Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 517
9400611517
ZEXEL
101606-0150
1016060150
ISUZU
8976004550
8976004550
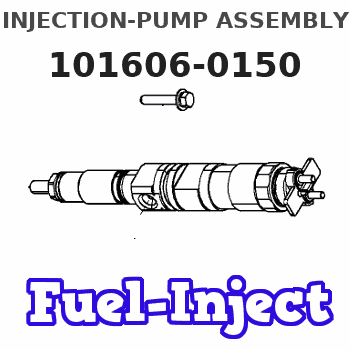
Rating:
Service parts 101606-0150 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
8-94391-291-4
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
16.2{165}/19.6{200}
14.
NOZZLE
Include in #1:
101606-0150
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104742-1490
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 517
9400611517
ZEXEL
101606-0150
1016060150
ISUZU
8976004550
8976004550
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8260
Bosch type code
9 430 610 133
Nozzle
105780-0120
Bosch type code
1 688 901 990
Nozzle holder
105780-2190
Opening pressure
MPa
18
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
184
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-8620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
206
172
240
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.1
1.75
2.45
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.8
3.75
3.85
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
14.1
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
128.5
126.9
130.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15.5
14.2
16.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(14.1)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
128.5
127.5
129.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
(R1+1.15
)+0.05-0
.15
Pump speed
r/min
1450
1450
1450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
130
126.8
133.2
Fixing the lever
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
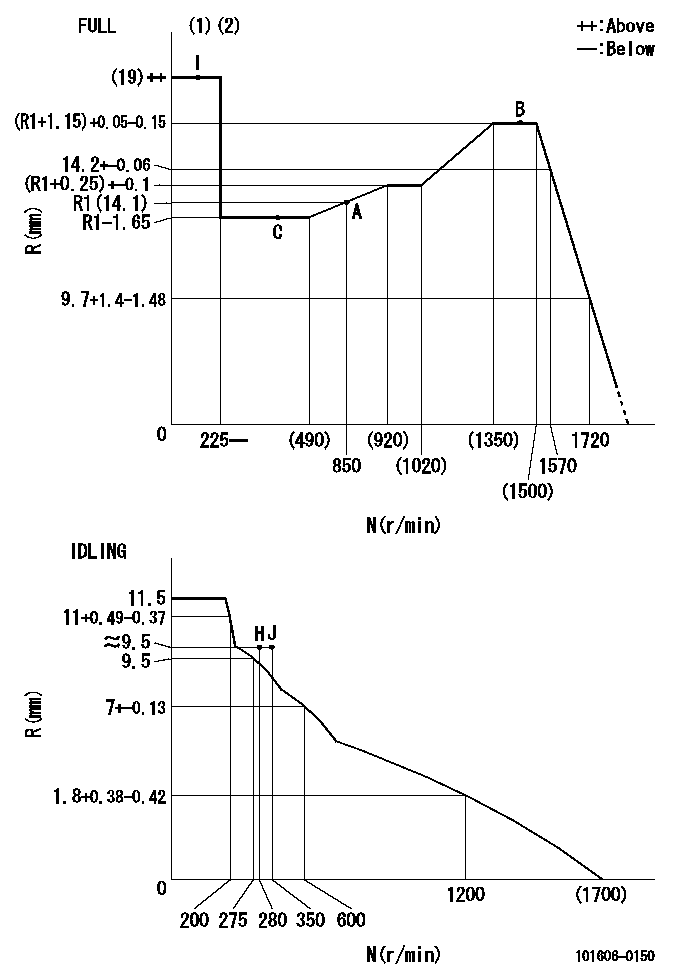
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
----------
T1=N97
----------
----------
T1=N97
----------
Timer adjustment
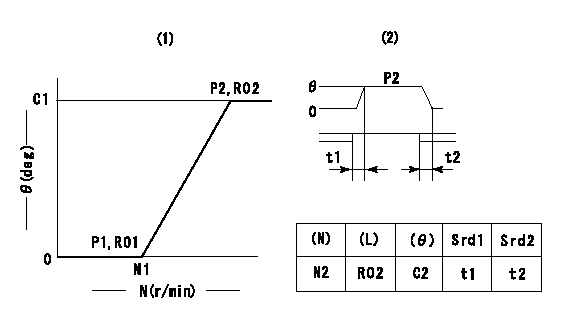
(1)Adjusting range
(2)Step response time
(N): Speed of the pump
(L): Load
(theta) Advance angle
(Srd1) Step response time 1
(Srd2) Step response time 2
1. Adjusting conditions for the variable timer
(1)Adjust the clearance between the pickup and the protrusion to L.
----------
L=1.5+-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(8)deg t1=2--sec. t2=2--sec.
----------
N1=1300++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=8+-0.3deg R01=0/4load R02=4/4load
----------
L=1.5+-0.2mm N2=800r/min C2=(8)deg t1=2--sec. t2=2--sec.
