Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 613 119
9400613119
ZEXEL
101603-8170
1016038170
ISUZU
1156028890
1156028890
Rating:
Service parts 101603-8170 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
1-15300-104-2
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
18.1{185}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 613 119
9400613119
ZEXEL
101603-8170
1016038170
ISUZU
1156028890
1156028890
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101603-8170
9 400 613 119
1156028890 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6BG1 K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
6BG1 K 14BE INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE6A PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
132424-0620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
65.5
63.9
67.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9.6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
260
260
260
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9.4
8.1
10.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11)
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
65.5
64.5
66.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
(R1+0.2)
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
79.2
75.2
83.2
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
86
86
96
Fixing the lever
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
550--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
4
3.5
4.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
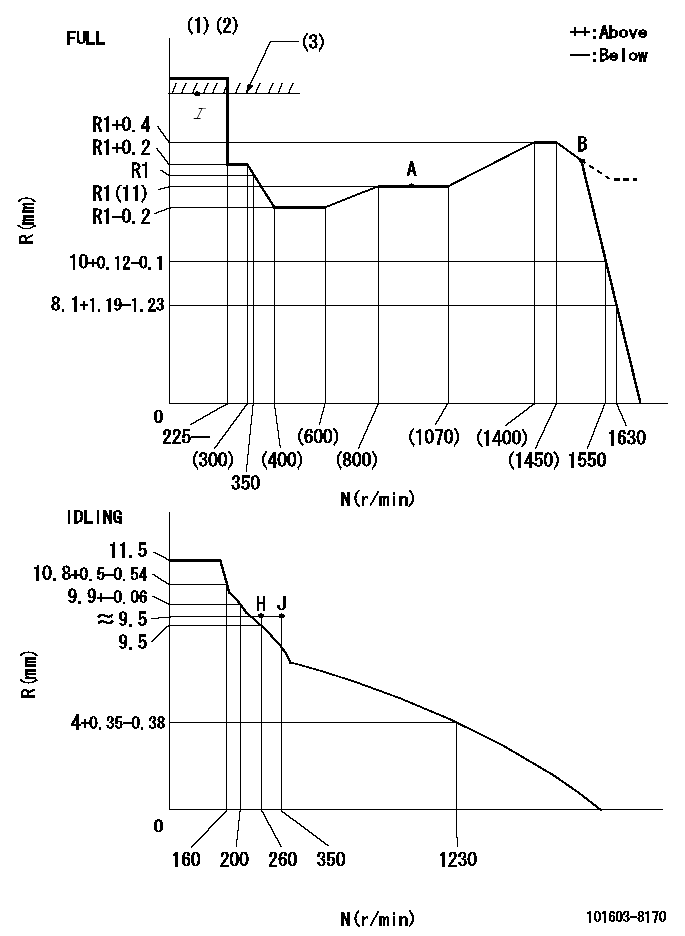
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=H78
----------
----------
T1=H78
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt setting
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=42deg+-5deg b=35deg+-3deg
----------
aa=35mm
----------
a=42deg+-5deg b=35deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
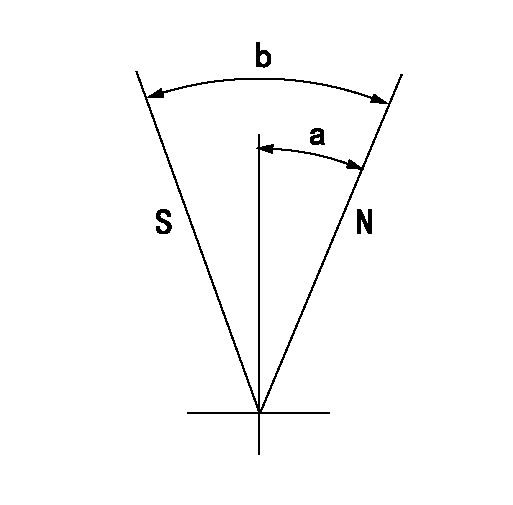
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=25deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
Timing setting
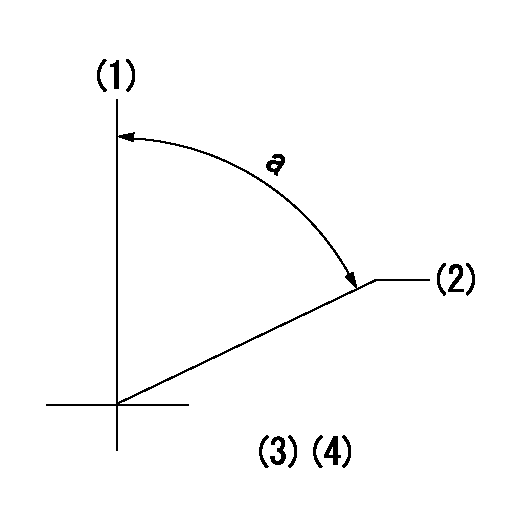
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=14deg
----------
a=(60deg)
----------
aa=14deg
----------
a=(60deg)
Information:
Crankshaft
The crankshaft changes the combustion forces in the cylinders into usable rotating torque which powers the machine. There is a timing gear at each end of the crankshaft which drives the respective timing gears.The bearing surfaces on the crankshaft get oil for lubrication through passages drilled in the crankshaft.Vibration Damper
The twisting of the crankshaft, due to the regular power impacts along its length, is called twisting (torsional) vibration. The vibration damper is installed on the front end of the crankshaft. It is used for reduction of torsional vibrations and stops the vibration from building up to amounts that cause damage.
