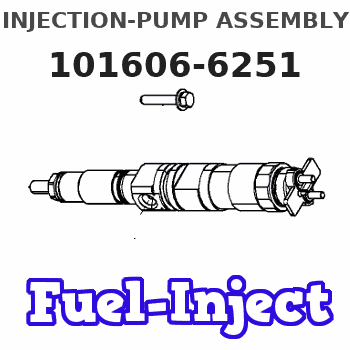
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 615 500
9400615500
ZEXEL
101606-6251
1016066251
MITSUBISHI
ME086578
me086578
Rating:
Service parts 101606-6251 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME086567
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6(220)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101606-6251
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104741-5327
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 615 500
9400615500
ZEXEL
101606-6251
1016066251
MITSUBISHI
ME086578
me086578
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101606-6251
9 400 615 500
ME086578 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D31T * K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
6D31T * K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-6220
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.25
3.35
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
10.6
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
48.8
47.2
50.4
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
10.6+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15
13.7
16.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(10.6)
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
48.8
47.8
49.8
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.55
Pump speed
r/min
1600
1600
1600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
64.9
60.9
68.9
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
(R1-0.05
)
Pump speed
r/min
550
550
550
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
32.9
28.9
36.9
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60.5
60.5
65.5
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1500--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1450
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
1
0.5
1.5
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1600
Advance angle
deg.
3.5
3
4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
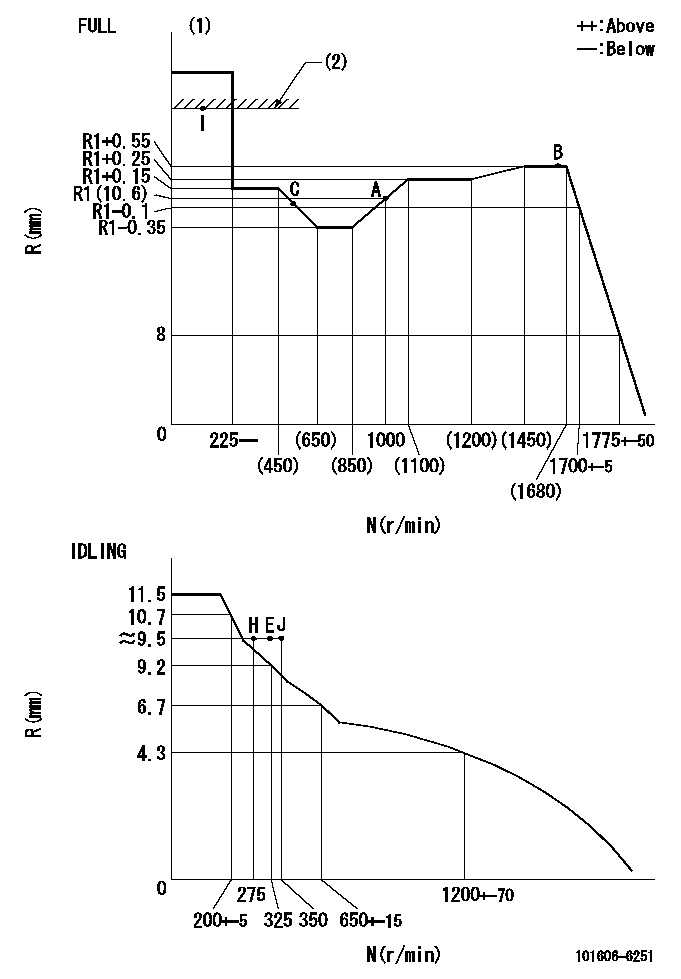
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=D19
----------
----------
T1=D19
----------
Speed control lever angle
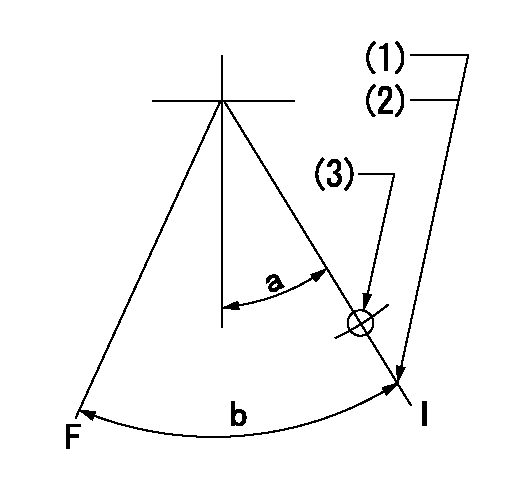
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
(2)Rack position = aa, speed = bb
(3)Use the hole above R = cc
----------
aa=9.5mm bb=275r/min cc=40mm
----------
a=26deg+-5deg b=40deg+-3deg
----------
aa=9.5mm bb=275r/min cc=40mm
----------
a=26deg+-5deg b=40deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Engine manufacturer's normal use
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Free (at shipping)
(2)Use the hole at R = aa
(3)Rack position corresponding to bb
(4)Set the stopper bolt so that speed = cc and rack position = dd and confirm non-injection.
