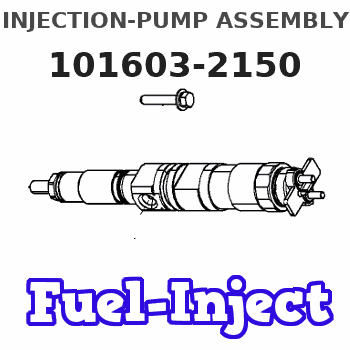
Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101603-2150
1016032150
HINO
220008590A
220008590a
Rating:
Service parts 101603-2150 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
23600-1593A
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101603-2150
1016032150
HINO
220008590A
220008590a
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-5720
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
3.1
3.07
3.13
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9.5
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60.2
58.2
62.2
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3.5
3.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
250
250
250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
6.8
5.3
8.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(9.5)
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
60.2
59.2
61.2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.1
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
67.3
63.3
71.3
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1-0.45
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
37.9
33.9
41.9
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
R1+0.15
Pump speed
r/min
1200
1200
1200
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
67.8
63.8
71.8
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_07
Adjusting point
E
Rack position
R1(9.5)
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
32.9
28.9
36.9
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_08
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
13.9+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
99
99
109
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Injection quantity adjustment_09
Adjusting point
F
Rack position
R2(10)
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
72.765
67.765
77.765
Fixing the lever
*
Remarks
Set tamper proofing.
Set tamper proofing.
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1000+50
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
3.5
3.2
3.8
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
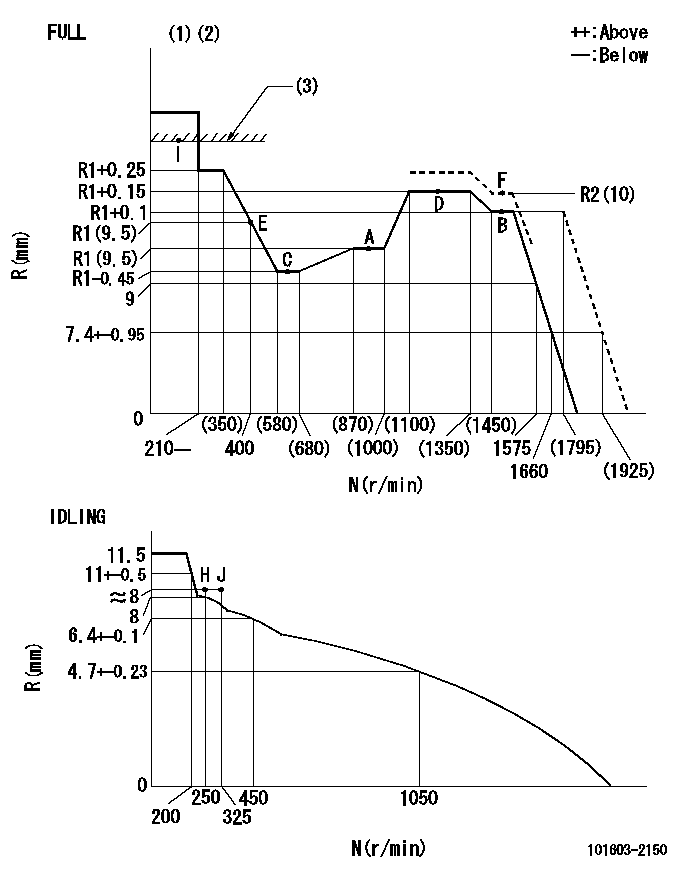
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=C10
----------
----------
T1=C10
----------
Speed control lever angle
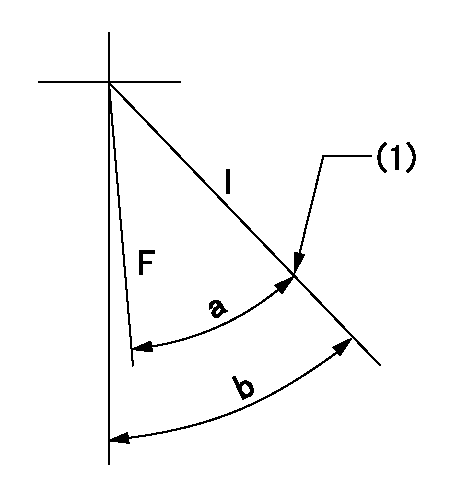
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
----------
a=32deg+-3deg b=34deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=32deg+-3deg b=34deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
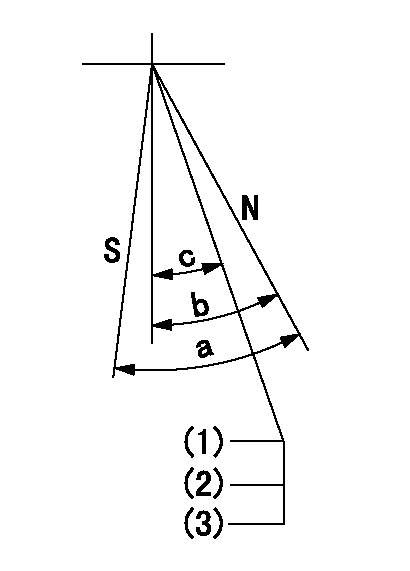
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Stopper bolt setting
(2)(Apply red paint after setting.)
