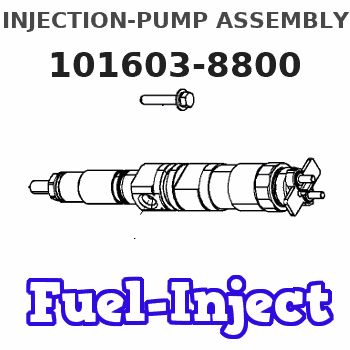
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 615 280
9400615280
ZEXEL
101603-8800
1016038800
ISUZU
1156030360
1156030360
Rating:
Compare Prices: .
As an associate, we earn commssions on qualifying purchases through the links below
Fuel Injection Pump 1156030360 101603-8800 for Isuzu Engine 6SD1 Truck FVM FVR GVR FVZ
100% Apollo part number: 1156030360 101603-8800 || application: for Isuzu Engine 6SD1 Truck FVM FVR GVR FVZ
100% Apollo part number: 1156030360 101603-8800 || application: for Isuzu Engine 6SD1 Truck FVM FVR GVR FVZ
WZCNLXLX Fuel Injection Pump 115603-0360 1156030360 For ISUZU 6SD1 Engine
WZCNLXLX Item Name:Fuel Injection Pump || Item Number:115603-0360 1156030360 || Application:For ISUZU 6SD1 Engine || Note: If you are unsure if the product is suitable.In order not to delay your use of the parts, please provide your engine nameplate or serial number and part number, and we will help you confirm if it is suitable. To avoid unnecessary returns, please check the product image and part number to ensure it is the product you want. || Tip: Please contact us - we are a professional sales team and we have many products to offer to you. Many buyers are very satisfied with our service. You can get first-class products and high-quality services from us, believe me, you will have a pleasant shopping experience here.
WZCNLXLX Item Name:Fuel Injection Pump || Item Number:115603-0360 1156030360 || Application:For ISUZU 6SD1 Engine || Note: If you are unsure if the product is suitable.In order not to delay your use of the parts, please provide your engine nameplate or serial number and part number, and we will help you confirm if it is suitable. To avoid unnecessary returns, please check the product image and part number to ensure it is the product you want. || Tip: Please contact us - we are a professional sales team and we have many products to offer to you. Many buyers are very satisfied with our service. You can get first-class products and high-quality services from us, believe me, you will have a pleasant shopping experience here.
115603-0360 High Pressure Oil Pump Compatible With 6sd1 Engine
LIYOGWUL Wide applicability: The oil pump is suitable for various types of gasoline engines, such as engines, diesel engines, etc || Easy to install: Mechanical oil pump compact structure, reduce installation time and easy maintenance, reduce the cost of use || Enhanced driving experience: Engine lubrication pumps improve driving comfort and experience with low noise and smooth operation || Heat dissipation function: self-priming oil pump helps the engine heat dissipation through oil circulation, reduce the working temperature and better heat dissipation || 115603-0360 High Pressure Oil Pump Compatible With 6sd1 Engine
LIYOGWUL Wide applicability: The oil pump is suitable for various types of gasoline engines, such as engines, diesel engines, etc || Easy to install: Mechanical oil pump compact structure, reduce installation time and easy maintenance, reduce the cost of use || Enhanced driving experience: Engine lubrication pumps improve driving comfort and experience with low noise and smooth operation || Heat dissipation function: self-priming oil pump helps the engine heat dissipation through oil circulation, reduce the working temperature and better heat dissipation || 115603-0360 High Pressure Oil Pump Compatible With 6sd1 Engine
You can express buy:
Service parts 101603-8800 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
22.1(225)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101603-8800
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104741-5530
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 615 280
9400615280
ZEXEL
101603-8800
1016038800
ISUZU
1156030360
1156030360
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101603-8800
9 400 615 280
1156030360 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6SD1 K 14BF INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6AD PE
6SD1 K 14BF INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6AD PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.7
3.65
3.75
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.9
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
89.8
88.2
91.4
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
290
290
290
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
11.2
9.2
13.2
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.9)
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
89.8
88.8
90.8
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
88
88
93
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
550--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1250
Advance angle
deg.
