Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 610 214
9400610214
ZEXEL
101605-3561
1016053561
KOMATSU
6138721340
6138721340

Rating:
Service parts 101605-3561 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6138-12-3300
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
24.5{250}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 610 214
9400610214
ZEXEL
101605-3561
1016053561
KOMATSU
6138721340
6138721340
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101605-3561
9 400 610 214
6138721340 KOMATSU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S6D110 * K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
S6D110 * K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4
3.95
4.05
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.8
Pump speed
r/min
1050
1050
1050
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
78.7
77.7
79.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
425
425
425
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13.1
11.9
14.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
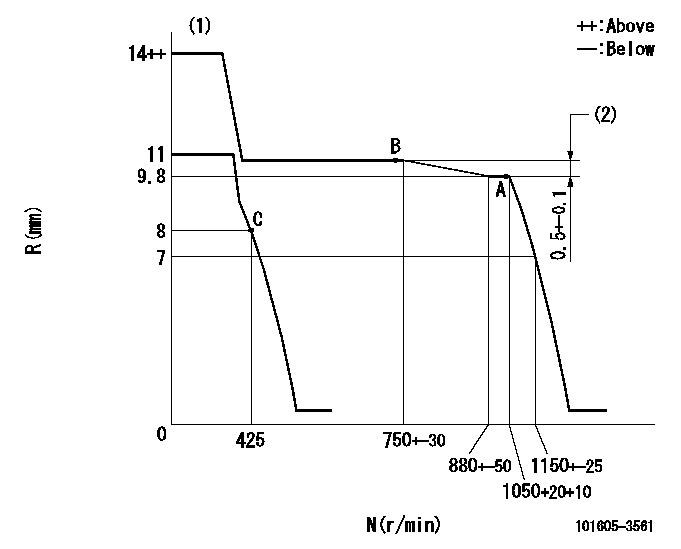
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=18 N1=1050r/min N2=700r/min
----------
----------
K=18 N1=1050r/min N2=700r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
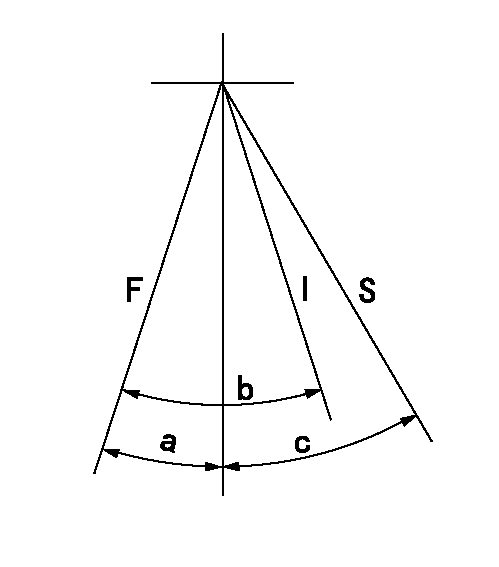
F:Full speed
I:Idle
S:Stop
----------
----------
a=16deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg c=32deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=16deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg c=32deg+-3deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
----------
----------
a=(0deg)
Information:
Engine Crankshaft Will Not Turn
Possible Causes/Corrections
Low Or No Battery VoltageCheck battery voltage. If battery voltage is less than 8 volts for a 12 volt system, or 16 volts for a 24 volt system, put a charge to the battery. If battery will not hold a charge, load test the battery as shown in the Electrical System of the Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Defective Switch, Defective Wiring Or Connection In Swith CircuitWith ignition switch in START position, check voltage at switch connection on starter solenoid. If there is no voltage, or if the voltage is low at this connection, check wiring, connections, ignition switch, and magnetic switch (if used). Defective Cable Or Connection; Battery To StarterWith ignition switch in the START position, check voltage at connection of battery cable to starter. If there is no voltage, or if the voltage is low at this connection and there is good voltage at the battery, check for defective cable or connection between the battery and the starter. Defective Starter SolenoidRemove and repair a solenoid which does not work when voltage is correct at both the battery and ignition switch connections. Defective Starter MotorIf the solenoid works and the starter motor does not turn the crankshaft, the starter motor is defective. Before removing the starter motor, turn the crankshaft by hand to be sure a mechanical failure inside the engine, transmission, or power take-off is not preventing the crankshaft from turning. If crankshaft turns freely by hand, engage the starter motor again. If the starter motor still will not work, remove the starter motor and repair it, or install a new starter motor. Transmission Or Power Take-off (if so equipped) Problem Prevents Crankshaft From TurningIf crankshaft can not be turned by hand, disconnect the transmission and power take-off. If crankshaft will now turn, find the cause of the problem in the transmission or power take-off and make necessary corrections. Inside Problem Prevents Engine Crankshaft From TurningIf the crankshaft can not be turned after disconnecting the transmission and power take-off, remove the fuel nozzles and check for fluid in the cylinders while turning the crankshaft. If fluid in the cylinders is not the problem, the engine must be disassembled to check for other inside problems. Some of these inside problems are bearing seizure, piston seizure, and valves making contact with pistons.Engine Crankshaft Turns Too Slowly
