Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 613 051
9400613051
ZEXEL
101605-0270
1016050270
ISUZU
1156034800
1156034800
Rating:
Service parts 101605-0270 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
1-15300-432-0
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
15.7{160}/22.1{225}
14.
NOZZLE
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 613 051
9400613051
ZEXEL
101605-0270
1016050270
ISUZU
1156034800
1156034800
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101605-0270
9 400 613 051
1156034800 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6BG1-T K
6BG1-T K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
134424-4120
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
4.2
4.15
4.25
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.9
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
111
109.5
112.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
113
113
Boost pressure
mmHg
850
850
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
7.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
450
450
450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12
10.7
13.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
11.1++
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
95
90
100
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R1-1.35
Boost pressure
kPa
34
30
38
Boost pressure
mmHg
255
225
285
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Rack position
R1(10.9)
Boost pressure
kPa
100
93.3
106.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
750
700
800
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
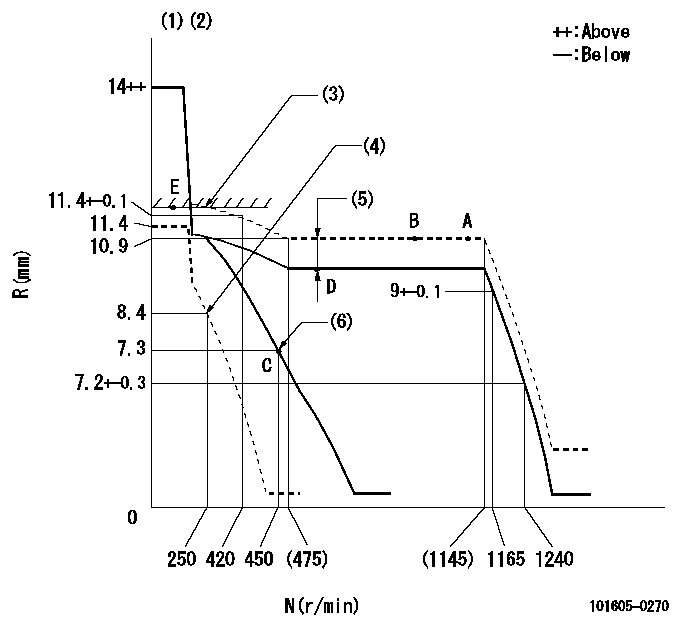
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Set idle sub-spring
(5)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
(6)Main spring setting
----------
K=18 BCL=1.35+-0.1mm
----------
----------
K=18 BCL=1.35+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
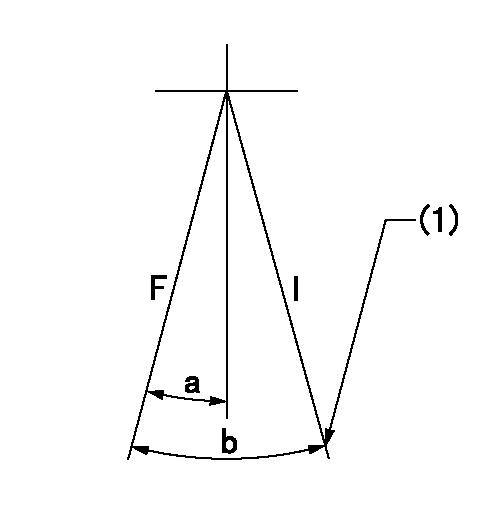
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=16deg+-5deg b=21deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=16deg+-5deg b=21deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
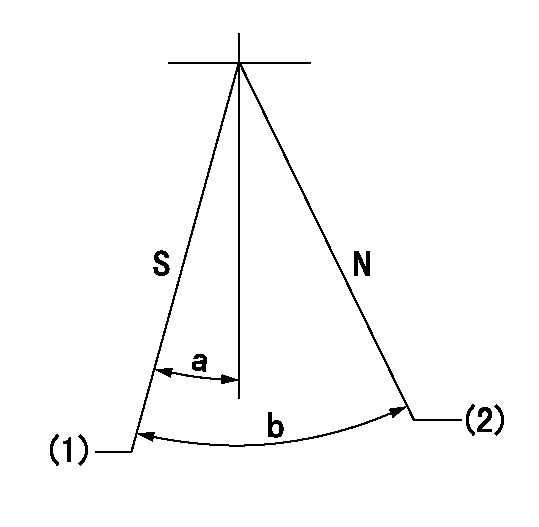
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Pump speed aa and rack position bb (to be sealed at delivery)
(2)Normal
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.5mm
----------
a=32deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.5mm
----------
a=32deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
0000001501 TAMPER PROOF
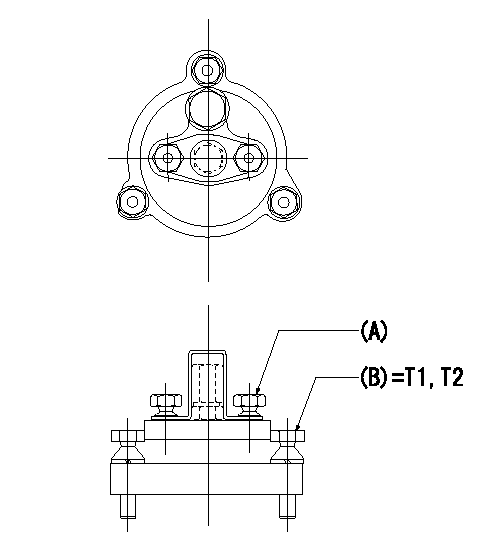
Tamperproofing-equipped boost compensator cover installation procedure
(A): After adjusting the boost compensator, assemble then tighten the bolts to remove the heads.