CROSS SECTION OF A TYPICAL RUBBER VIBRATION DAMPER
1. Flywheel ring. 2. Rubber ring. 3. Inner hub.The rubber damper is made of a flywheel ring (1) connected to an inner hub (3) by a rubber ring (2). The rubber makes a flexible coupling between the flywheel ring and the inner hub.The viscous damper is made of a weight (1) in a metal case (3). The small space (2) between the case and weight is filled with a thick fluid. The fluid permits the weight to move in the case to cause a reduction of vibrations of the crankshaft.
CROSS SECTION OF A TYPICAL VISCOUS VIBRATION DAMPER
1. Solid cast iron weight. 2. Space between weight and case. 3. Case.Electrical System
The electrical system has three separate circuits: the charging circuit, the starting circuit and the low amperage circuit. Some of the electrical system components are in more than one circuit. The battery (batteries), circuit breaker, ammeter, cables and wires from the battery are all common in each of the circuits.
The disconnect switch must be in the ON position to let the electrical system operate. There will be damage to some of the charging circuit components if the engine is running with the disconnect switch in the OFF position.
The charging circuit is in operation when the engine is running. An alternator makes electricity for the charging circuit. A voltage regulator in the circuit controls the electrical output to keep the battery at full charge.The starting circuit is in operation only when the disconnect switch is put in the ON position and the start switch is activated.The starting circuit has a glow plug for each cylinder of the diesel engine. Glow plugs are small heating units in the precombustion chambers. Glow plugs give aid for ignition of the fuel when the engine is started in temperatures that are low.The low amperage load circuit and the charging circuit are both connected to the same side of the ammeter. The starting circuit connects to the opposite side of the ammeter.Charging System Components
Alternator (Prestolite) 2P1204
2P1204 ALTERNATORThe alternator is driven by two V type belts from the fan pulley. It is a 24 volt, 19 ampere unit with a regulator which has no moving parts (solid state) installed on the side opposite the pulley. The alternator is made up of the following parts: head assembly on the drive end, rotor assembly, stator assembly, rectifier and heat removal assemblies, brush
The crankshaft changes the combustion forces in the cylinders into usable rotating torque which powers the machine. There is a timing gear at each end of the crankshaft which drives the respective timing gears.The bearing surfaces on the crankshaft get oil for lubrication through passages drilled in the crankshaft.Vibration Damper
The twisting of the crankshaft, due to the regular power impacts along its length, is called twisting (torsional) vibration. The vibration damper is installed on the front end of the crankshaft. It is used for reduction of torsional vibrations and stops the vibration from building up to amounts that cause damage.
CROSS SECTION OF A TYPICAL RUBBER VIBRATION DAMPER
1. Flywheel ring. 2. Rubber ring. 3. Inner hub.The rubber damper is made of a flywheel ring (1) connected to an inner hub (3) by a rubber ring (2). The rubber makes a flexible coupling between the flywheel ring and the inner hub.The viscous damper is made of a weight (1) in a metal case (3). The small space (2) between the case and weight is filled with a thick fluid. The fluid permits the weight to move in the case to cause a reduction of vibrations of the crankshaft.
CROSS SECTION OF A TYPICAL VISCOUS VIBRATION DAMPER
1. Solid cast iron weight. 2. Space between weight and case. 3. Case.Electrical System
The electrical system has three separate circuits: the charging circuit, the starting circuit and the low amperage circuit. Some of the electrical system components are in more than one circuit. The battery (batteries), circuit breaker, ammeter, cables and wires from the battery are all common in each of the circuits.
The disconnect switch must be in the ON position to let the electrical system operate. There will be damage to some of the charging circuit components if the engine is running with the disconnect switch in the OFF position.
The charging circuit is in operation when the engine is running. An alternator makes electricity for the charging circuit. A voltage regulator in the circuit controls the electrical output to keep the battery at full charge.The starting circuit is in operation only when the disconnect switch is put in the ON position and the start switch is activated.The starting circuit has a glow plug for each cylinder of the diesel engine. Glow plugs are small heating units in the precombustion chambers. Glow plugs give aid for ignition of the fuel when the engine is started in temperatures that are low.The low amperage load circuit and the charging circuit are both connected to the same side of the ammeter. The starting circuit connects to the opposite side of the ammeter.Charging System Components
Alternator (Prestolite) 2P1204
2P1204 ALTERNATORThe alternator is driven by two V type belts from the fan pulley. It is a 24 volt, 19 ampere unit with a regulator which has no moving parts (solid state) installed on the side opposite the pulley. The alternator is made up of the following parts: head assembly on the drive end, rotor assembly, stator assembly, rectifier and heat removal assemblies, brush
Have questions with 101603-8170?
Group cross 101603-8170 ZEXEL
Isuzu
Isuzu
Isuzu
101603-8170
9 400 613 119
1156028890
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6BG1
6BG1