----------
N1=1300++r/min P1=0kPa(0kgf/cm2) P2=392kPa(4kgf/cm2) C1=8+-0.3deg R01=0/4load R02=4/4load
Speed control lever angle
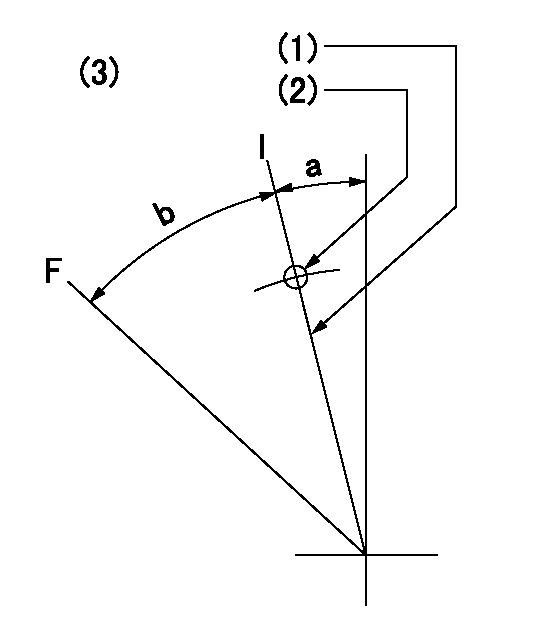
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
(2)Use the pin at R = aa
(3)Viewed from feed pump side.
----------
aa=33mm
----------
a=12deg+-5deg b=47.5deg+-3deg
----------
aa=33mm
----------
a=12deg+-5deg b=47.5deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
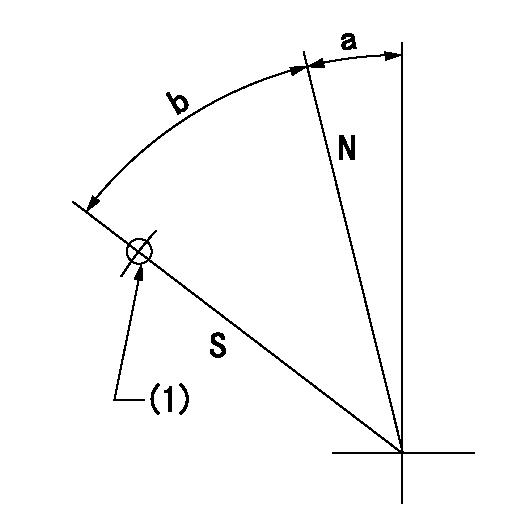
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
----------
aa=45mm
----------
a=12.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
aa=45mm
----------
a=12.5deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
0000001501 RACK SENSOR
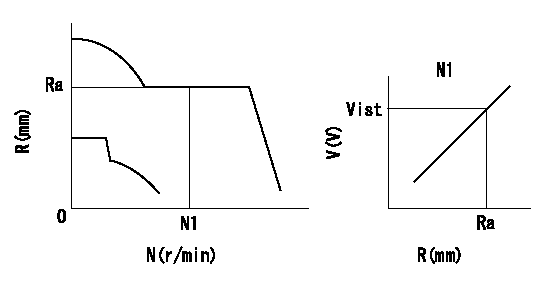
Rack sensor adjustment
1. Flange type rack sensor (rack sensor adjustment -5*20)
(1)These types of rack sensors do not need adjustment. Confirm the performance with the following procedures.
(2)Mount the rack sensor main body to the pump main body.
(3)Fix the pump lever at full.
(4)At supply voltage V1, pump speed N1 and rack position Ra, confirm that the amp's output voltage is Vist.
(5)Move the pump lever two or three times.
(6)Set again to full.
(7)Confirm that the amplifier output voltage is Vist.
(8)Fix the caution plate to the upper part of the rack sensor.
(For those without the caution plate instructions, make sure the nameplate of the rack sensor carries the "Don't hold here" caution.)
(9)Apply red paint to the rack sensor mounting bolts (2 places).
----------
V1=5+-0.01V N1=850r/min Ra=R1(14.1)mm Vist=3.55+-0.28V
----------
----------
V1=5+-0.01V N1=850r/min Ra=R1(14.1)mm Vist=3.55+-0.28V
----------
Timing setting
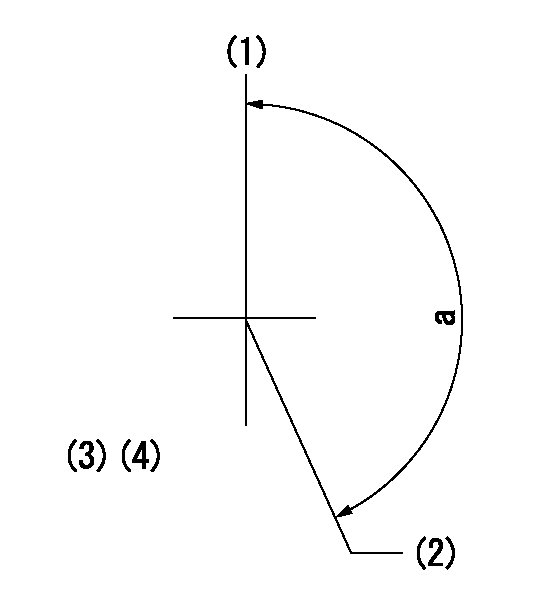
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Positions of coupling's threaded installation holes at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=6deg
----------
a=(160deg)
----------
aa=6deg
----------
a=(160deg)
Information:
You must read and understand the warnings and instructions contained in the Safety section of this manual before performing any operation or maintenance procedures.Before proceeding with Every 1000 Hour maintenance, perform all previous maintenance interval requirements.Engine Protection Devices
Inspect for Proper Operation
Refer to the Service Manual for the procedure. All engine protective devices must be checked and maintained to provide the engine with proper protection if a component malfunction or failure should occur. Check all engine protective devices. Never use the Emergency Shutdown controls for a normal stopping procedure.SR4 Generator and Control Panel (If Equipped)
SR4 Generator
Before working inside the generator, make sure that the starting motor can not be activated by any automatic or manual signal.When the engine-generator is operating, voltages up to 600V are present in these areas near or on the regulator: 1. the regulator terminal strip2. the excitation transformer terminal strip (self-excited generator only)Do not short these terminals to ground with any part of the body or any conductive material. Loss of life or injury could result from electrical shock or injury from molten metal.