4
3.5
4.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
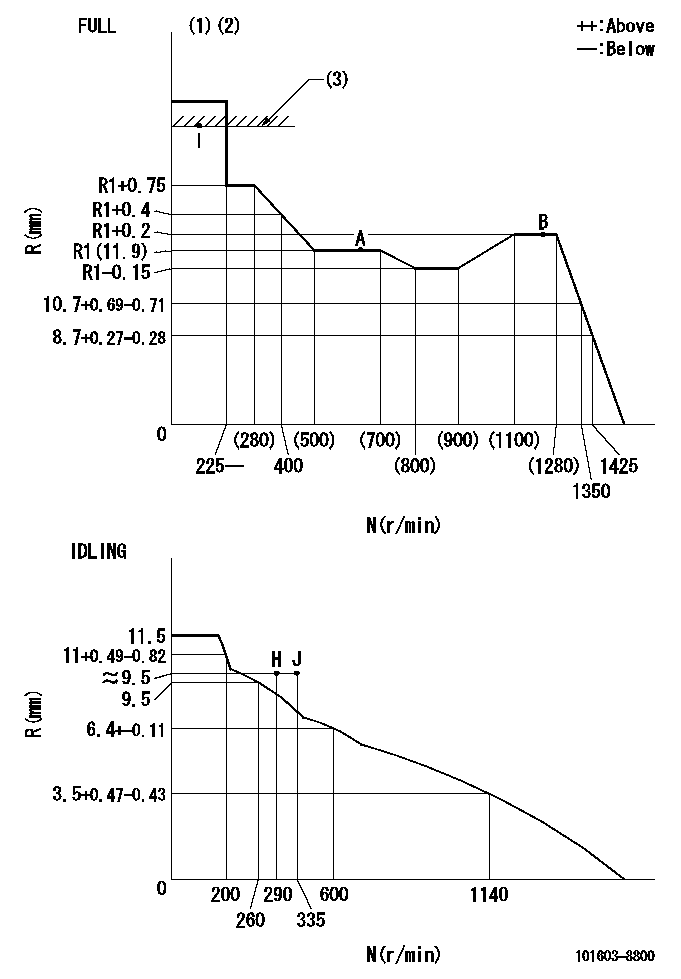
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=K80
----------
----------
T1=K80
----------
Speed control lever angle
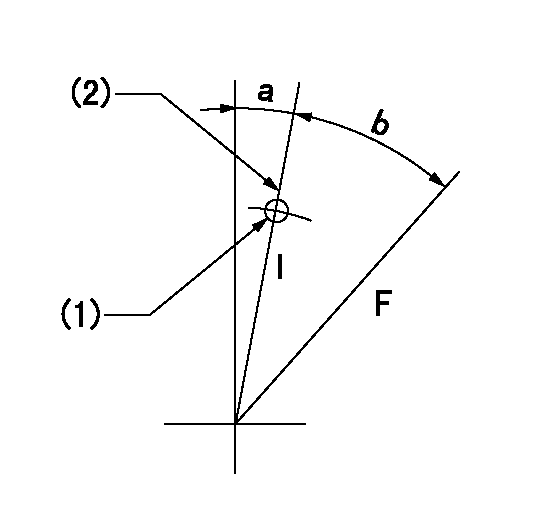
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=35.5mm
----------
a=18deg+-5deg b=36deg+-3deg
----------
aa=35.5mm
----------
a=18deg+-5deg b=36deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
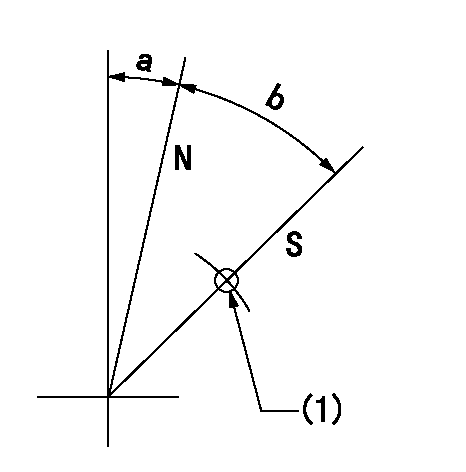
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the pin at R = aa
----------
aa=45mm
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
aa=45mm
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
0000001501 ACS
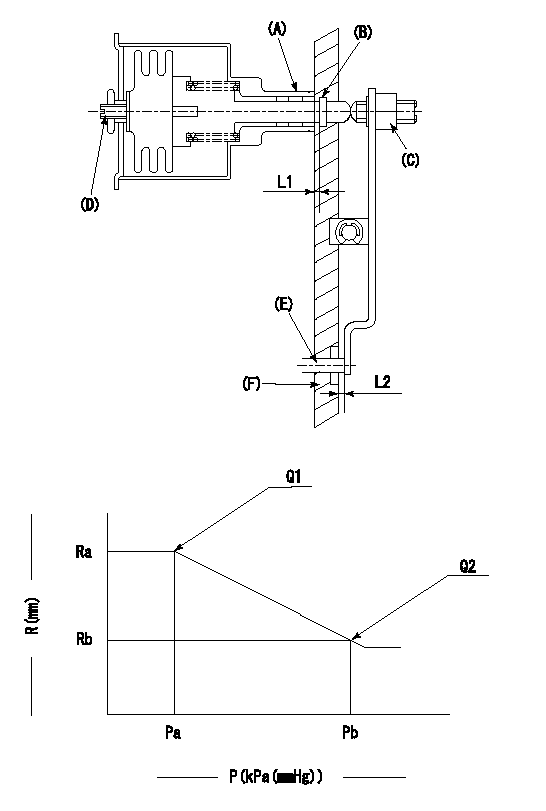
(A) Housing
(B) Snap ring
(C) adjusting screw
(D) Set screw
(E): Push rod
(F) Spacer
1. Adjustment of the aneroid compensator
(1)Adjust with the (D) set screw so that the clearance between the (A) housing and (B) snap ring is L1.
(2)Select the push rod (E) so that the distance from the end surface of the (F) spacer becomes L2.
