Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 614 588
9400614588
ZEXEL
101601-4290
1016014290
ISUZU
5156004987
5156004987
Rating:
Service parts 101601-4290 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
10.
NOZZLE AND HOLDER ASSY
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
13.
NOZZLE-HOLDER
14.
NOZZLE
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 614 588
9400614588
ZEXEL
101601-4290
1016014290
ISUZU
5156004987
5156004987
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101601-4290
9 400 614 588
5156004987 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6BB1 * K
6BB1 * K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
132424-0620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-5-3-6-
2-4
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Cal 1-5 deg. 60 59.5 60.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 120 119.5 120.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-6 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 4
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 240 239.5 240.5
Difference between angles 5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 300 299.5 300.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
325
325
325
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9.9
8.6
11.2
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(10.6+
-0.5)
Pump speed
r/min
1600
1600
1600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
52.8
51.8
53.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
10.5+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
1300
1300
1300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
54.2
52.6
55.8
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
10.6+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
54.3
52.7
55.9
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
10.7+-0.
5
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
45.8
44.2
47.4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
R2(13.1+
-0.5)
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
66.4
61.4
71.4
Fixing the rack
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1350+-50
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
2.1
1.6
2.6
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1600
Advance angle
deg.
4
3.5
4.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
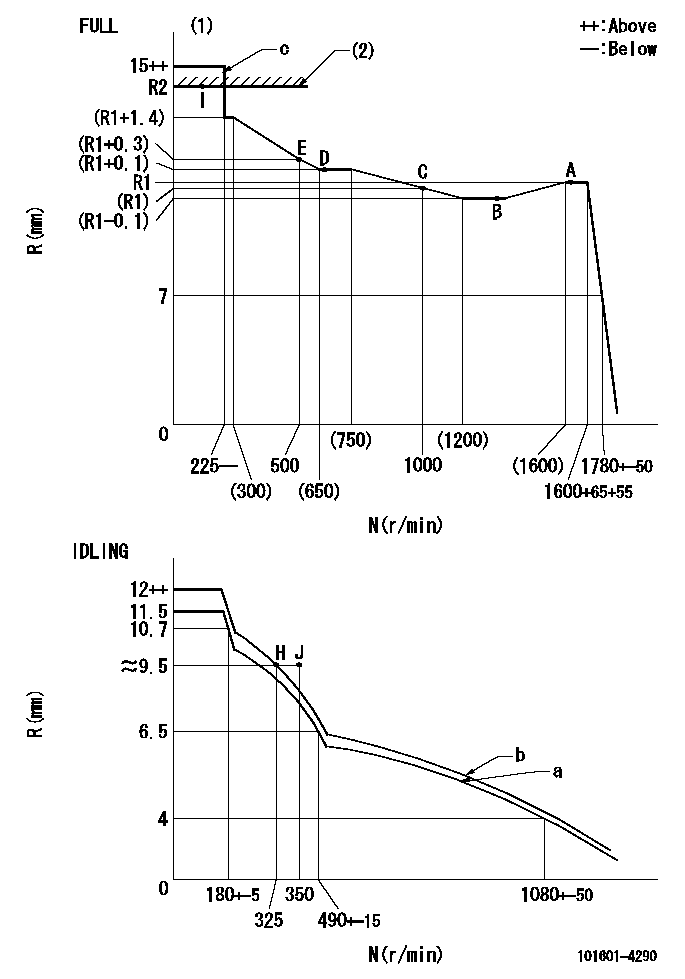
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
(3)Because the figures in brackets are the target values at torque cam adjustment, perform final adjustment in accordance with governor and injection quantity adjustment standards.
(4)Perform governor spring adjustment by setting lever a.
(5)After adjustment of the lever a setting, set the lever so that idle set point H can be obtained and confirm standard b.
(6)After completing final adjustment, set the lever to obtain J.
(7)Next, confirm rack position R1 or more is obtained when rotation is stopped.
(8)In this condition, move the lever to the full position and confirm standard c. (excess fuel for starting operation limit).
(9)After completing final adjustment, set speed at N1 using lever b.
(10)In this condition, after operating the lever to the full position, confirm no excess fuel for starting (black smoke prevention limit).
(11)For the excess fuel setting for starting rack position point I set the lever to obtain standard c in step (8) and then set the rack limit.
