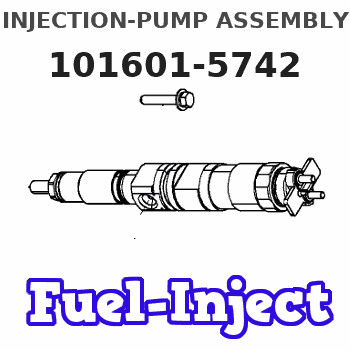
Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101601-5742
1016015742
HINO
220007001A
220007001a
Rating:
Service parts 101601-5742 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
23600-2133
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
19.6{200}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101601-5742
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
104205-2031
as _
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101601-5742
1016015742
HINO
220007001A
220007001a
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-8320
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
108
88
128
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.1
0.9
1.3
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
RED3 control unit part number
407910-2
470
RED3 rack sensor specifications
mm
15
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-4-2-6-
3-5
Pre-stroke
mm
3.8
3.77
3.83
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 60 59.75 60.25
Difference between angles 2
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 120 119.75 120.25
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 4
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 240 239.75 240.25
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Cal 1-5 deg. 300 299.75 300.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Rack position
(8.8)
Vist
V
2.24
2.24
2.24
Pump speed
r/min
850
850
850
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
76.5
75.5
77.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3.5
3.5
Basic
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Rack position
(6.6)
Vist
V
2.7
2.6
2.8
Pump speed
r/min
250
250
250
Each cylinder's injection qty
mm3/st.
15.5
14.5
16.5
Governor adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
925--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Load
1/4
Remarks
Start
Start
Governor adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
875
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Load
1/4
Governor adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
(920--)
Advance angle
deg.
1
0.7
1.3
Load
4/4
Governor adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1175+50
Advance angle
deg.
1
0.7
1.3
Load
3/4
Governor adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
1400+50
Advance angle
deg.
5.5
5.2
5.8
Load
4/4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Speed control lever angle
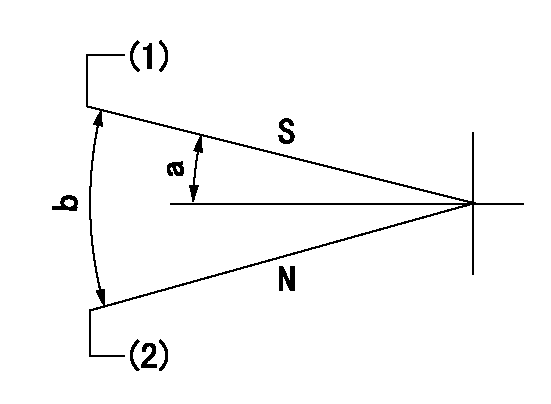
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Rack position bb
----------
aa=1mm bb=16mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=27deg+-5deg
----------
aa=1mm bb=16mm
----------
a=2deg+-5deg b=27deg+-5deg
0000000901
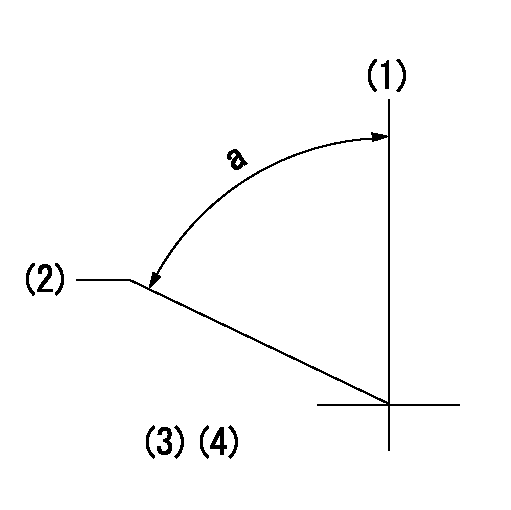
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Coupling's key groove position at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(50deg)
----------
----------
a=(50deg)
Stop lever angle

(Rs) rack sensor specifications
(C/U) control unit part number
(V) Rack sensor output voltage
(R) Rack position (mm)
1. Confirming governor output characteristics (rack 15 mm, span 6 mm)
(1)When the output voltages of the rack sensor are V1 and V2, check that the rack positions R1 and R2 in the table above are satisfied.
