Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 615 344
9400615344
ZEXEL
101605-3570
1016053570
KOMATSU
6137721280
6137721280
Rating:
Service parts 101605-3570 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6137-12-3200
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
22.1{225}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 615 344
9400615344
ZEXEL
101605-3570
1016053570
KOMATSU
6137721280
6137721280
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101605-3570
9 400 615 344
6137721280 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S6D105 K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
S6D105 K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.25
3.35
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.9
Pump speed
r/min
1175
1175
1175
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
73.7
72.7
74.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1(7.8)
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9.6
8.1
11.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
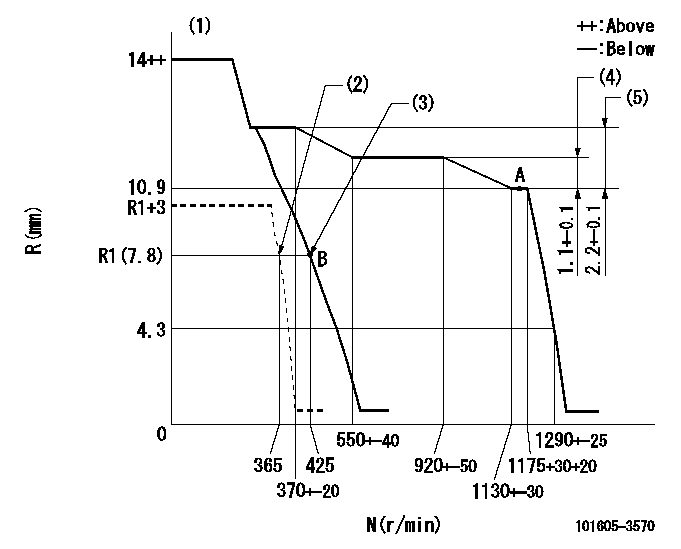
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Set idle sub-spring
(3)Main spring setting
(4)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
(5)Rack difference between N = N3 and N = N4
----------
K=7 N1=1175r/min N2=800r/min N3=1175r/min N4=350r/min
----------
----------
K=7 N1=1175r/min N2=800r/min N3=1175r/min N4=350r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
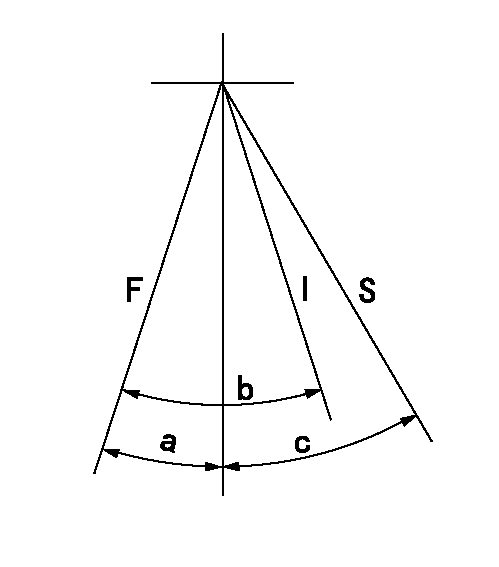
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
----------
----------
a=(2deg)+-5deg b=(22deg)+-5deg c=32deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=(2deg)+-5deg b=(22deg)+-5deg c=32deg+-3deg
0000001501 LEVER

(F) P/N: Part number of the shim
L1:Thickness (mm)
1. Adjustment of the control lever
(1)Perform idling with the control lever (A) contacting the pushrod (B). At this time, confirm that the spring (C) is not compressed by control lever (A)'s operating torque.
(2)To set the stop position, compress spring (C) using the control lever (A) and adjust the rack so that it contacts the guide screw (D) at position L2. Then, set and fix using the lock nut (E). Adjust the rack position L2 at this time using the shim (F).
(3)Confirm that the control lever (A) returns to the idling position when pulled in the stop direction and then released.
