Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101601-5931
1016015931
HINO
220007513B
220007513b
Rating:
Service parts 101601-5931 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
23600-2373A
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
19.6{200}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101601-5931
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104139-4022
as _
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101601-5931
1016015931
HINO
220007513B
220007513b
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-8320
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
108
88
128
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.1
0.9
1.3
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
4.3
4.27
4.33
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
12.4
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
85.1
83.5
86.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3.5
3.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
250
250
250
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
15.4
14.4
16.4
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(12.4)
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
85.1
84.1
86.1
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.6
Pump speed
r/min
1450
1450
1450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
89.3
85.3
93.3
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1-0.55
Pump speed
r/min
580
580
580
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
73.6
69.6
77.6
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
136
136
146
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
950--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Load
1/4
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Load
1/4
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
(1000)
Advance angle
deg.
1.5
1.2
1.8
Load
4/4
Remarks
Measure the actual speed.
Measure the actual speed.
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1240+50
Advance angle
deg.
1.5
1.2
1.8
Load
4/4
Timer adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1450-50
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.7
5.3
Load
4/4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
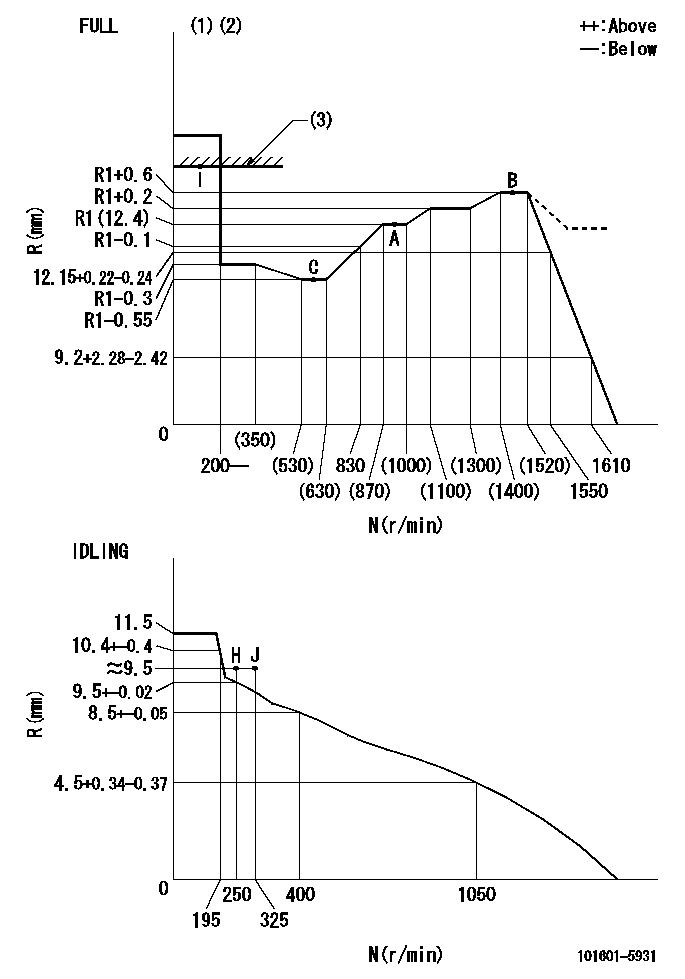
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=G90
----------
----------
T1=G90
----------
Speed control lever angle
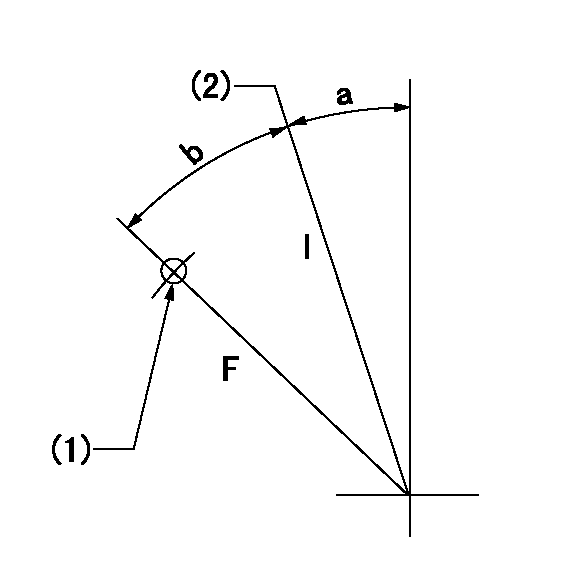
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=41mm
----------
a=34deg+-5deg b=(45.5deg)+-3deg
----------
aa=41mm
----------
a=34deg+-5deg b=(45.5deg)+-3deg
Stop lever angle
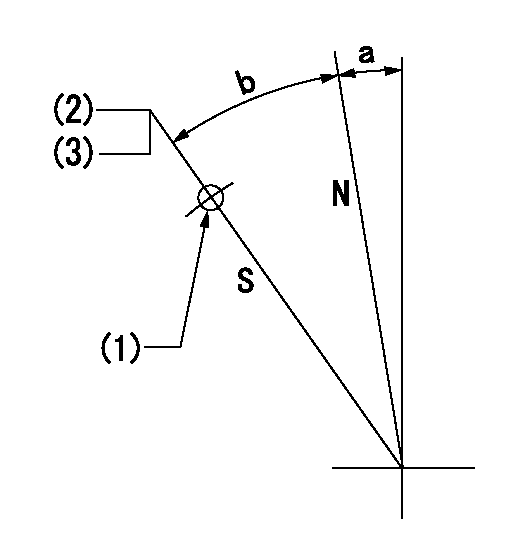
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
(2)Set the stopper bolt at speed = bb and rack position = cc (non-injection rack position). Confirm non-injection.
