Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101606-1731
1016061731
MITSUBISHI
ME076209
me076209
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101606-1731
1016061731
MITSUBISHI
ME076209
me076209
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101606-1731
ME076209 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D14T * K
6D14T * K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3
2.95
3.05
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
12.1
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
88
85.4
90.6
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
10.5
9
12
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(12.1)
Pump speed
r/min
800
800
800
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
88
87
89
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
49.3
49.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
370
370
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
(R1-0.8)
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
67
65
69
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
18.7
18.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
140
140
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
110
90
130
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R1-1.1
Boost pressure
kPa
13.3
13.3
13.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
100
100
100
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
(R1-0.8)
Boost pressure
kPa
18.7
17.4
20
Boost pressure
mmHg
140
130
150
Boost compensator adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R1(12.1)
Boost pressure
kPa
36
29.3
42.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
270
220
320
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1250--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1300
Advance angle
deg.
1.6
1.1
2.1
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1400
Advance angle
deg.
3.5
3
4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
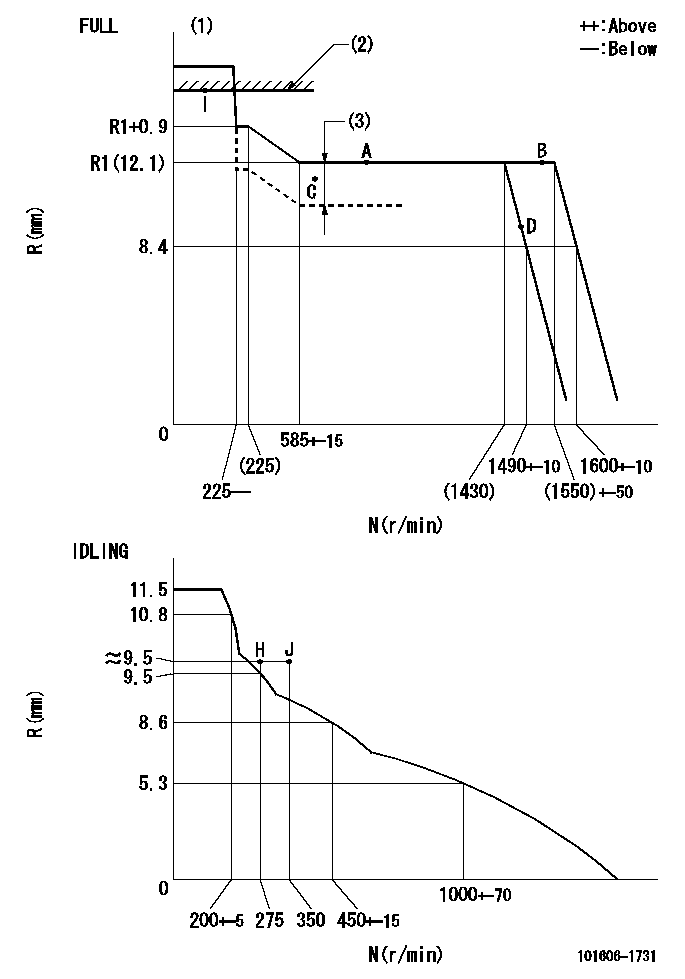
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=B45 BCL=1.1+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=B45 BCL=1.1+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
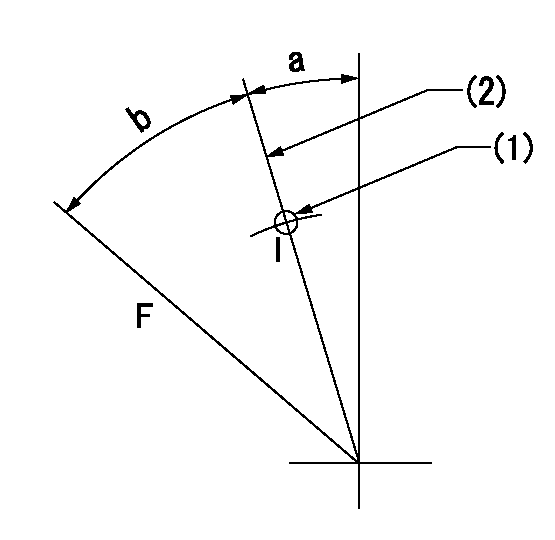
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=29mm
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=(46deg)+-3deg
----------
aa=29mm
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=(46deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Engine manufacturer's normal use
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Set the stopper bolt at pump speed = aa and rack position = bb (non-injection rack position). Confirm non-injection.
