed when you are on-line.When the keyswitch is in the remote position, a qualified technician can use the programmer interface device in order to change the processor's mode.Processor's Fault Indicators
A fault should be immediately serviced. A fault indicator is illuminated when a problem exists. When the PLC has an active fault, find the appropriate procedure in the troubleshooting section.The Processor's Indicators
Six LED indicators are on the front of the CPU module. The indicators show the operating status of your processor. The indicators have the labels that are in the following list:"RUN", "FLT", "BATT", "FORCE", "DH+" and "RS232"Thermocouple Module
The thermocouple module contains diagnostic features that can identify sources of problems. The problems may occur during power up. The problems may occur during normal operation. Each channel can receive a signal from the sensors or from the analog input devices.
Illustration 2 g00562940
LED indicatorsResistance Temperature Detector Module
The RTD module contains diagnostic features that
Have questions with 101607-1990?
Group cross 101607-1990 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
101607-1990
9 400 615 660
ME076886
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D14
6D14