Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 615 127
9400615127
ZEXEL
101603-6450
1016036450
MITSUBISHI
ME035518
me035518
Rating:
Service parts 101603-6450 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME035655
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101603-6450
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104740-1490
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 615 127
9400615127
ZEXEL
101603-6450
1016036450
MITSUBISHI
ME035518
me035518
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.25
3.35
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
10.8
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
65
63
67
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
10.5
9
12
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(10.8)
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
65
64
66
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1(10.8)
Pump speed
r/min
1450
1450
1450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
77.5
75.5
79.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1(10.8)
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
51.5
49.5
53.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
14.1+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
90
70
110
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
900--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
850
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
0.8
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
2.6
2.1
3.1
Timer adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
5.5
5
6
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
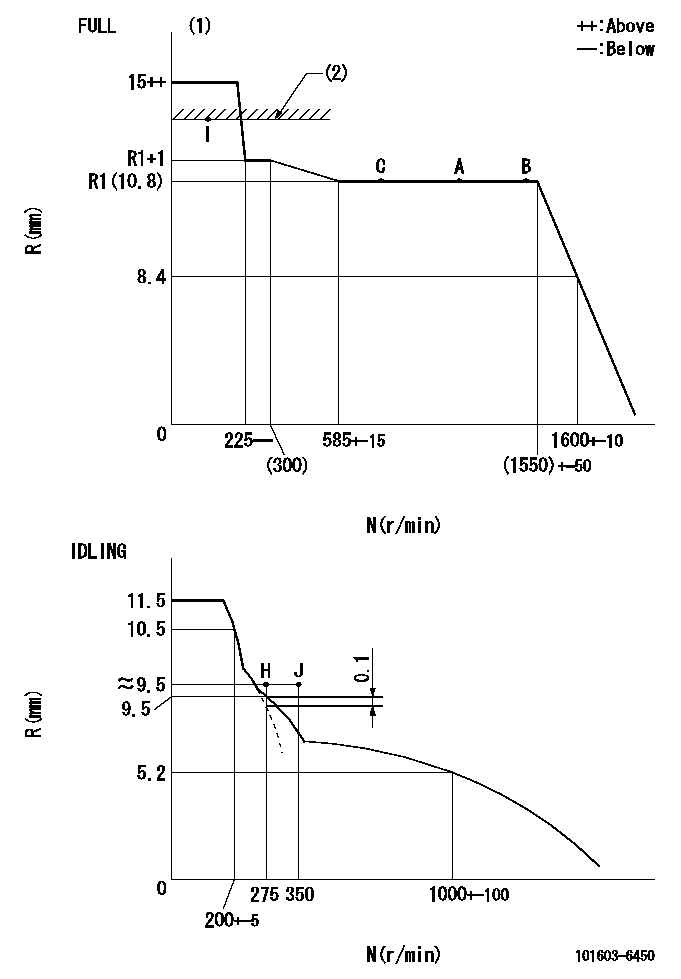
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=A70
----------
----------
T1=A70
----------
Speed control lever angle
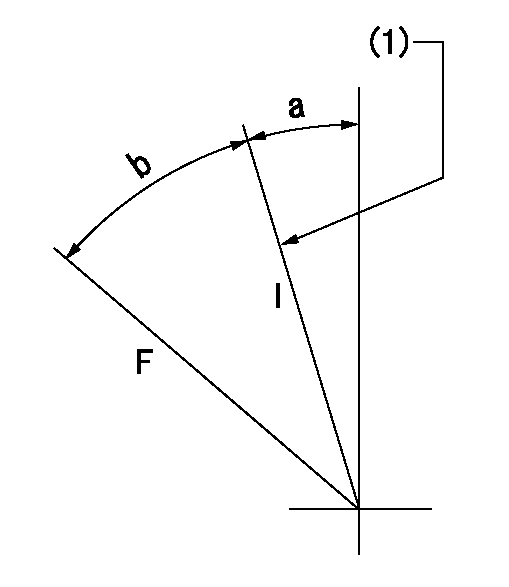
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=42deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=42deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
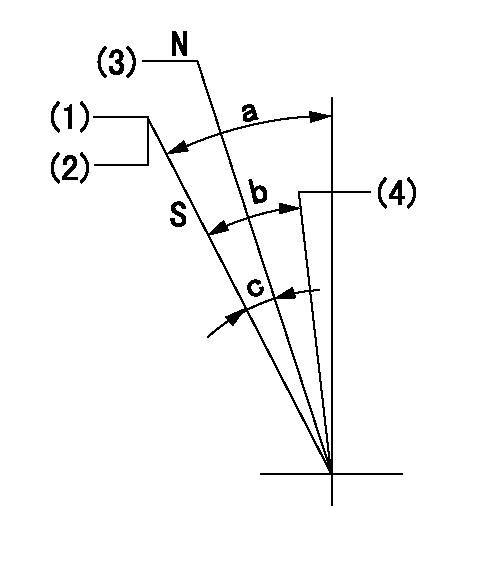
N:Engine manufacturer's normal use
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Set the stopper bolt at speed = aa and rack position = bb and confirm non-injection.