(3)Engine normal
----------
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg c=35deg+-2deg
----------
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg c=35deg+-2deg
0000001501 TAMPER PROOF
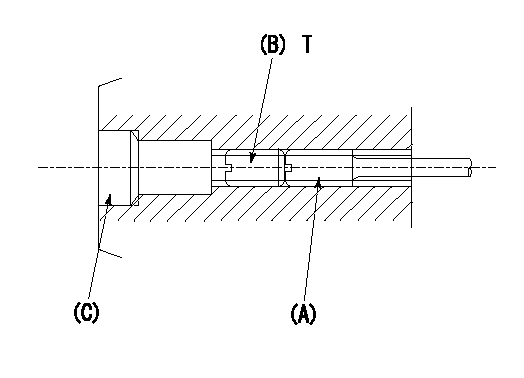
1. Method for setting tamperproof proofing
(1)Perform after governor adjustment (torque cam phase adjustment).
(2)Increase the full rack position to Ra using the load lever.
(3)Push in screw (A) to Rb.
(4)Temporarily caulk using the tip of a screwdriver
(5)Confirm that the rack at that time is at Rb .
(6)Lock using setscrew (B). (Tightening torque = T)
(7)Pressfit (C) after applying adhesive.
(8)Readjust the full rack using the load lever.
----------
Ra=R2(10)mm Rb=R2(10)mm
----------
T=3.4~4.9N-m(0.35~0.5Kgf-m)
----------
Ra=R2(10)mm Rb=R2(10)mm
----------
T=3.4~4.9N-m(0.35~0.5Kgf-m)
0000001601 ACS
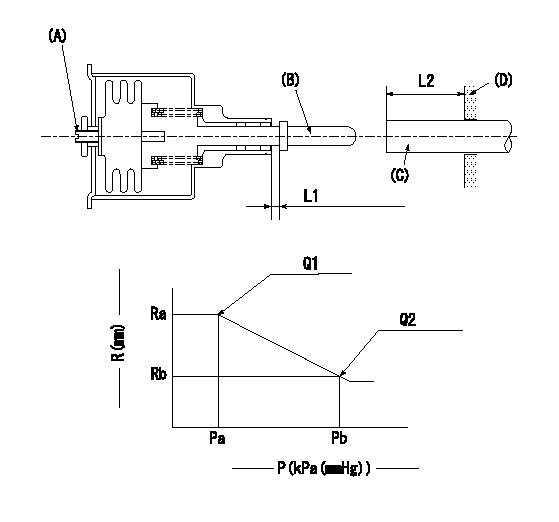
(A) Set screw
(B) Push rod 1
(C) Push rod 2
(D) Cover
1. Aneroid compensator unit adjustment
(1)Select the push rod 2 to obtain L2.
(2)Screw in (A) to obtain L1.
2. Adjustment when mounting the governor.
(1)Set the speed of the pump to N1 r/min and fix the control lever at the full set position.
(2)Screw in the aneroid compensator to obtain the performance shown in the graph above.
(3)As there is hysterisis, measure when the absolute pressure drops.
(4)Hysterisis must not exceed rack position = h1.
----------
N1=1500r/min L1=(1.5)mm L2=7+-0.5mm h1=-
----------
Ra=R1+0.1mm Rb=R1-1.65mm Pa=(94.6)+-2.7kPa((710)+-20mmHg) Pb=61.6+-0.7kPa(462+-5mmHg) Q1=(67.3)+-2cm3/1000st Q2=44+-1cm3/1000st
----------
N1=1500r/min L1=(1.5)mm L2=7+-0.5mm h1=-
----------
Ra=R1+0.1mm Rb=R1-1.65mm Pa=(94.6)+-2.7kPa((710)+-20mmHg) Pb=61.6+-0.7kPa(462+-5mmHg) Q1=(67.3)+-2cm3/1000st Q2=44+-1cm3/1000st
Timing setting
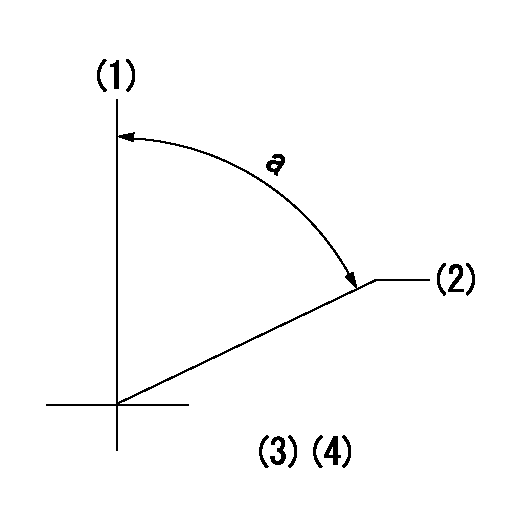
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear's standard threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(70deg)
----------
----------
a=(70deg)
Information:
3T1888 Alternator 24V 50A (Delco-Remy Number 117248)
3T1888 Alternator1. Remove the covers from the end of the alternator to get access to the voltage regulator.
