Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101603-8210
1016038210
ISUZU
1156029000
1156029000
Rating:
Service parts 101603-8210 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
1-15300-105-2
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
18.1{185}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101603-8210
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104749-5180
as _
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101603-8210
1016038210
ISUZU
1156029000
1156029000
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.4
3.35
3.45
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.25 60.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.25 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.25 120.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.25 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.25 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.25 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.25 240.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.25 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.25 300.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.25 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
75.5
73.9
77.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9.6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
290
290
290
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10
8.7
11.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11)
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
75.5
74.5
76.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
22.7
22.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
170
170
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1-0.25
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
80.5
77.3
83.7
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
22.7
22.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
170
170
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R2(R1-0.
5)
Pump speed
r/min
550
550
550
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
48.9
45.7
52.1
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
22.7
22.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
170
170
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
80
80
85
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Rack limit
*
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R2-0.5
Boost pressure
kPa
4.7
4.7
7.4
Boost pressure
mmHg
35
35
55
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R2-0.25
Boost pressure
kPa
8
6.7
9.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
60
50
70
Boost compensator adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Rack position
R2(R1-0.
5)
Boost pressure
kPa
9.3
9.3
9.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
70
70
70
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1300--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1250
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1350
Advance angle
deg.
0.7
0.2
1.2
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1450
Advance angle
deg.
1.5
1.2
1.8
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
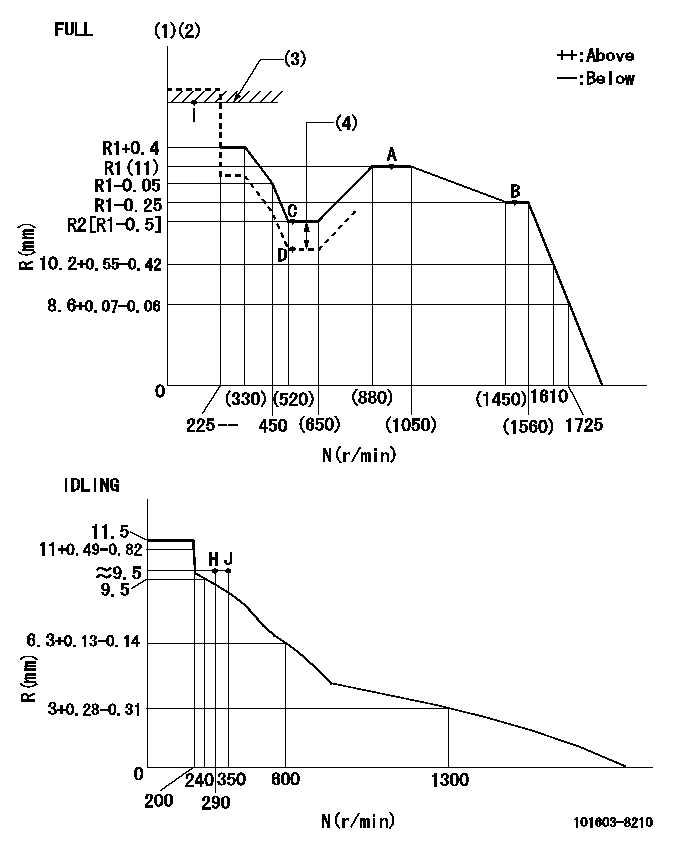
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=C15 BCL=0.5+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=C15 BCL=0.5+-0.1mm
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=41.5deg+-5deg b=34deg+-3deg
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=41.5deg+-5deg b=34deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
Timing setting
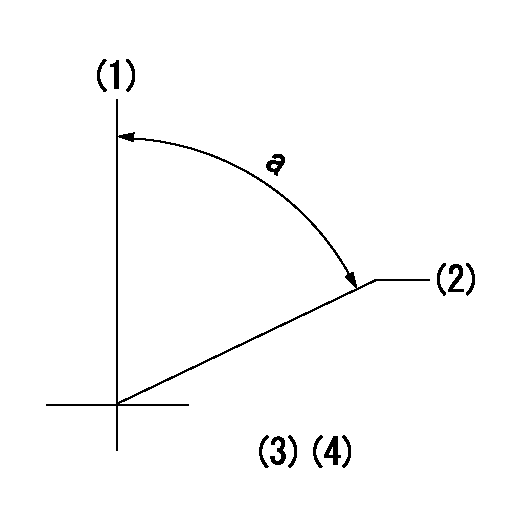
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=16deg
----------
a=(60deg)
----------
aa=16deg
----------
a=(60deg)
Information:
b. Operate vehicle at 60% of rated speed with moderate load until oil and coolant temperatures reach their normal range for operation. If there is a heavy vibration, drive shaft whip, tire bounce, etc., do not continue with dynamometer test until cause of the problem is corrected. Engines that have had new internal parts installed should be operated on a run-in schedule before operation at full load. For run-in schedule information, make reference to General Instructions section of this Service Manual.2. Put transmission in direct gear and the differential in the highest speed ratio. Operate vehicle at maximum engine speed and increase chassis dynamometer load until a speed of 50 rpm less than rated speed is reached (continuity light should be on). Maintain this speed for one minute and record the engine speed and wheel horsepower. If horsepower is low and poor maintenance is suspected, remove air cleaner or inlet piping to turbocharger and check horsepower again to see if a plugged air cleaner could be the problem.3a. If the wheel horsepower is correct, find the balance point of the engine (speed at which the load stop pin just touches the torque spring or stop bar). At this point the continuity light should flicker (go off and on dimly). If the balance point is correct, then the low power complaint can not be validated. No further test or repairs are necessary.If the balance point is low, see Procedure No. 5.3b. If the wheel horsepower is below the correct value, find the balance point of the engine (speed at which the load stop pin just touches the torque spring or stop bar). At this point the continuity light should flicker (go off and on dimly). If the balance point is correct, see Procedure No. 6.If the balance point is low, see Procedure No. 4.4. Stop the engine. Remove the AFRC (air-fuel ratio control). Put a cover over the hole where the AFRC was installed. Start the engine and check the balance point and horsepower again. If both of these are now correct, the problem is in AFRC. Repair or replace the AFRC. If, with the AFRC removed, horsepower is now acceptable and balance point is low, the problem is still with AFRC. Repair or replace the AFRC. Then adjust balance point according to Procedure No. 5.5. If the balance point is low, the high idle will have to be increased to raise the balance point to the correct rpm (the point at which the continuity light just comes on). If the balance point is still low and high idle has been adjusted to maximum, disengage clutch while maximum throttle position is maintained. Now observe high idle rpm and, if lower than previously adjusted, check frame-to-engine-mount. A damaged or loose engine mount may put the linkage in a bind and thus prevent maximum governor position at load conditions.6. If the balance point was correct and the wheel horsepower was low, install the 4S6553 Engine Test Group and do the wheel
