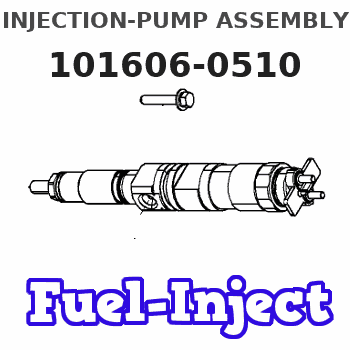
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
F 019 Z10 733
f019z10733
ZEXEL
101606-0510
1016060510
ISUZU
8976023990
8976023990
Rating:
Service parts 101606-0510 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
16.2(165)/19.6(200)
14.
NOZZLE
Cross reference number
BOSCH
F 019 Z10 733
f019z10733
ZEXEL
101606-0510
1016060510
ISUZU
8976023990
8976023990
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
F 019 Z10 733
8976023990 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6HL1-S * K 14BF PE6AD PE
6HL1-S * K 14BF PE6AD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8310
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2240
Opening pressure
MPa
18
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
184
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-8620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
206
206
206
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.1
2.1
2.1
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.8
3.75
3.85
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
14.2
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
65
63.4
66.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
9.7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
295
295
295
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13
11.7
14.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(14.2)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
65
64
66
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
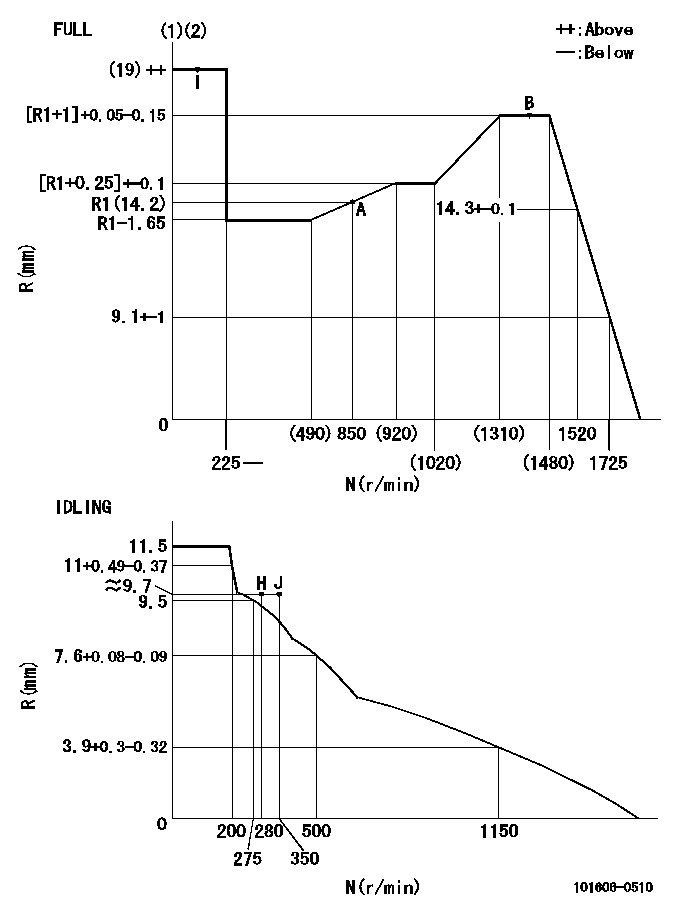
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
----------
T1=P28
----------
----------
T1=P28
----------
Timer adjustment
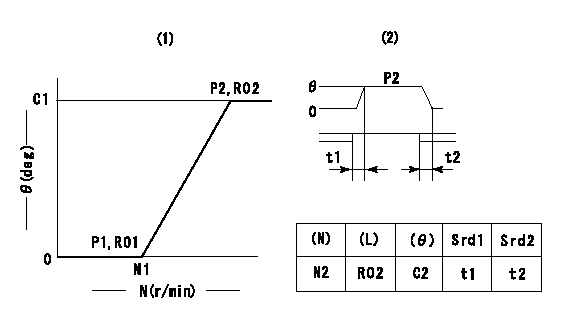
(1)Adjusting range
(2)Step response time
(N): Speed of the pump
(L): Load
(theta) Advance angle
(Srd1) Step response time 1
(Srd2) Step response time 2
1. Adjusting conditions for the variable timer
(1)Adjust the clearance between the pickup and the protrusion to L.
----------
L=1.5+-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(8)deg t1=2--sec. t2=2--sec.
----------
N1=1300++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=8+-0.3deg R01=0/4load R02=4/4load
----------
L=1.5+-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(8)deg t1=2--sec. t2=2--sec.
