Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
F 01G 09U 056
f01g09u056
ZEXEL
101607-1212
1016071212

Rating:
Include in #2:
104746-6561
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
F 01G 09U 056
f01g09u056
ZEXEL
101607-1212
1016071212
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.2
3.15
3.25
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.6
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
72.5
70.3
74.7
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
8.3
7.1
9.5
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.6)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
72.5
71.5
73.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1-0.15
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
79.5
75.5
83.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1+0.65
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
71.5
67.5
75.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
14.8+-0.
2
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
120
100
140
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1150
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
0.9
0.4
1.4
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1380
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
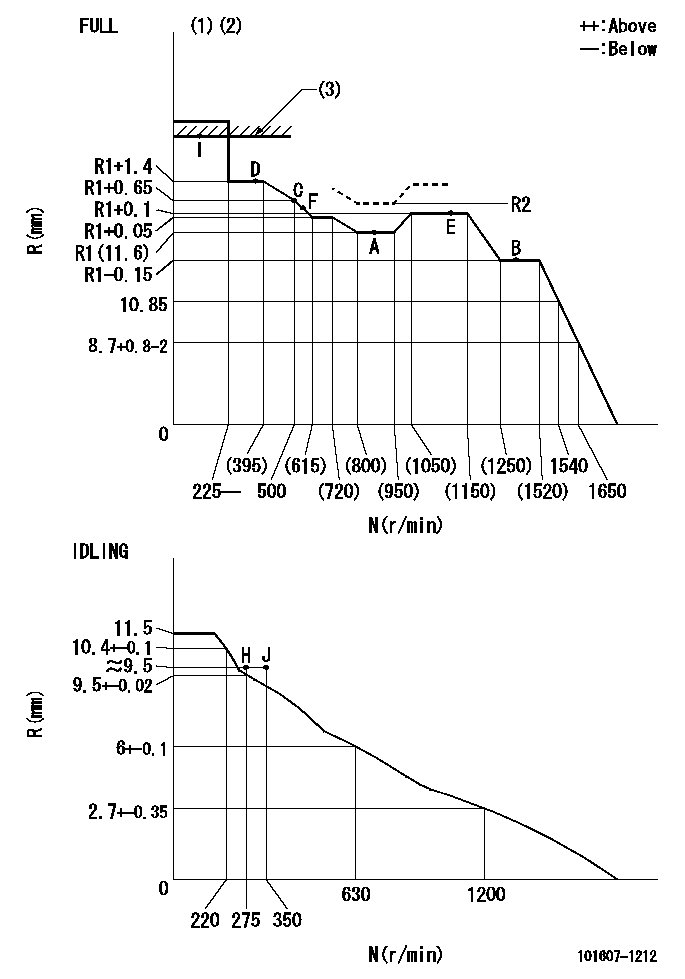
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT: RAL
----------
T1=F14 RAL=14.8+-0.2mm
----------
----------
T1=F14 RAL=14.8+-0.2mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
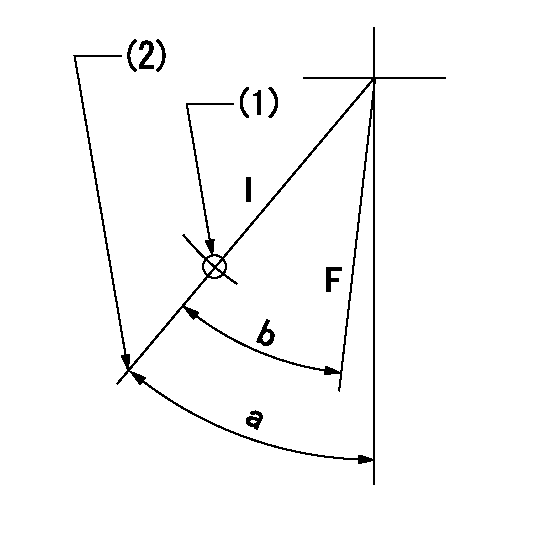
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=41deg+-5deg b=(40deg)+-3deg
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=41deg+-5deg b=(40deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle
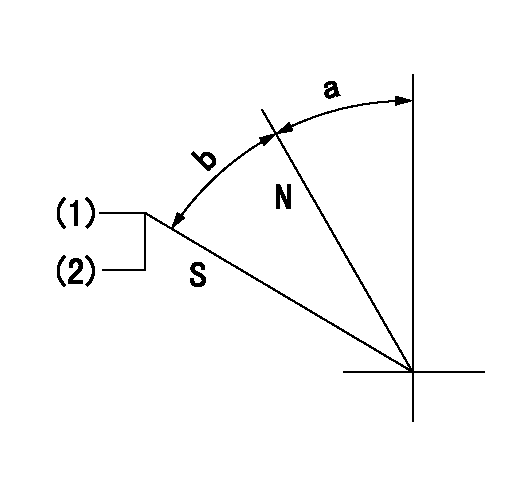
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Pump speed = aa and rack position = bb (non-injection rack position)
(2)Set the stopper bolt (confirm non-injection).