Electronic components in the regulator can be damaged during generator operation if contact is made between the part and ground.
Clean/Inspect Voltage Regulator
If moisture is allowed to remain in contact with an electrical winding, some of the moisture will eventually be absorbed. This will lower the resistance of the winding insulation. The insulation used on the windings of Caterpillar generators is moisture resistant, but constant exposure to moisture will gradually lower the insulation's resistance.Dirt can make the problem worse because it can hold the moisture in contact with the insulation. Salt (from coastal location sea air) can also make the problem much worse. This is because salt tends to absorb moisture from the air. When the salt and moisture combine, they make a good electrical conductor.* Clean the voltage regulator and generator of dirt and debris. Use a brush to loosen accumulations of dirt and a vacuum system for removal. Use of compressed air is not recommended, because of moisture present in the form of condensate.Carbon tracking on insulators can be caused by dirt or loose connections. These carbon paths must be cleaned or the insulators replaced. Failure to correct a carbon tracking problem will eventually result in a short in the electrical circuit.* Visually check for loose or broken wires and connections. Check the wires and connections on the regulator assembly. Check all wires and connections in the generator. Make any necessary repairs to the wiring as required.Visually inspect the generator and control panel. Check for loose, broken, or damaged wiring or components. The inspection only takes a few minutes and could avert a potential problem that could cause your generator set to fail.Operational Checks
Start the engine. Use the starting procedure found in the SR4 Generators and Control Panels Operation and Maintenance Manual, SEBU6150.The following operational checks include: * generator operation and engine starting* lubricating and fuel systems* overall operationThe checks should take no longer than five minutes to complete. A
Inspect for Proper Operation
Refer to the Service Manual for the procedure. All engine protective devices must be checked and maintained to provide the engine with proper protection if a component malfunction or failure should occur. Check all engine protective devices. Never use the Emergency Shutdown controls for a normal stopping procedure.SR4 Generator and Control Panel (If Equipped)
SR4 Generator
Before working inside the generator, make sure that the starting motor can not be activated by any automatic or manual signal.When the engine-generator is operating, voltages up to 600V are present in these areas near or on the regulator: 1. the regulator terminal strip2. the excitation transformer terminal strip (self-excited generator only)Do not short these terminals to ground with any part of the body or any conductive material. Loss of life or injury could result from electrical shock or injury from molten metal.
Electronic components in the regulator can be damaged during generator operation if contact is made between the part and ground.
Clean/Inspect Voltage Regulator
If moisture is allowed to remain in contact with an electrical winding, some of the moisture will eventually be absorbed. This will lower the resistance of the winding insulation. The insulation used on the windings of Caterpillar generators is moisture resistant, but constant exposure to moisture will gradually lower the insulation's resistance.Dirt can make the problem worse because it can hold the moisture in contact with the insulation. Salt (from coastal location sea air) can also make the problem much worse. This is because salt tends to absorb moisture from the air. When the salt and moisture combine, they make a good electrical conductor.* Clean the voltage regulator and generator of dirt and debris. Use a brush to loosen accumulations of dirt and a vacuum system for removal. Use of compressed air is not recommended, because of moisture present in the form of condensate.Carbon tracking on insulators can be caused by dirt or loose connections. These carbon paths must be cleaned or the insulators replaced. Failure to correct a carbon tracking problem will eventually result in a short in the electrical circuit.* Visually check for loose or broken wires and connections. Check the wires and connections on the regulator assembly. Check all wires and connections in the generator. Make any necessary repairs to the wiring as required.Visually inspect the generator and control panel. Check for loose, broken, or damaged wiring or components. The inspection only takes a few minutes and could avert a potential problem that could cause your generator set to fail.Operational Checks
Start the engine. Use the starting procedure found in the SR4 Generators and Control Panels Operation and Maintenance Manual, SEBU6150.The following operational checks include: * generator operation and engine starting* lubricating and fuel systems* overall operationThe checks should take no longer than five minutes to complete. A