Delco-Remy Regulator Adjustment
(1) Potentiometer adjustment screw. (2) Transistor pins.2. Remove the rubber from the potentiometer so that the small screw can be seen.3. Connect a voltmeter across the batteries to measure the regulation of the voltage. The batteries must have a good charge for this measurement.4. Operate the alternator at medium speed for 30 seconds and take a measurement of the voltage. The voltage must be 27.5 1.0 volts. Turn the small screw counterclockwise to get less voltage output and clockwise to get more voltage output.5. After adjustment has been made, put a think layer of 3S6252 Silicone Rubber Sealant on the adjustment screw and install the covers. Make sure the location of the wires to the voltage regulator is not over the transistor pins. The transistor pins could make holes in the insulation for the wires and cause a short circuit.7N9720 Alternator 24V 35A (Bosch Number 0-122-469-001); 9G9538 Alternator 24V 50A (Bosch Number 0-122-469-002)
7N9720 AlternatorThe solid state regulator used with the Bosch Alternator is totally enclosed and non-adjustable. If the rate of charge is not correct a replacement of the regulator is necessary.9G4574 24V 35A (Nippondenso Number 100211-0860); 6T7223 24V 50A (Nippondenso Number 100211-0890)
9G4574 AlternatorNo adjustment can be made to change the rate of charge on the alternator regulator. If rate of charge is not correct, a replacement of the regulator is necessary.Starting System
Use the multimeter in the DCV range to find starting system components which do not function.Move the start control switch to activate the starter solenoid. Starter solenoid operation can be heard as the pinion of the starter motor is engaged with the ring gear on the engine flywheel.If the solenoid for the starter motor will not operate, it is possible that the current from the battery did not get to the solenoid. Fasten one lead of the multimeter to the connection (terminal) for the battery cable on the solenoid. Put the other lead to a good ground. A zero reading is an indication that there is a broken circuit from the battery. More testing is necessary when there is a voltage reading on the multimeter.The solenoid operation also closes the electric circuit to the motor. Connect one lead of the multimeter to the solenoid connection (terminal) that is fastened to the motor. Put the other lead to a good ground. Activate the starter solenoid and look at the multimeter. A reading of battery voltage shows the problem is in the motor. The motor must be removed for further testing. A zero reading on the multimeter shows that the solenoid contacts do not close. This is an indication of the need for repair to the solenoid or an adjustment to be made to the starter pinion clearance.Make a test with one multimeter lead fastened to the connection (terminal) for the small wire at the solenoid and the other lead to the
3T1888 Alternator1. Remove the covers from the end of the alternator to get access to the voltage regulator.
Delco-Remy Regulator Adjustment
(1) Potentiometer adjustment screw. (2) Transistor pins.2. Remove the rubber from the potentiometer so that the small screw can be seen.3. Connect a voltmeter across the batteries to measure the regulation of the voltage. The batteries must have a good charge for this measurement.4. Operate the alternator at medium speed for 30 seconds and take a measurement of the voltage. The voltage must be 27.5 1.0 volts. Turn the small screw counterclockwise to get less voltage output and clockwise to get more voltage output.5. After adjustment has been made, put a think layer of 3S6252 Silicone Rubber Sealant on the adjustment screw and install the covers. Make sure the location of the wires to the voltage regulator is not over the transistor pins. The transistor pins could make holes in the insulation for the wires and cause a short circuit.7N9720 Alternator 24V 35A (Bosch Number 0-122-469-001); 9G9538 Alternator 24V 50A (Bosch Number 0-122-469-002)
7N9720 AlternatorThe solid state regulator used with the Bosch Alternator is totally enclosed and non-adjustable. If the rate of charge is not correct a replacement of the regulator is necessary.9G4574 24V 35A (Nippondenso Number 100211-0860); 6T7223 24V 50A (Nippondenso Number 100211-0890)
9G4574 AlternatorNo adjustment can be made to change the rate of charge on the alternator regulator. If rate of charge is not correct, a replacement of the regulator is necessary.Starting System
Use the multimeter in the DCV range to find starting system components which do not function.Move the start control switch to activate the starter solenoid. Starter solenoid operation can be heard as the pinion of the starter motor is engaged with the ring gear on the engine flywheel.If the solenoid for the starter motor will not operate, it is possible that the current from the battery did not get to the solenoid. Fasten one lead of the multimeter to the connection (terminal) for the battery cable on the solenoid. Put the other lead to a good ground. A zero reading is an indication that there is a broken circuit from the battery. More testing is necessary when there is a voltage reading on the multimeter.The solenoid operation also closes the electric circuit to the motor. Connect one lead of the multimeter to the solenoid connection (terminal) that is fastened to the motor. Put the other lead to a good ground. Activate the starter solenoid and look at the multimeter. A reading of battery voltage shows the problem is in the motor. The motor must be removed for further testing. A zero reading on the multimeter shows that the solenoid contacts do not close. This is an indication of the need for repair to the solenoid or an adjustment to be made to the starter pinion clearance.Make a test with one multimeter lead fastened to the connection (terminal) for the small wire at the solenoid and the other lead to the