Possible Causes/Corrections
Low Battery VoltageCheck battery voltage. If battery voltage is less than 8 volts for a 12 volt system, or 16 volts for a 24 volt system, put a charge to the battery. If the battery will not hold a charge, load test the battery as shown in the Electrical System of the Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Defective Cable Or Connection; Battery To StarterWith switch in START position, check voltage at battery cable connection to starter. If voltage is low at this connection and there is good voltage at the battery, check for defective cable or connection between the battery and
Possible Causes/Corrections
Low Or No Battery VoltageCheck battery voltage. If battery voltage is less than 8 volts for a 12 volt system, or 16 volts for a 24 volt system, put a charge to the battery. If battery will not hold a charge, load test the battery as shown in the Electrical System of the Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Defective Switch, Defective Wiring Or Connection In Swith CircuitWith ignition switch in START position, check voltage at switch connection on starter solenoid. If there is no voltage, or if the voltage is low at this connection, check wiring, connections, ignition switch, and magnetic switch (if used). Defective Cable Or Connection; Battery To StarterWith ignition switch in the START position, check voltage at connection of battery cable to starter. If there is no voltage, or if the voltage is low at this connection and there is good voltage at the battery, check for defective cable or connection between the battery and the starter. Defective Starter SolenoidRemove and repair a solenoid which does not work when voltage is correct at both the battery and ignition switch connections. Defective Starter MotorIf the solenoid works and the starter motor does not turn the crankshaft, the starter motor is defective. Before removing the starter motor, turn the crankshaft by hand to be sure a mechanical failure inside the engine, transmission, or power take-off is not preventing the crankshaft from turning. If crankshaft turns freely by hand, engage the starter motor again. If the starter motor still will not work, remove the starter motor and repair it, or install a new starter motor. Transmission Or Power Take-off (if so equipped) Problem Prevents Crankshaft From TurningIf crankshaft can not be turned by hand, disconnect the transmission and power take-off. If crankshaft will now turn, find the cause of the problem in the transmission or power take-off and make necessary corrections. Inside Problem Prevents Engine Crankshaft From TurningIf the crankshaft can not be turned after disconnecting the transmission and power take-off, remove the fuel nozzles and check for fluid in the cylinders while turning the crankshaft. If fluid in the cylinders is not the problem, the engine must be disassembled to check for other inside problems. Some of these inside problems are bearing seizure, piston seizure, and valves making contact with pistons.Engine Crankshaft Turns Too Slowly
Possible Causes/Corrections
Low Battery VoltageCheck battery voltage. If battery voltage is less than 8 volts for a 12 volt system, or 16 volts for a 24 volt system, put a charge to the battery. If the battery will not hold a charge, load test the battery as shown in the Electrical System of the Testing and Adjusting Section of this Service Manual. Defective Cable Or Connection; Battery To StarterWith switch in START position, check voltage at battery cable connection to starter. If voltage is low at this connection and there is good voltage at the battery, check for defective cable or connection between the battery and
Have questions with 101605-3561?
Group cross 101605-3561 ZEXEL
Komatsu
101605-3561
9 400 610 214
6138721340
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
S6D110
S6D110