----------
N1=1300++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=8+-0.3deg R01=0/4load R02=4/4load
Speed control lever angle
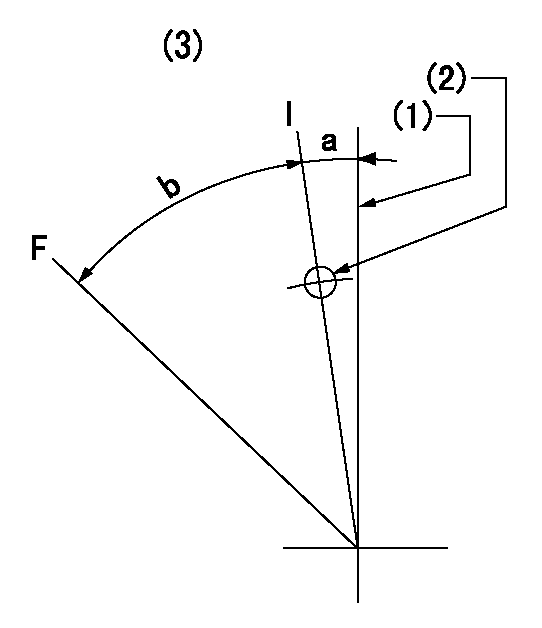
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
(3)Viewed from feed pump side.
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=11deg+-5deg b=40deg+-3deg
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=11deg+-5deg b=40deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
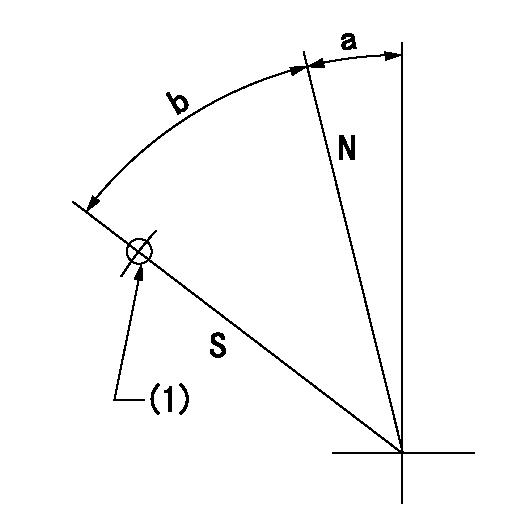
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
----------
aa=45mm
----------
a=12.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
aa=45mm
----------
a=12.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
0000001501 RACK SENSOR
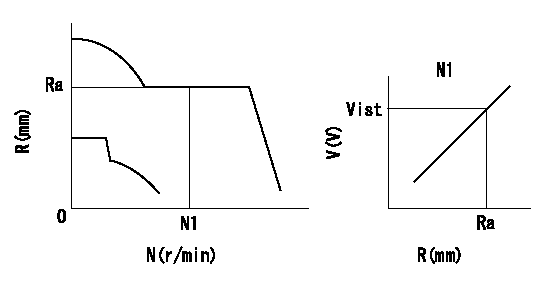
Rack sensor adjustment
1. Flange type rack sensor (rack sensor adjustment -5*20)
(1)These types of rack sensors do not need adjustment. Confirm the performance with the following procedures.
(2)Mount the rack sensor main body to the pump main body.
(3)Fix the pump lever at full.
(4)At supply voltage V1, pump speed N1 and rack position Ra, confirm that the amp's output voltage is Vist.
(5)Move the pump lever two or three times.
(6)Set again to full.
(7)Confirm that the amplifier output voltage is Vist.
(8)Fix the caution plate to the upper part of the rack sensor.
(For those without the caution plate instructions, make sure the nameplate of the rack sensor carries the "Don't hold here" caution.)
(9)Apply red paint to the rack sensor mounting bolts (2 places).
----------
V1=5+-0.01V N1=850r/min Ra=R1(14.2)mm Vist=3.49+-0.28V
----------
----------
V1=5+-0.01V N1=850r/min Ra=R1(14.2)mm Vist=3.49+-0.28V
----------
Timing setting
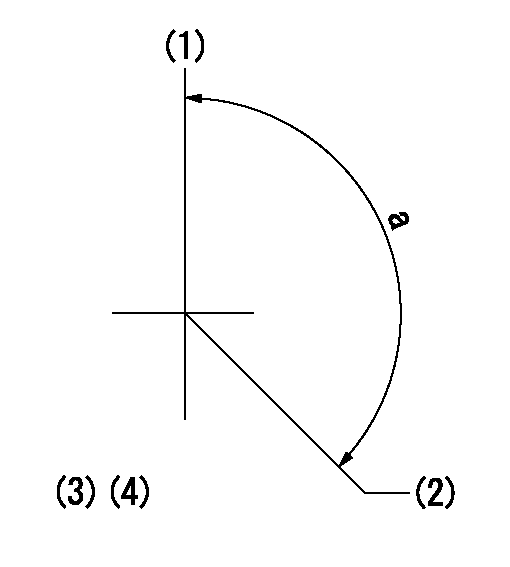
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Positions of coupling's threaded installation holes at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=6deg
----------
a=(160deg)
----------
aa=6deg
----------
a=(160deg)
Information:
Driver Techniques
The manner in which a vehicle is driven can have a dramatic effect on fuel consumption. Operators can maximize fuel economy and engine life by practicing the techniques of using minimum power and low engine rpm. The following tips can optimize fuel economy by making maximum use of the potential efficiency of the engine and vehicle.The 3176 can be programmed to ensure that the engine and vehicle are operated within specific limits for maximum fuel economy. (Refer to topic, Customer Specified Parameters, in this publication for information.)Caterpillar engines are designed to operate at lower engine rpm (speed) and have demonstrated excellent fuel savings and longer service life when operated in this manner.Starting Out
This truck engine does not require long warm-up times that waste fuel. Below 63°F (17°C), the 3176 system automatically idles at 1000 rpm. It takes just a few minutes in the summer and a bit longer in the winter to warm up the mechanical engine, and for the 3176 engine to reduce engine rpm to the programmed low idle rpm.A load can be applied to the engine after normal oil pressure is reached and the water temperature gauge begins to rise. To get the vehicle in motion, use a gear that will result in a smooth, easy start without increasing engine speed above low idle or slipping the clutch. Engage the clutch smoothly. Interrupted and jerky clutch engagement put stress on the drive train and wastes fuel.Keep engine rpm (speed) at a minimum. Use just enough rpm to pick up the next gear. This technique is called progressive shifting. It can improve fuel consumption and will not harm the engine.Progressive Shifting
