Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 612 113
9400612113
ZEXEL
101605-3951
1016053951
KOMATSU
6209711361
6209711361
Rating:
Service parts 101605-3951 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6207-11-3200
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
24.5{250}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 612 113
9400612113
ZEXEL
101605-3951
1016053951
KOMATSU
6209711361
6209711361
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101605-3951
9 400 612 113
6209711361 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6M95A-2 K 14BF INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6AD PE
6M95A-2 K 14BF INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6AD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.2
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
94.9
93.9
95.9
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9.1+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
265
265
265
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8
7
9
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
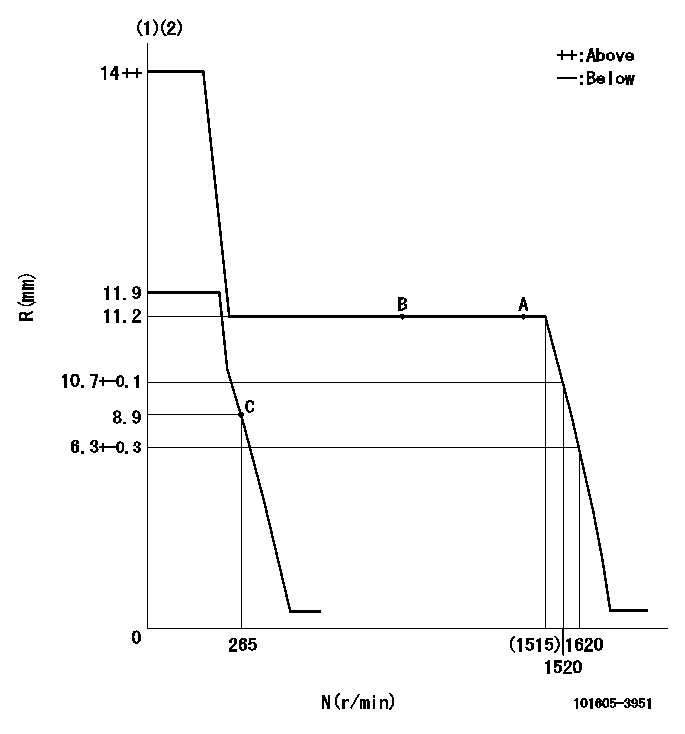
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
----------
K=4
----------
----------
K=4
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=53deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=53deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Normal
----------
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(30deg)
----------
----------
a=(30deg)
Information:
PRESSURIZING THE SYSTEMIf the pressure isn't maintained, overflow loss can occur as cooling system temperature rises. Do not remove the cap while the system is at operating temperature. Check coolant level only when cold.If the system does not hold pressure, find the leak.Carefully inspect the radiator cap, seals, sealing surfaces and the top tank filler neck surface for damage.
RADIATOR CAPTesting The Temperature Gauge
Remember that boiling point temperature and pressure go hand-in-hand and neither one can be tested logically without considering the other. For example, the effect of pressurization and altitude on the boiling point of water is shown in the chart. If overheating and loss of coolant is a problem, a pressure loss in the system could be the cause. If an overheating condition is indicated on the temperature gauge and loss of coolant is not evident, check the accuracy of the temperature gauge. Make this check by installing a thermometer with a suitable bushing into the cylinder head.Start the engine. Partially cover the radiator to reduce air flow and cooling. The reading on the instrument panel gauge should agree with the reading on the thermometer.
Use CAUTION when working around moving parts with the engine running.
CHECKING COOLANT TEMPERATURE WITH THERMOMETERTemperature Regulators
There is a temperature regulator located at the front of each cylinder head.The opening temperature of the regulator (bench test in antmospheric pressure) should be 180 2°F (82 2°C). The regulator should be fully open at approximately 197°F (92°C). 1. Remove the regulator from the housing.2. Submerge the regulator and a thermometer in a pan of water as shown.3. Apply heat to the pan and stir the water to maintain uniformity.4. Observe the opening temperature of the regulator.If the regulator does not operate correctly, install a new one. Cooling System Hoses
Inspect all coolant hoses annually and replace if they show signs of cracking or leaking. Periodically replace all hoses, as it is many times difficult to determine the condition of a water hose by visual inspection and feel. Coolant hoses are expendable items and periodic replacement is considered good maintenance practice.Air, Gases And Steam In The System
Incomplete or improper filling is a major cause of air in the cooling system. Also, leaks in various components such as the aftercooler, and hoses allow air to enter the cooling system, especially on the inlet side of the water pump.Air in the system produces foaming or aeration and affects water pump performance. The air bubbles insulate various parts of the engine from the coolant, and hot spots form. As the air bubbles circulate or break up, coolant contacts the hot surfaces, creating steam. The steam pockets have basically the same effect as air bubbles, accelerating the formation of more steam. Consequently, coolant discharges through the overflow.Exhaust gas leakage into the system causes similar conditions. Exhaust gas can enter through internal cracks or defective cylinder head gaskets.Most of the causes can be checked by a visual inspection, while others require disassembly or a simple test.Air in the cooling system is
Have questions with 101605-3951?
Group cross 101605-3951 ZEXEL
Komatsu
101605-3951
9 400 612 113
6209711361
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6M95A-2
6M95A-2