(3)After setting the stopper bolt, confirm non-injection at speed dd. Rack position = non-injection rack position (actual measurement)
----------
aa=38mm bb=1450r/min cc=7-0.5mm dd=250r/min
----------
a=28deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg
----------
aa=38mm bb=1450r/min cc=7-0.5mm dd=250r/min
----------
a=28deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(20deg)
----------
----------
a=(20deg)
Information:
Proper operation and maintenance are key factors in obtaining the maximum life and economy of the engine. Following the directions in this manual will lower operating costs.After the engine is started and the cold idle operation is completed, the truck can be operated at low speed and low power. The engine will reach normal operating temperature faster when driven at low speed and low power demand than when idled at no load. Typically the engine should be up to operating temperature by just driving through the yard toward the open road.Engine Operation
* Begin operating the engine at low load. After normal oil pressure is reached and the temperature gauge begins to move, the engine may be operated at full load.* To get the vehicle in motion, use a gear that will result in a smooth, easy start without increasing engine speed above low idle or slipping the clutch. Engage the clutch smoothly. Abrupt or jerky starts put stress on the drive train and waste fuel.* Use progressive shifting to reduce fuel consumption. Progressive shifting is using only the rpm required to make an upshift into the next gear. The amount of rpm required to make an upshift increases as the truck speed increases unless upshifts are made on upgrades. Experience with your truck will show you how much rpm is required to make upshifts under various conditions.* If the truck can be operated in a higher gear after the desired speed is reached, select the highest gear available that will pull the load. By following this recommendation, you will lower your fuel costs, since your engine will be operating at the lowest rpm required to pull the load.Uphill Operation
On upgrades, begin downshifting when the engine rpm starts to approach peak torque (1100-1200 rpm) speed. Fuel economy will be best if you let the engine lug back to around this speed before you downshift. Downshift until a gear is reached in which the engine will pull the load. Allowing the engine to lug below peak torque is permissible if the truck is cresting the top of a hill without downshifting.However, note that extended operation in a lug condition will raise exhaust temperature and cylinder pressure and can lead to reduced engine life.Downhill Operation
Do NOT allow the engine rpm to exceed 2300 rpm, engine damage can result. If equipped with an exhaust brake, do not exceed 2100 rpm.
* When operating the vehicle downhill, do not coast or put the transmission in NEUTRAL.* Select the correct gear that does not allow the engine speed (rpm) to exceed the limits above and use the engine retarder and/or brakes to limit the speed of the truck.* A simple rule to follow is to select the same gear that would be required to go up the grade. However, DO NOT allow the engine to overspeed.For more information on economical operation of this engine, refer to form LEDT5092, Driving Techniques for Maximum Fuel Economy.
* Begin operating the engine at low load. After normal oil pressure is reached and the temperature gauge begins to move, the engine may be operated at full load.* To get the vehicle in motion, use a gear that will result in a smooth, easy start without increasing engine speed above low idle or slipping the clutch. Engage the clutch smoothly. Abrupt or jerky starts put stress on the drive train and waste fuel.* Use progressive shifting to reduce fuel consumption. Progressive shifting is using only the rpm required to make an upshift into the next gear. The amount of rpm required to make an upshift increases as the truck speed increases unless upshifts are made on upgrades. Experience with your truck will show you how much rpm is required to make upshifts under various conditions.* If the truck can be operated in a higher gear after the desired speed is reached, select the highest gear available that will pull the load. By following this recommendation, you will lower your fuel costs, since your engine will be operating at the lowest rpm required to pull the load.Uphill Operation
On upgrades, begin downshifting when the engine rpm starts to approach peak torque (1100-1200 rpm) speed. Fuel economy will be best if you let the engine lug back to around this speed before you downshift. Downshift until a gear is reached in which the engine will pull the load. Allowing the engine to lug below peak torque is permissible if the truck is cresting the top of a hill without downshifting.However, note that extended operation in a lug condition will raise exhaust temperature and cylinder pressure and can lead to reduced engine life.Downhill Operation
Do NOT allow the engine rpm to exceed 2300 rpm, engine damage can result. If equipped with an exhaust brake, do not exceed 2100 rpm.
* When operating the vehicle downhill, do not coast or put the transmission in NEUTRAL.* Select the correct gear that does not allow the engine speed (rpm) to exceed the limits above and use the engine retarder and/or brakes to limit the speed of the truck.* A simple rule to follow is to select the same gear that would be required to go up the grade. However, DO NOT allow the engine to overspeed.For more information on economical operation of this engine, refer to form LEDT5092, Driving Techniques for Maximum Fuel Economy.