(2)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed cc. Rack position = dd (non-injection rack position).
(3)Rack position = approximately ee.
(4)Free (at shipping)
(5)At hole above R = ff.
----------
aa=1550r/min bb=(7.5)mm cc=275r/min dd=(9)mm ee=17.4mm ff=50mm
----------
a=38.5deg+-5deg b=(27deg) c=17deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1550r/min bb=(7.5)mm cc=275r/min dd=(9)mm ee=17.4mm ff=50mm
----------
a=38.5deg+-5deg b=(27deg) c=17deg+-5deg
0000001201
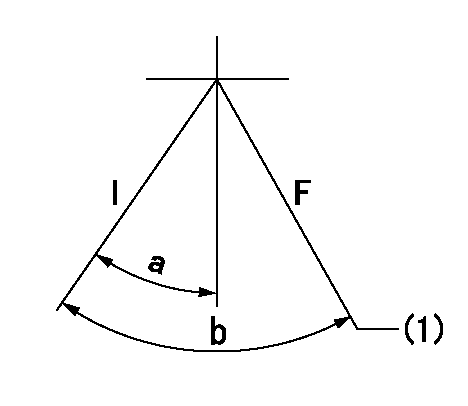
I:Idle
F:At operation, hold it in the full speed position.
(1)Rack position = aa, speed = bb.
----------
aa=8.4mm bb=1490r/min
----------
a=15deg+-5deg b=(41deg)+-3deg
----------
aa=8.4mm bb=1490r/min
----------
a=15deg+-5deg b=(41deg)+-3deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=400+-5r/min Ra=9.2mm
----------
----------
N1=400+-5r/min Ra=9.2mm
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=15deg
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
aa=15deg
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
Turbocharger
Turbocharger bearing failures can cause large quantities of oil to enter the air intake and exhaust systems. Loss of engine lubricant can result in serious engine damage.Minor leakage of a turbocharger housing under extended low idle operation will not cause problems as long as a turbocharger bearing failure has NOT occurred.When a turbocharger bearing failure is accomplished by a significant engine performance loss (exhaust smoke or engine speed up at no load), DO NOT continue engine operation until the turbocharger is repaired or replaced.
An inspection/check of your turbocharger will minimize unscheduled downtime and reduce the chance for potential damage to other engine parts.Inspect/Check
1. Remove the exhaust outlet and air inlet piping from the turbocharger. Visually check for oil leaks.2. Turn the turbine and compressor wheel by hand. The assembly should turn freely.3. Inspect the turbine wheel and compressor wheel for contact with the turbocharger housing. There should NOT be any visible signs of contact between the turbine or compressor wheels and the turbocharger housing.4. Check the compressor wheel for cleanliness. If only the blade side of the wheel is dirty, dirt and/or moisture is passing through the air filtering system. If oil is found only on the back side of the wheel, it indicates a possible turbocharger oil seal leak.The leak may be the result of extended engine operation at low idle or an intake air line restriction (plugged air filters), which causes the turbocharger to "slobber".* Maintain the compressor wheel/turbine housing by cleaning with standard shop solvents and a soft bristle brush.5. Check the end play and bearing clearance on the turbine wheel and shaft. If the measurements are not within specifications (see the Service Manual), the turbocharger must be repaired or replaced.6. When installing or replacing V-band clamps, position the gap (tightening screw) down if possible so any accumulation of moisture will drain away. Turbocharger components require precision clearances and balancing due to operation at high rotation (torsional) speeds. Severe Service Applications can accelerate component wear and may suggest the need to Inspect/Repair/Replace the cartridge at reduced intervals to ensure maximum reliability and retention of the full core.Removal and Installation
For removal and installation, or repair/replacement options of turbochargers, see your Caterpillar dealer. Refer to the Service Manual for this engine or consult your Caterpillar dealer for the procedure and specifications.Engine Mounts and Crankshaft Vibration Damper
Inspect/Check Engine Mounts
Caterpillar recommends checking the engine mounts for deterioration and proper bolt torque. This will prevent excessive engine vibration caused from improper mounting. See your Service Manual or Caterpillar dealer for recommended torque values.Inspect/Check Camshaft Vibration Damper