----------
aa=1400r/min bb=6.9-0.5mm
----------
a=32.5deg+-5deg b=25deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1400r/min bb=6.9-0.5mm
----------
a=32.5deg+-5deg b=25deg+-5deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=400r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=400r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm
----------
0000001601 TAMPER PROOF
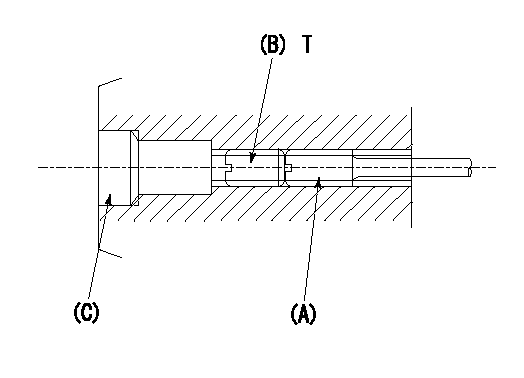
1. Method for setting tamperproof proofing
(1)After governor adjustment (torque cam phase adjustment), move the load lever to increase the full rack position to Ra.
(2)At speed N1 screw in screw (A) to obtain the rack position (actual measurement: Rb) for injection quantity Q1.
(3)Temporarily caulk using the tip of a screwdriver
(4)Confirm that the rack at that time is at Rc.
(5)Lock using setscrew (B). (Tightening torque = T)
(6)Next, coat (C) with adhesive and then pressfit.
(7)Then, readjust the full rack position using the load lever.
----------
N1=850r/min Q1=78.3+-1mm3/st Ra=(0.4)mm Rb=R2mm Rc=R2mm
----------
T=3.4~4.9N-m(0.35~0.5Kgf-m)
----------
N1=850r/min Q1=78.3+-1mm3/st Ra=(0.4)mm Rb=R2mm Rc=R2mm
----------
T=3.4~4.9N-m(0.35~0.5Kgf-m)
0000001701 LEVER

(A) Accelerator lever stopper bolt
(B) Link
(c) Nut
(D) Lever
(E) Pin
(f) lever
(G) Stopper bolt
(H) Return spring
(J) Pin (E) contacts lever.
(K) Load sensor terminal
(1)Black
(2)Blue-yellow
(3)Blue-red
Setting the accelerator lever angle, load sensor adjustment
1. Accelerator lever setting method
(1)Position the speed lever against the idle stopper bolt and fix.
(2)Screw in the accelerator lever stopper bolt (A) and back off the stopper bolt (A) from the position where the accelerator lever pin contacts the speed lever and set. (Gap: approx. 1 mm)
Tightening torque: 4.9~7 N.m {0.5~0.7 kgf.m}
2. Load sensor adjustment (See fig 1)
(1)Load sensor output measuring circuit
Apply DC5+-0.01V to the load sensor terminals and measure the output voltage.
(2)Load sensor output adjustment procedure
Hold the speed lever against the full side stopper bolt and fix. Adjust the load sensor output voltage to VF = 0.417+-0.1 V using the link (B) and then fix temporarily using nut (C).
Turn the speed lever from the idle side to the full side and confirm that output voltage VF = 0.417+-0.1 V is obtained. Confirm several times and then fix using nut (C).
Tightening torque: 3.4~4.9 N.m {0.35~0.5 kgf.m}
3. Setting the step motor's idle side stopper bolt
After adjustment in previous 1 and 2, position speed lever against idle stopper bolt and fix. Then, screw in stopper bolt G until step motor lever D's pin E contacts lever F. Back off 10+2 deg (approx. 3.5 mm) from this position and fix G. (See fig. 3)
4. Speed lever return confirmation
(1)Remove return spring (H) and confirm that the speed lever is returned to the idle position by the torsion spring.
(2)Reinstall the return spring (H) in its original position.