----------
T1=10 R1=12mm N1=225r/min
----------
----------
T1=10 R1=12mm N1=225r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
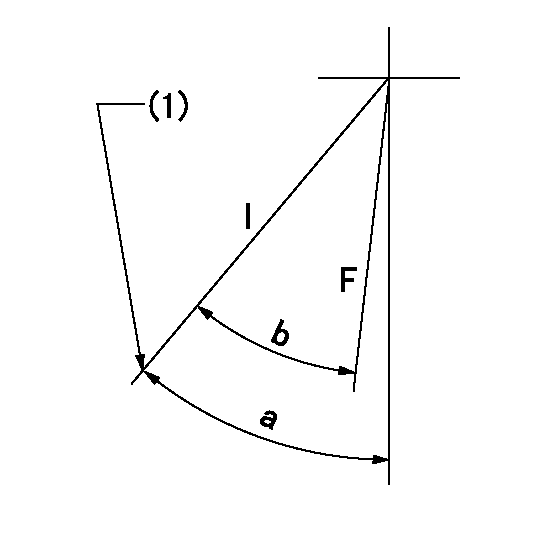
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=39deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=40deg+-5deg b=39deg+-3deg
Information:
Lubrication For A Rebuilt Engine
It is very important for a rebuilt engine to have "adequate" (needed) lubrication during the first seconds of operation. A "dry start" (without needed lubrication) on a rebuilt engine or an engine that has been in storage can cause bearing damage.To prevent the possibility of a "dry start" and bearing damage during the first few seconds of running, use the 1P0540 Flow Checking Tool Group and shop air pressure to pressure lubricate (fill the main oil passage with oil under pressure) all rebuilt engines and all engines that have been in storage.Procedure For Pressure Lubrication
1. Clean the tank of the 1P0540 Flow Checking Tool Group thoroughly, and set the pressure regulator to 240 35 kPa (35 5 psi).
Air pressure should not be more than 345 kPa (50 psi) at any time.
2. Put the correct engine oil into the tank. Use a minimum of 30% of the engine oil capacity. For some engines it will be necessary to fill the tank several times to get the correct amount of oil in the engine.3. Connect the tooling to the main oil passage of the engine.4. Add air pressure to the tank, with the regulator set at 240 35 kPa (35 5 psi). Although the tank has a hand pump, it is difficult to get enough air pressure to do the job with the hand pump. Therefore, use of shop air is recommended.5. Let the engine oil flow into the oil passage under pressure.Fill the crankcase with the correct engine oil. The amount of oil used in the pressure lubrication procedure must be subtracted from the recommended refill capacity in the Operation Maintenance Manual. If the engine is not going to be used for a long time, do the above procedure again before the first start.If shop air is not available, for charging the tank, the hand pump may be used to get the minimum required pressure.
DO NOT use the same 1P0540 Flow Checking Tool Group for both "pressure lubrication application" and for checking fuel flow. Incorrect cleaning is probable if the tool is used for both fuel and lubrication oil. Even a minute amount of dirt in the fuel system can cause fuel nozzle failure.
It is very important for a rebuilt engine to have "adequate" (needed) lubrication during the first seconds of operation. A "dry start" (without needed lubrication) on a rebuilt engine or an engine that has been in storage can cause bearing damage.To prevent the possibility of a "dry start" and bearing damage during the first few seconds of running, use the 1P0540 Flow Checking Tool Group and shop air pressure to pressure lubricate (fill the main oil passage with oil under pressure) all rebuilt engines and all engines that have been in storage.Procedure For Pressure Lubrication
1. Clean the tank of the 1P0540 Flow Checking Tool Group thoroughly, and set the pressure regulator to 240 35 kPa (35 5 psi).
Air pressure should not be more than 345 kPa (50 psi) at any time.
2. Put the correct engine oil into the tank. Use a minimum of 30% of the engine oil capacity. For some engines it will be necessary to fill the tank several times to get the correct amount of oil in the engine.3. Connect the tooling to the main oil passage of the engine.4. Add air pressure to the tank, with the regulator set at 240 35 kPa (35 5 psi). Although the tank has a hand pump, it is difficult to get enough air pressure to do the job with the hand pump. Therefore, use of shop air is recommended.5. Let the engine oil flow into the oil passage under pressure.Fill the crankcase with the correct engine oil. The amount of oil used in the pressure lubrication procedure must be subtracted from the recommended refill capacity in the Operation Maintenance Manual. If the engine is not going to be used for a long time, do the above procedure again before the first start.If shop air is not available, for charging the tank, the hand pump may be used to get the minimum required pressure.
DO NOT use the same 1P0540 Flow Checking Tool Group for both "pressure lubrication application" and for checking fuel flow. Incorrect cleaning is probable if the tool is used for both fuel and lubrication oil. Even a minute amount of dirt in the fuel system can cause fuel nozzle failure.
Have questions with 101601-4290?
Group cross 101601-4290 ZEXEL
Isuzu
101601-4290
9 400 614 588
5156004987
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
6BB1
6BB1