Damage to, or failure of the damper will increase torsional vibrations and result in damage to the crankshaft and other engine components. A deteriorating vibration damper will cause excessive gear train noise at variable points in the engine speed range.Rubber Damper
Your engine may be equipped with a standard Rubber Crankshaft Torsional Vibration Damper. A standard damper uses a rubber mounted ring to reduce crankshaft vibration. Some engines also have a Visconic Torsional Vibration Damper. A
Turbocharger bearing failures can cause large quantities of oil to enter the air intake and exhaust systems. Loss of engine lubricant can result in serious engine damage.Minor leakage of a turbocharger housing under extended low idle operation will not cause problems as long as a turbocharger bearing failure has NOT occurred.When a turbocharger bearing failure is accomplished by a significant engine performance loss (exhaust smoke or engine speed up at no load), DO NOT continue engine operation until the turbocharger is repaired or replaced.
An inspection/check of your turbocharger will minimize unscheduled downtime and reduce the chance for potential damage to other engine parts.Inspect/Check
1. Remove the exhaust outlet and air inlet piping from the turbocharger. Visually check for oil leaks.2. Turn the turbine and compressor wheel by hand. The assembly should turn freely.3. Inspect the turbine wheel and compressor wheel for contact with the turbocharger housing. There should NOT be any visible signs of contact between the turbine or compressor wheels and the turbocharger housing.4. Check the compressor wheel for cleanliness. If only the blade side of the wheel is dirty, dirt and/or moisture is passing through the air filtering system. If oil is found only on the back side of the wheel, it indicates a possible turbocharger oil seal leak.The leak may be the result of extended engine operation at low idle or an intake air line restriction (plugged air filters), which causes the turbocharger to "slobber".* Maintain the compressor wheel/turbine housing by cleaning with standard shop solvents and a soft bristle brush.5. Check the end play and bearing clearance on the turbine wheel and shaft. If the measurements are not within specifications (see the Service Manual), the turbocharger must be repaired or replaced.6. When installing or replacing V-band clamps, position the gap (tightening screw) down if possible so any accumulation of moisture will drain away. Turbocharger components require precision clearances and balancing due to operation at high rotation (torsional) speeds. Severe Service Applications can accelerate component wear and may suggest the need to Inspect/Repair/Replace the cartridge at reduced intervals to ensure maximum reliability and retention of the full core.Removal and Installation
For removal and installation, or repair/replacement options of turbochargers, see your Caterpillar dealer. Refer to the Service Manual for this engine or consult your Caterpillar dealer for the procedure and specifications.Engine Mounts and Crankshaft Vibration Damper
Inspect/Check Engine Mounts
Caterpillar recommends checking the engine mounts for deterioration and proper bolt torque. This will prevent excessive engine vibration caused from improper mounting. See your Service Manual or Caterpillar dealer for recommended torque values.Inspect/Check Camshaft Vibration Damper
Damage to, or failure of the damper will increase torsional vibrations and result in damage to the crankshaft and other engine components. A deteriorating vibration damper will cause excessive gear train noise at variable points in the engine speed range.Rubber Damper
Your engine may be equipped with a standard Rubber Crankshaft Torsional Vibration Damper. A standard damper uses a rubber mounted ring to reduce crankshaft vibration. Some engines also have a Visconic Torsional Vibration Damper. A
Have questions with 101606-1731?
Group cross 101606-1731 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
101606-1731
ME076209
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6D14T
6D14T