----------
----------
----------
----------
Timing setting
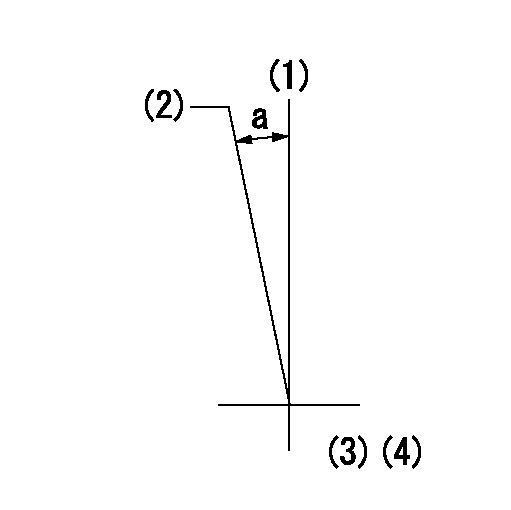
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=11deg
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
aa=11deg
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
Temporary corrections to the charts in this book will be printed in the publication ENGINE NEWS. Announcement for revised reprints of this book will be made in PREVIEW.These instructions are intended to acquaint you with the content of the rack setting charts. A description is given of the information to be found under each column heading. Read these instructions carefully so you can better understand the information presented.After reading and understanding these instructions, use the following suggestions to aid in the actual use of the rack setting charts.1. Determine and write down the engine model and engine serial number.2. Locate the correct rack setting chart.3. Locate the correct segment of the chart being used. Particular attention must be focused on the model and serial number.4. Read all notes pertaining to the engine being repaired. The notes are just as important as any other information that is presented on the rack setting chart.Column Headings
Column headings and arrangement of material can vary from chart to chart according to data requirements for the engines. A brief description of each column heading, note and symbol follows. See Fig. 1.Model
The MODEL column lists the description of the engine, and the serial number range to which the data applies. Be sure to use the data from the correct serial number range for the engine being repaired.Engine Full Load RPM
The column lists the engine speed (under load) at which the rack is positioned to permit maximum allowable amount of fuel to the engine per unit of time. Turbocharger speed, inlet manifold pressure and horsepower output are at their maximum for the listed rack setting. A tolerance of 10 RPM is allowed.Engine High Idle RPM
This column lists the high idle speed of the bare engine when driving a dynamometer. Use the figures in the chart when adjusting high idle in the truck. A tolerance of 30 RPM is allowed in most applications.Brake Horsepower
This column lists the power available at the flywheel, without fan, and within the limitations indicated in the charts. A tolerance of 3% of this value is normal from a new or reconditioned engine.
Fig. 1Rack Setting
The rack setting is the distance the rack must travel from the centered (sometimes referred to as zero) position, to supply sufficient fuel, to produce the expected power output of the engine. Rack setting is controlled by a stop bar or torque spring that is located within the governor. The stop bar and/or torque spring limits the maximum travel of the fuel rack. Rack setting procedure is explained and illustrated in the TESTING AND ADJUSTING Section of the applicable service manual.All rack settings are plus (+) settings unless otherwise indicated with a minus (-) sign. See Fig. 2.Torque Spring And Spacer
This column lists the part number and thickness of the torque spring, and only those spacers or shims installed between the torque spring and stop. Any shims located behind the stop are not listed. The dimensions are in inches and are for means of identification.
Fig.
Column headings and arrangement of material can vary from chart to chart according to data requirements for the engines. A brief description of each column heading, note and symbol follows. See Fig. 1.Model
The MODEL column lists the description of the engine, and the serial number range to which the data applies. Be sure to use the data from the correct serial number range for the engine being repaired.Engine Full Load RPM
The column lists the engine speed (under load) at which the rack is positioned to permit maximum allowable amount of fuel to the engine per unit of time. Turbocharger speed, inlet manifold pressure and horsepower output are at their maximum for the listed rack setting. A tolerance of 10 RPM is allowed.Engine High Idle RPM
This column lists the high idle speed of the bare engine when driving a dynamometer. Use the figures in the chart when adjusting high idle in the truck. A tolerance of 30 RPM is allowed in most applications.Brake Horsepower
This column lists the power available at the flywheel, without fan, and within the limitations indicated in the charts. A tolerance of 3% of this value is normal from a new or reconditioned engine.
Fig. 1Rack Setting
The rack setting is the distance the rack must travel from the centered (sometimes referred to as zero) position, to supply sufficient fuel, to produce the expected power output of the engine. Rack setting is controlled by a stop bar or torque spring that is located within the governor. The stop bar and/or torque spring limits the maximum travel of the fuel rack. Rack setting procedure is explained and illustrated in the TESTING AND ADJUSTING Section of the applicable service manual.All rack settings are plus (+) settings unless otherwise indicated with a minus (-) sign. See Fig. 2.Torque Spring And Spacer
This column lists the part number and thickness of the torque spring, and only those spacers or shims installed between the torque spring and stop. Any shims located behind the stop are not listed. The dimensions are in inches and are for means of identification.
Fig.