----------
----------
----------
----------
Information:
Engine Performance
Poor vehicle performance is traditionally believed to be the result of a lack (or loss) of engine performance, when in fact the engine is only one of numerous factors that influence the overall performance of a vehicle. The previous section on fuel economy describes the factors that determine the power demand on an engine. The engine has no control over the demand made upon it by the vehicle or the operator.A vehicle that requires 225 hp (168 kW) to operate at 55 mph (88 km/h) will get worse fuel economy than a vehicle that requires only 175 hp (130 kW).These same factors also affect the amount of power available to perform additional work such as climb a grade or pass another vehicle. With a 310 hp (231 kW) engine, the first vehicle will have only 85 hp (63 kW) available to perform additional work compared to 135 hp (100 kW) on the second vehicle (mentioned above).If you feel you have a vehicle performance problem, first consider the impact of vehicle efficiency and operating characteristics (vehicle speed, design, etc.), on power demand before questioning engine performance. In the case of poor fuel economy, the engine is not likely to be the cause without the presence of excessive exhaust smoke and/or a significant loss of power.If you feel you have a valid engine performance problem, contact an authorized Caterpillar dealer for assistance. If your engine is under warranty, then the Caterpillar warranty or extended service coverage willcover the cost of resolving a valid engine performance deficiency.However, if the engine is not found at fault, all costs incurred will be the responsibility of the owner.
Adjustment of the fuel system outside Caterpillar specified limits will not improve fuel efficiency and can result in damage to the engine.
Performance Analysis Report (PAR)
PAR complements a good preventive maintenance program and Caterpillar recommends a regularly scheduled PAR analysis to monitor the condition and maintenance requirements of your engine and to ensure your engine is operating at peak efficiency.Potential problems can be identified early, thus preventing unnecessary repair costs and unscheduled downtime. Consult your Caterpillar dealer for complete information and assistance in establishing a PAR program for your engine.PAR reflects the results of various tests normally conducted by your Caterpillar dealer for the purpose of:* confirming your engine is operating efficiently and within specification.* identifying potential problems.* determining components or systems that should be adjusted, replaced, etc.Approximately 80 to 85% of your truck engine's operation and maintenance cost is the cost of the fuel. Therefore, substantial cost reductions can be achieved by keeping your engine operating at peak efficiency. The fuel economy and performance of the engine is affected by the truck specifications, how it is operated and the condition of the engine. Each plays an important part in minimizing your overall owning and operating cost.Caterpillar has an exclusive Performance Analysis Report (PAR) Program that can help you keep the engine portion of this equation up to PAR. The PAR Program uses a chassis dynamometer to
Poor vehicle performance is traditionally believed to be the result of a lack (or loss) of engine performance, when in fact the engine is only one of numerous factors that influence the overall performance of a vehicle. The previous section on fuel economy describes the factors that determine the power demand on an engine. The engine has no control over the demand made upon it by the vehicle or the operator.A vehicle that requires 225 hp (168 kW) to operate at 55 mph (88 km/h) will get worse fuel economy than a vehicle that requires only 175 hp (130 kW).These same factors also affect the amount of power available to perform additional work such as climb a grade or pass another vehicle. With a 310 hp (231 kW) engine, the first vehicle will have only 85 hp (63 kW) available to perform additional work compared to 135 hp (100 kW) on the second vehicle (mentioned above).If you feel you have a vehicle performance problem, first consider the impact of vehicle efficiency and operating characteristics (vehicle speed, design, etc.), on power demand before questioning engine performance. In the case of poor fuel economy, the engine is not likely to be the cause without the presence of excessive exhaust smoke and/or a significant loss of power.If you feel you have a valid engine performance problem, contact an authorized Caterpillar dealer for assistance. If your engine is under warranty, then the Caterpillar warranty or extended service coverage willcover the cost of resolving a valid engine performance deficiency.However, if the engine is not found at fault, all costs incurred will be the responsibility of the owner.
Adjustment of the fuel system outside Caterpillar specified limits will not improve fuel efficiency and can result in damage to the engine.
Performance Analysis Report (PAR)
PAR complements a good preventive maintenance program and Caterpillar recommends a regularly scheduled PAR analysis to monitor the condition and maintenance requirements of your engine and to ensure your engine is operating at peak efficiency.Potential problems can be identified early, thus preventing unnecessary repair costs and unscheduled downtime. Consult your Caterpillar dealer for complete information and assistance in establishing a PAR program for your engine.PAR reflects the results of various tests normally conducted by your Caterpillar dealer for the purpose of:* confirming your engine is operating efficiently and within specification.* identifying potential problems.* determining components or systems that should be adjusted, replaced, etc.Approximately 80 to 85% of your truck engine's operation and maintenance cost is the cost of the fuel. Therefore, substantial cost reductions can be achieved by keeping your engine operating at peak efficiency. The fuel economy and performance of the engine is affected by the truck specifications, how it is operated and the condition of the engine. Each plays an important part in minimizing your overall owning and operating cost.Caterpillar has an exclusive Performance Analysis Report (PAR) Program that can help you keep the engine portion of this equation up to PAR. The PAR Program uses a chassis dynamometer to