Drive line efficiency is best in the low to mid rpm range (1100 to 1600 rpm) of the engine due to reduced frictional losses of the engine, transmission and rear axles. When accelerating under normal level road conditions, the engine should be operated in this most efficient rpm range by using only enough power to pick up the next higher gear. This technique of upshifting at the lowest possible rpm is called progressive shifting.Progressive shifting also reduces the time to accelerate to the desired vehicle speed. Top gear is reached sooner because engine rpm does not have to fall off as far to synchronize the gears of the transmission. The key to progressive shifting is to use minimum rpm, minimum power and upshift early while accelerating the truck.The 3176 can be programmed to limit engine acceleration above pre-programmed engine rpm settings. This feature encourages the operator to practice progressive shifting techniques.Refer to Driving Techniques for Maximum Fuel Economy, form LEDT5092 for more information.Cruising Speed
It's a simple fact that the faster a vehicle is driven, the more fuel it will consume. A few miles per hour (kilometers per hour) can make a significant difference in fuel economy.Increasing cruising speed from 55 to 65 mph (88 to 104 km/h) will increase fuel consumption of a typical class 8 truck approximately 1.0 mpg (0.4 km/L). A practice of
The manner in which a vehicle is driven can have a dramatic effect on fuel consumption. Operators can maximize fuel economy and engine life by practicing the techniques of using minimum power and low engine rpm. The following tips can optimize fuel economy by making maximum use of the potential efficiency of the engine and vehicle.The 3176 can be programmed to ensure that the engine and vehicle are operated within specific limits for maximum fuel economy. (Refer to topic, Customer Specified Parameters, in this publication for information.)Caterpillar engines are designed to operate at lower engine rpm (speed) and have demonstrated excellent fuel savings and longer service life when operated in this manner.Starting Out
This truck engine does not require long warm-up times that waste fuel. Below 63°F (17°C), the 3176 system automatically idles at 1000 rpm. It takes just a few minutes in the summer and a bit longer in the winter to warm up the mechanical engine, and for the 3176 engine to reduce engine rpm to the programmed low idle rpm.A load can be applied to the engine after normal oil pressure is reached and the water temperature gauge begins to rise. To get the vehicle in motion, use a gear that will result in a smooth, easy start without increasing engine speed above low idle or slipping the clutch. Engage the clutch smoothly. Interrupted and jerky clutch engagement put stress on the drive train and wastes fuel.Keep engine rpm (speed) at a minimum. Use just enough rpm to pick up the next gear. This technique is called progressive shifting. It can improve fuel consumption and will not harm the engine.Progressive Shifting
Drive line efficiency is best in the low to mid rpm range (1100 to 1600 rpm) of the engine due to reduced frictional losses of the engine, transmission and rear axles. When accelerating under normal level road conditions, the engine should be operated in this most efficient rpm range by using only enough power to pick up the next higher gear. This technique of upshifting at the lowest possible rpm is called progressive shifting.Progressive shifting also reduces the time to accelerate to the desired vehicle speed. Top gear is reached sooner because engine rpm does not have to fall off as far to synchronize the gears of the transmission. The key to progressive shifting is to use minimum rpm, minimum power and upshift early while accelerating the truck.The 3176 can be programmed to limit engine acceleration above pre-programmed engine rpm settings. This feature encourages the operator to practice progressive shifting techniques.Refer to Driving Techniques for Maximum Fuel Economy, form LEDT5092 for more information.Cruising Speed
It's a simple fact that the faster a vehicle is driven, the more fuel it will consume. A few miles per hour (kilometers per hour) can make a significant difference in fuel economy.Increasing cruising speed from 55 to 65 mph (88 to 104 km/h) will increase fuel consumption of a typical class 8 truck approximately 1.0 mpg (0.4 km/L). A practice of