Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 750
9400611750
ZEXEL
101606-6090
1016066090
MITSUBISHI
ME070912
me070912
Rating:
Service parts 101606-6090 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME047488
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
17.7{180}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 750
9400611750
ZEXEL
101606-6090
1016066090
MITSUBISHI
ME070912
me070912
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
9 400 611 750
ME070912 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D16 * K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
6D16 * K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.25
3.35
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.2
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
73.8
72.8
74.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12.6
11.1
14.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
850--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
800
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1400
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
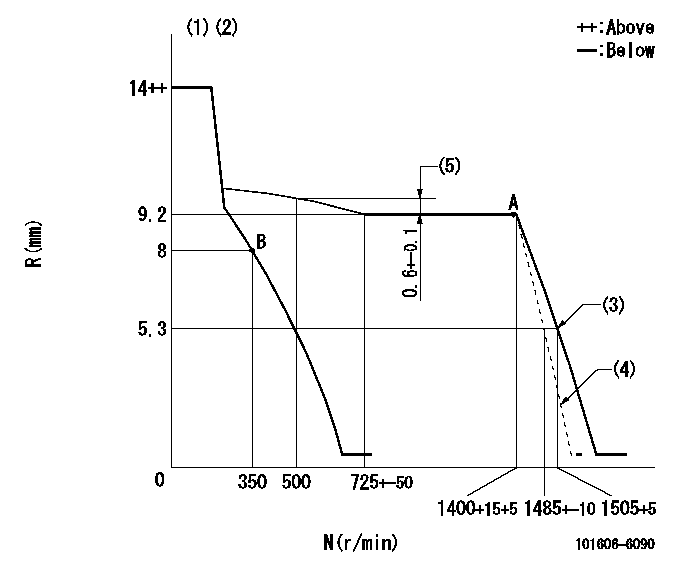
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Torque spring does not operate.
(3)Set idle sub-spring
(4)Main spring setting
(5)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=11 N1=1400r/min N2=500r/min
----------
----------
K=11 N1=1400r/min N2=500r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=27deg+-5deg b=17deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=27deg+-5deg b=17deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)At delivery
----------
----------
a=26deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=26deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=18deg
----------
a=(2deg)
----------
aa=18deg
----------
a=(2deg)
Information:
Illustration 8: (12) Injection plunger. (13) Plunger gear. (G) Location. (H) Location.1. Inspect injection plunger (12), especially at scroll location (G).Any scratches, rust, or erosion (uneven wear) at location (G) can be an indication that the unit injector will not pump the correct amount of fuel.If a scratch, rust, etc. at location (G) can be felt with your fingernail, the plunger is worn too much and the unit injector should be replaced.2. Some surface conditions to look for at location (G) are: SCRATCHES: Scratches are caused by dirt in the fuel or other foreign material that get into the unit injector.RUST DAMAGE: Rust damage that is caused either by water in the fuel, or by incorrect storage procedures for unit injectors.CAVITATION EROSION: The surface condition of the plunger, especially in the area of location (G), will look and feel similar to emery cloth.This condition is normally seen in a unit injector that has high operating hours, and is caused by the constant impact of high velocity fuel as it strikes the surface of the plunger.3. Surface defects away from the scroll area are less likely to affect fuel delivery but can cause sticking or seizure of the plunger. Any condition that causes the plunger to stick or bind is NOT acceptable.Place the plunger in clean test fluid to ensure good lubrication before checking the plunger movement.If the plunger still sticks, the unit injector should be replaced. A plunger can look satisfactory and not stick; but still be worn too much to deliver the correct amount of fuel. It may also leak. Usually, if a plunger looks good and feels good, it probably is in good condition.4. It is normal for plunger gear (13) to have wear mark(s) or polished area(s) on the gear teeth at [location (H)] that is caused by contact with rack (15).If the wear marks at each location (H) can be felt with the point of a pencil, or if the teeth are worn to a sharp edge, the gear is worn too much.Cleaning Of Unit Injector Barrel
Illustration 9: (1) Case. (2) Unit injector body. (3) Tappet spring. (4) Tip assembly (part of check assembly). (5) Check (part of check assembly). (6) Stop (part of check assembly). (7) Sleeve (part of check assembly). (8) Spill deflector. (9) Spring (check). (10) Plate. (11) Barrel (part of plunger assembly). (12) Injector plunger (part of plunger assembly). (13) Plunger gear (part of plunger assembly). (14) Retainer. (15) Rack. (16) Tappet retainer pin. (17) Keeper. (18) Tappet assembly.1. Place a unit injector body in Pedestal (Tool B) with the tip up.This will allow cleaning fluid to drain from barrel (11).2. Flush barrel (11) with cleaning solution filtered to the 5 micron level.Use clean 6V-6067 or 6V-6068 Test Fluid or equivalent test fluid that meets SAE967 or ISO4113 Standards as a cleaning solution.A 6V-7093 Brush Assembly can be used to remove varnish deposits.Do NOT remove barrel (11) from the unit injector. The barrel can NOT be removed from the unit