(B): Specified torque
(1)Before adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten the screw to the specified torque.
(Tightening torque T = T1 maximum)
(2)After adjusting the governor and the boost compensator, tighten to the specified torque to break off the bolt heads.
(Tightening torque T = T2)
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
----------
T1=2.5N-m(0.25kgf-m) T2=2.9~4.4N-m(0.3~0.45kgf-m)
----------
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark 'CC' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=9deg
----------
a=(100deg)
----------
aa=9deg
----------
a=(100deg)
Information:
Problem 36: Soot In The Inlet Manifold
Probable Cause:1. On 3116 Engines a small amount of soot is normal. This is due to the design characteristics of the engine. Valve overlap allows the intake to open slightly before the exhaust stroke has been completed, which will allow some soot to be pushed into the inlet manifold.Problem 37: Air In Fuel
Probable Cause:With air in the fuel system the engine will normally be difficult to start, run rough and release a large amount of white smoke. If air is in the system, it will generally get in on the suction side of the fuel transfer pump. Check for leakage at the connections between the fuel tank and the fuel transfer pump. If leaks are found, tighten the connections or replace the lines. The fuel priming pump (if equipped) may be used to remove the air from the fuel filter and fuel gallery (in the cylinder head), and fill the fuel system with fuel from the fuel tank before the engine is started.If there are no visual leaks, remove the fuel supply line from the tank and connect it to an outside fuel supply. If this corrects the problem, the suction line (standpipe) inside the fuel tank has a leak.If this does not correct the problem, install a sight tube in the fuel return line and check the injectors to verify that they are properly seated. This can be accomplished by moving each injector (one at a time) to the "FUEL ON" position momentarily and checking the sight tube for any increase in air bubbles. Push on the rack bar on the exhaust manifold side of the injector to move the injector to the "FUEL ON" position. If an increase in air is found, then remove that injector. Check the tip seal (O-ring) and replace it if it is found to be defective. Inspect the injector sleeve for a smooth sealing surface for the injector to seat on. If any defects are noted, the sleeve can be reamed or it can be replaced if necessary.The temperature of an exhaust manifold port can be an indication of a cylinder that has air being delivered to it. Check the exhaust manifold temperatures and compare the results. A lower than normal cylinder temperature indicates that the cylinder may be receiving air from the injector.The color of the exhaust smoke can also indicate which cylinder has a combustion leak. Move each injector (one at a time) to the "FUEL ON" position momentarily while checking the color of the exhaust smoke. The cylinder that has air will produce smoke that is gray or white in color.
Probable Cause:1. On 3116 Engines a small amount of soot is normal. This is due to the design characteristics of the engine. Valve overlap allows the intake to open slightly before the exhaust stroke has been completed, which will allow some soot to be pushed into the inlet manifold.Problem 37: Air In Fuel
Probable Cause:With air in the fuel system the engine will normally be difficult to start, run rough and release a large amount of white smoke. If air is in the system, it will generally get in on the suction side of the fuel transfer pump. Check for leakage at the connections between the fuel tank and the fuel transfer pump. If leaks are found, tighten the connections or replace the lines. The fuel priming pump (if equipped) may be used to remove the air from the fuel filter and fuel gallery (in the cylinder head), and fill the fuel system with fuel from the fuel tank before the engine is started.If there are no visual leaks, remove the fuel supply line from the tank and connect it to an outside fuel supply. If this corrects the problem, the suction line (standpipe) inside the fuel tank has a leak.If this does not correct the problem, install a sight tube in the fuel return line and check the injectors to verify that they are properly seated. This can be accomplished by moving each injector (one at a time) to the "FUEL ON" position momentarily and checking the sight tube for any increase in air bubbles. Push on the rack bar on the exhaust manifold side of the injector to move the injector to the "FUEL ON" position. If an increase in air is found, then remove that injector. Check the tip seal (O-ring) and replace it if it is found to be defective. Inspect the injector sleeve for a smooth sealing surface for the injector to seat on. If any defects are noted, the sleeve can be reamed or it can be replaced if necessary.The temperature of an exhaust manifold port can be an indication of a cylinder that has air being delivered to it. Check the exhaust manifold temperatures and compare the results. A lower than normal cylinder temperature indicates that the cylinder may be receiving air from the injector.The color of the exhaust smoke can also indicate which cylinder has a combustion leak. Move each injector (one at a time) to the "FUEL ON" position momentarily while checking the color of the exhaust smoke. The cylinder that has air will produce smoke that is gray or white in color.
Have questions with 101605-0270?
Group cross 101605-0270 ZEXEL
Isuzu
101605-0270
9 400 613 051
1156034800
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6BG1-T
6BG1-T