----------
L2=0.2~2mm
----------
----------
L2=0.2~2mm
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
Overheating
Possible Causes/Corrections
Low Coolant LevelIf the coolant level is too low, not enough coolant will go through the engine and radiator. This lack of coolant will not take enough heat from the engine and there will not be enough flow of coolant through the radiator to release the heat into the cooling air. Low coolant level is caused by leaks or wrong filling of the radiator. With the engine cool, be sure that coolant can be seen at the low end of the fill neck on the radiator top tank. Defective Temperature GaugeA temperature gauge which does not work correctly will not show the correct temperature. If the temperature gauge shows that the coolant temperature is too hot but other conditions are normal, either install a gauge you know is good or check the cooling system with the 4C6500 Digital Thermometer Group. Dirty RadiatorCheck the radiator for debris between the fins of the radiator core which prevents free air flow through the radiator core. Check the radiator for debris, dirt, or deposits on the inside of the radiator core which prevents free flow of coolant through the radiator. Loose Belt(s)Loose fan or water pump belts will cause a reduction in air or water flow. Tighten the belts according to Belt Tension Chart that is shown in Specification Section of this Service Manual. Defective Hose(s)Defective hoses with leaks can normally be seen. Hoses that have no visual leaks can "collapse" (pull together) during operation and cause a restriction in the flow of coolant. Hoses become soft and/or get cracks after a period of time. Hoses must be changed after 50,000 miles or a year of use. The inside can become loose, and the loose particles of the hose can cause a restriction in the flow of coolant. Shunt Line RestrictionA restriction of the shunt line from the radiator top tank to the engine front cover, or a shunt line not installed correctly, will cause a reduction in water pump efficiency. The result will be low coolant flow and overheating. Shutters Not Opening CorrectlyCheck the opening temperature of the shutters. The shutters must be completely closed at a temperature below the fully open temperature of the water temperature regulators. Also, verify that fan control switches or viscous fans are operating correctly. Defective Water Temperature RegulatorsA regulator that does not open, or only opens part of the way, can cause above normal heating. To test the thermostats, see the Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Defective Water PumpA water pump with a loose impeller does not pump enough coolant for correct engine cooling. A loose impeller can be found by removing the water pump, and by pushing the shaft back and pulling it forward. If the impeller has no damage, check the impeller clearance. The clearance between the impeller and the housing is 0.56 to 1.50 mm (.022 to .059 in). Air In Cooling SystemAir can get into the cooling system in different ways. The most common causes are not
Possible Causes/Corrections
Low Coolant LevelIf the coolant level is too low, not enough coolant will go through the engine and radiator. This lack of coolant will not take enough heat from the engine and there will not be enough flow of coolant through the radiator to release the heat into the cooling air. Low coolant level is caused by leaks or wrong filling of the radiator. With the engine cool, be sure that coolant can be seen at the low end of the fill neck on the radiator top tank. Defective Temperature GaugeA temperature gauge which does not work correctly will not show the correct temperature. If the temperature gauge shows that the coolant temperature is too hot but other conditions are normal, either install a gauge you know is good or check the cooling system with the 4C6500 Digital Thermometer Group. Dirty RadiatorCheck the radiator for debris between the fins of the radiator core which prevents free air flow through the radiator core. Check the radiator for debris, dirt, or deposits on the inside of the radiator core which prevents free flow of coolant through the radiator. Loose Belt(s)Loose fan or water pump belts will cause a reduction in air or water flow. Tighten the belts according to Belt Tension Chart that is shown in Specification Section of this Service Manual. Defective Hose(s)Defective hoses with leaks can normally be seen. Hoses that have no visual leaks can "collapse" (pull together) during operation and cause a restriction in the flow of coolant. Hoses become soft and/or get cracks after a period of time. Hoses must be changed after 50,000 miles or a year of use. The inside can become loose, and the loose particles of the hose can cause a restriction in the flow of coolant. Shunt Line RestrictionA restriction of the shunt line from the radiator top tank to the engine front cover, or a shunt line not installed correctly, will cause a reduction in water pump efficiency. The result will be low coolant flow and overheating. Shutters Not Opening CorrectlyCheck the opening temperature of the shutters. The shutters must be completely closed at a temperature below the fully open temperature of the water temperature regulators. Also, verify that fan control switches or viscous fans are operating correctly. Defective Water Temperature RegulatorsA regulator that does not open, or only opens part of the way, can cause above normal heating. To test the thermostats, see the Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Defective Water PumpA water pump with a loose impeller does not pump enough coolant for correct engine cooling. A loose impeller can be found by removing the water pump, and by pushing the shaft back and pulling it forward. If the impeller has no damage, check the impeller clearance. The clearance between the impeller and the housing is 0.56 to 1.50 mm (.022 to .059 in). Air In Cooling SystemAir can get into the cooling system in different ways. The most common causes are not
Have questions with 101605-3570?
Group cross 101605-3570 ZEXEL
Komatsu
101605-3570
9 400 615 344
6137721280
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S6D105
S6D105