(2)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed cc. Rack position = dd (non-injection rack position).
(3)Rack position = approximately ee.
(4)Free (at shipping)
----------
aa=1550r/min bb=7.2mm cc=275r/min dd=8.2mm ee=17.4mm
----------
a=38.5deg+-5deg b=(27deg) c=17deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1550r/min bb=7.2mm cc=275r/min dd=8.2mm ee=17.4mm
----------
a=38.5deg+-5deg b=(27deg) c=17deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of timer's tooth at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=16deg
----------
a=(1deg)
----------
aa=16deg
----------
a=(1deg)
Information:
Never use water alone as a coolant. Water alone is corrosive at engine operating temperatures. In addition, water alone does not provide adequate protection against boiling or freezing.
In engine cooling systems that use water alone, Caterpillar recommends the use of Cat SCA. Cat SCA helps to prevent the following conditions from occurring:
Corrosion
Formation of mineral deposits
Cavitation erosion of the cylinder liner
Foaming of the coolantIf Cat SCA is not used, select a fully formulated commercial SCA. The commercial SCA must provide a minimum of 2400 mg/L or 2400 ppm (140 grains/US gal) of nitrites in the final coolant mixture.The quality of the water is an important factor in this type of cooling system. Distilled water or deionized water is recommended for use in cooling systems. If distilled water or deionized water is not available, use water that meets or exceeds the minimum requirements that are listed in the table for recommended water properties in this Special Publication, "General Coolant Information" topic.A cooling system that uses a mixture of SCA and water only needs more SCA. The SCA concentration in a cooling system that uses SCA and water should be 6 to 8 percent by volume.Maintain the Cat SCA in the same way as you would maintain a cooling system that uses heavy-duty coolant/antifreeze. Adjust the maintenance for the amount ofCat SCA additions.Adding the Cat SCA to Water at the Initial Fill
Use the equation that is in this Special Publication, "Conventional Coolant/Antifreeze Cooling System Maintenance" to determine the amount of Cat SCA that is required at the initial fill. This equation is for a mixture of only Cat SCA and water.Adding the Cat SCA to Water for Maintenance
For the recommended service interval, refer to the Operation and Maintenance Manual, "Maintenance Interval Schedule" for your engine.Submit a coolant sample to your Cat dealer. See this Special Publication, "S O S Services Coolant Analysis" topic.Additions of Cat SCA are based on the results of the coolant analysis. The size of the cooling system determines the amount of Cat SCA that is required.Use the equation that is in this Special Publication, "Conventional Coolant/Antifreeze Cooling System Maintenance" to determine the amount of Cat SCA that is required for maintenance, if necessary:Note: Specific engine applications may require maintenance practices to be periodically evaluated in order to maintain properly the engine cooling system.SCA and part numbers are available from your Cat dealer.