(3)(C) Turn the screw to adjust the beginning of aneroid compensator operation.
2. Adjustment when mounting the governor.
(1)Set the speed of the pump to N1 r/min and fix the control lever at the full set position.
(2)Adjust using screw C to obtain the performance shown in the graph above.
(3)After final adjustment, confirm that the gap between housing (A) and snapring (B) is L3.
----------
N1=650r/min L1=1.4~1.7mm L2=0.5+-0.5mm L3=0.1~0.5mm
----------
Ra=R1(11.9)mm Rb=(R1-0.95)mm Pa=89.8+-2.7kPa(674+-20mmHg) Pb=70.1+-0.7kPa(526+-5mmHg) Q1=89.8+-1cm3/1000st Q2=67.5+-1.6cm3/1000st
----------
N1=650r/min L1=1.4~1.7mm L2=0.5+-0.5mm L3=0.1~0.5mm
----------
Ra=R1(11.9)mm Rb=(R1-0.95)mm Pa=89.8+-2.7kPa(674+-20mmHg) Pb=70.1+-0.7kPa(526+-5mmHg) Q1=89.8+-1cm3/1000st Q2=67.5+-1.6cm3/1000st
Timing setting
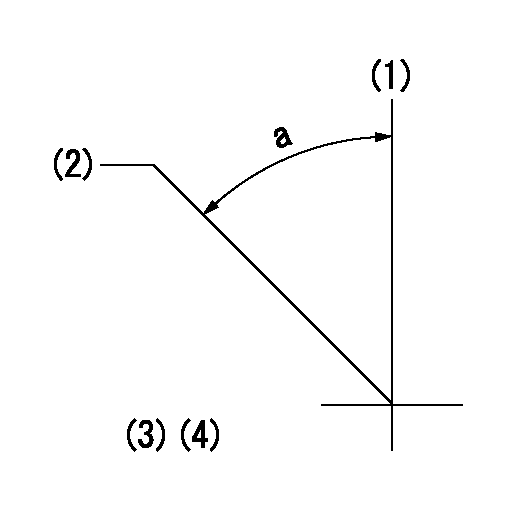
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's threaded hole at the No. 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=18deg
----------
a=(40deg)
----------
aa=18deg
----------
a=(40deg)
Information:
Recommended Procedure1. Fuel Return Manifold Leaks and/or Leaks at Fuel Return Boots or Connectors Remove the valve cover(s). Make a visual inspection of the fuel return manifold, fuel return boots, and connectors. Boots and/or connectors with damage or wrongly installed will let fuel get into the oil. If you do not see leaks during the visual inspection, start the engine and visually inspect while the engine is running. Boots and/or connectors can cause leakage if the fuel return line has a restriction.2. Loose Fuel Injection Nozzle Nut(s) A loose fuel injection nozzle nut can cause fuel leakage. Tighten nozzle nut(s) to 30 5 lb. ft. (4,1 0,7 mkg).3. Bad Fuel Nozzle(s) Check fuel nozzle(s) for cracks in inlet fitting, inlet line, or nozzle body. If you do not see a crack, start the engine and visually inspect each nozzle for leaks. Cracks in the inlet fitting and nozzle body are nozzle defects. Cracks in the inlet line are caused by the nozzle not being tightened correctly.4. Bad Diaphragm in Fuel Transfer Pump A bad diaphragm will cause fuel leakage through the "orifice" (small hole) in the fuel transfer pump housing. If you do not see leakage, make sure the orifice is open. Start the engine and again look for possible leakage. If the pump has leaks, install a new pump.5. Loose Fuel Injection Pump Retaining Bushing Loose retaining bushings will not hold the barrel of the injection pump correctly against the seat in the pump housing and fuel can get into the crankcase. A loose bushing can cause the engine to "misfire" (ignition not regular). A loose bushing can cause fuel leakage to the outside of the pump housing. Remove the fuel lines at the fuel injection pump and tighten each retaining bushing to 100 10 lb. ft. (13,8 1,4 mkg). Note: To tighten the three rear retaining bushings the pump housing must be removed from the engine.6. Fuel Leaks Between Injection Pump Barrel(s) and Injection Pump Housing Dirt or foreign material under the barrel of the fuel injection pump will cause fuel leakage into the crankcase. Remove the housing of the fuel injection pump and the governor from the engine. Remove the plunger and barrel assemblies from the pump housing. Inspect the seat area of the barrel and housing. Be sure the seat is smooth and flat. Check the timing dimension and adjust as necessary. Install the fuel injection pumps.7. Badly Worn Fuel Injection Pumps It is possible for one or more of the plunger and barrel assemblies to be worn enough to cause fuel leakage between the plunger and barrel. Remove the housing of the fuel injection pump and the governor from the engine. Test the fuel injection pump on the test bench for fuel injection pumps. If a test bench is not available, install new plunger and barrel assemblies in place of those with damage.
Have questions with 101603-8800?
Group cross 101603-8800 ZEXEL
Isuzu
101603-8800
9 400 615 280
1156030360
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6SD1
6SD1