(5)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed ee. Rack position = ff or less (non-injection rack position)
----------
aa=40mm bb=16mm cc=1700r/min dd=6.5-0.5mm ee=275r/min ff=8mm
----------
a=8deg+-5deg b=15deg+-5deg c=25deg+-5deg
----------
aa=40mm bb=16mm cc=1700r/min dd=6.5-0.5mm ee=275r/min ff=8mm
----------
a=8deg+-5deg b=15deg+-5deg c=25deg+-5deg
Timing setting
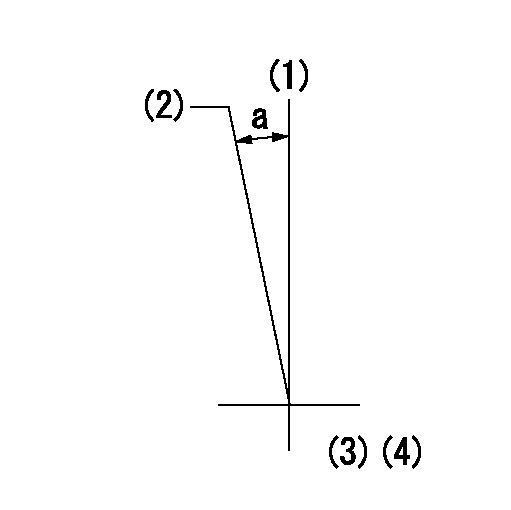
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=9deg
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
aa=9deg
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
Check Engine Light (Diagnostic) Output Circuit
The engine/vehicle harness provides information about the engine to the "check engine" light on the vehicle dash. The light flashes Diagnostic Code 34 when the ignition is ON and the engine is not running, to verify that the light works. When the engine is started the light will be ON solid until the PEEC system senses a minimum of 35 kPa (5 psi) oil pressure. If the engine light does not go out after the engine starts the light will begin to flash the Diagnostic Codes that are active in the PEEC System.The cruise ON/OFF and SET/RESUME switches can be used to interrogate the ECM for engine status. This is accomplished by placing the cruise ON/OFF switch in the OFF position and momentarily moving the Set/Resume switch to the RESUME position and then releasing it. The "check engine" light will emit a series of flashes which represent one or more, two digit numbers or diagnostic codes, which define engine status.An operating voltage of 12 Volts is supplied to the "check engine" light from the vehicle electrical system. The ECM turns on the light by connecting one side of the bulb to ground which completes the electrical circuit.Engine Electrical System
The electrical system can have three separate circuits: the charging circuit, the starting circuit and the low amperage circuit. Some of the electrical system components are used in more than one circuit. The battery (batteries), circuit breaker, ammeter, cables and wires from the battery are all common in each of the circuits.The charging circuit is in operation when the engine is running. An alternator makes electricity for the charging circuit. A voltage regulator in the circuit controls the electrical output to keep the battery at full charge.The starting circuit is in operation only when the start switch is activated.The low amperage circuit and the charging circuit are both connected through the ammeter. The starting circuit is not connected through the ammeter.Charging System Components
Alternator
The alternator is driven by V-type belts from the crankshaft pulley. This alternator is a three phase, self-rectifying charging unit, and the regulator is part of the alternator.This alternator design has no need for slip rings or brushes, and the only part that has movement is the rotor assembly. All conductors that carry current are stationary. The conductors are: the field winding, stator windings, six rectifying diodes, and the regulator circuit components.The rotor assembly has many magnetic poles like fingers with air space between each opposite pole. The poles have residual magnetism (like permanent magnets) that produce a small amount of magnet-like lines of force (magnetic field) between the poles. As the rotor assembly begins to turn between the field winding and the stator windings, a small amount of alternating current (AC) is produced in the stator windings from the small magnetic lines of force made by the residual magnetism of the poles. This AC current is changed to direct current (DC) when it passes through the diodes of the rectifier bridge. Most
The engine/vehicle harness provides information about the engine to the "check engine" light on the vehicle dash. The light flashes Diagnostic Code 34 when the ignition is ON and the engine is not running, to verify that the light works. When the engine is started the light will be ON solid until the PEEC system senses a minimum of 35 kPa (5 psi) oil pressure. If the engine light does not go out after the engine starts the light will begin to flash the Diagnostic Codes that are active in the PEEC System.The cruise ON/OFF and SET/RESUME switches can be used to interrogate the ECM for engine status. This is accomplished by placing the cruise ON/OFF switch in the OFF position and momentarily moving the Set/Resume switch to the RESUME position and then releasing it. The "check engine" light will emit a series of flashes which represent one or more, two digit numbers or diagnostic codes, which define engine status.An operating voltage of 12 Volts is supplied to the "check engine" light from the vehicle electrical system. The ECM turns on the light by connecting one side of the bulb to ground which completes the electrical circuit.Engine Electrical System
The electrical system can have three separate circuits: the charging circuit, the starting circuit and the low amperage circuit. Some of the electrical system components are used in more than one circuit. The battery (batteries), circuit breaker, ammeter, cables and wires from the battery are all common in each of the circuits.The charging circuit is in operation when the engine is running. An alternator makes electricity for the charging circuit. A voltage regulator in the circuit controls the electrical output to keep the battery at full charge.The starting circuit is in operation only when the start switch is activated.The low amperage circuit and the charging circuit are both connected through the ammeter. The starting circuit is not connected through the ammeter.Charging System Components
Alternator
The alternator is driven by V-type belts from the crankshaft pulley. This alternator is a three phase, self-rectifying charging unit, and the regulator is part of the alternator.This alternator design has no need for slip rings or brushes, and the only part that has movement is the rotor assembly. All conductors that carry current are stationary. The conductors are: the field winding, stator windings, six rectifying diodes, and the regulator circuit components.The rotor assembly has many magnetic poles like fingers with air space between each opposite pole. The poles have residual magnetism (like permanent magnets) that produce a small amount of magnet-like lines of force (magnetic field) between the poles. As the rotor assembly begins to turn between the field winding and the stator windings, a small amount of alternating current (AC) is produced in the stator windings from the small magnetic lines of force made by the residual magnetism of the poles. This AC current is changed to direct current (DC) when it passes through the diodes of the rectifier bridge. Most
Have questions with 101606-6251?
Group cross 101606-6251 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
101606-6251
9 400 615 500
ME086578
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D31T
6D31T
