Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 614 447
9400614447
ZEXEL
101492-3702
1014923702
KOMATSU
6202731130
6202731130
Rating:
Service parts 101492-3702 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
6202-13-3500
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
22.1{225}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 614 447
9400614447
ZEXEL
101492-3702
1014923702
KOMATSU
6202731130
6202731130
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-2-4-3
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cyl.1-2 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cal 1-3 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
33.4
32.4
34.4
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
400
400
400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10.5
9.5
11.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
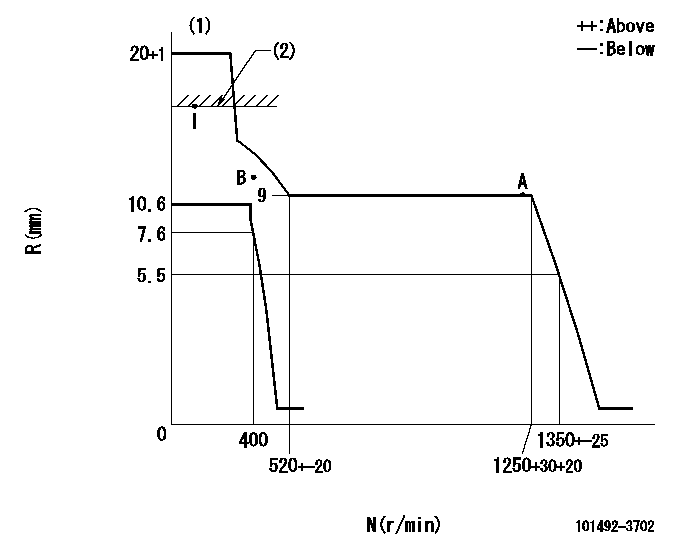
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)RACK CAP: R1
----------
K=19 R1=(17.5)mm
----------
----------
K=19 R1=(17.5)mm
----------
Speed control lever angle
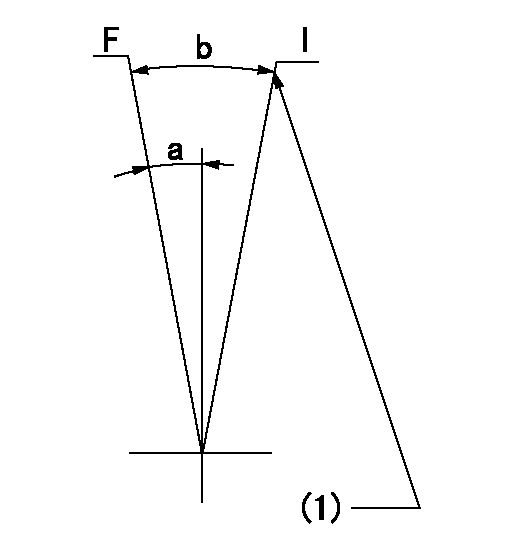
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=(23deg)+-5deg b=(30deg)+-5deg
----------
----------
a=(23deg)+-5deg b=(30deg)+-5deg
Stop lever angle
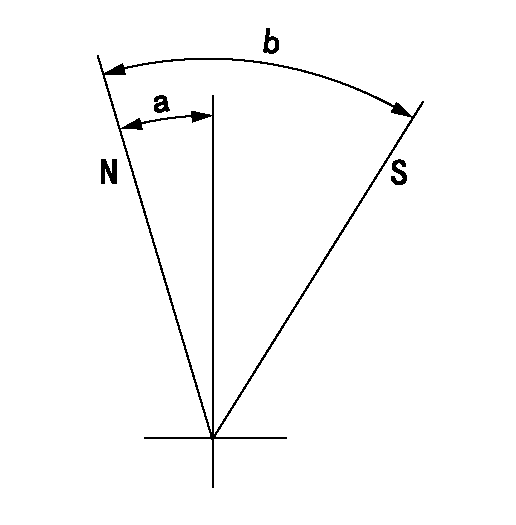
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=1deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=1deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting
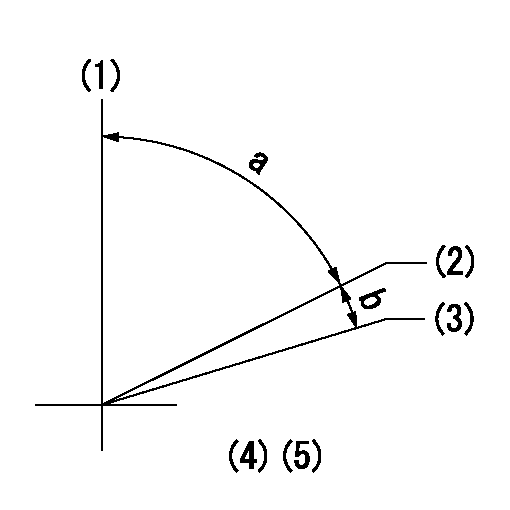
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of key groove at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)Stamp aligning marks on the pump housing flange.
(4)-
----------
----------
a=59deg36min+-3deg b=0deg24min+-30min
----------
----------
a=59deg36min+-3deg b=0deg24min+-30min
Information:
* NA: Naturally Aspirated* T: Turbocharged* TA: Turbocharged, Aftercooled* DI: Direct Injection* PC: Precombustion ChamberThis instruction gives the information needed to install a service replacement fuel injection pump and governor group for the above engines.1 Remove the fuel system from the engine. Make reference to the Service Manual for correct procedure.
When any replacement parts are put in the fuel system, the low idle, high idle and fuel setting must be checked and adjustments made as necessary. Only a mechanic with training in fuel system maintenance must be permitted to make these adjustments. The correct low idle and high idle rpm, and fuel setting are given in the FUEL SETTING INFORMATION.
2 Find and write down the serial number of the machine, the serial number of the engine and the engine arrangement number. All of these numbers are needed to find which parts to use for the fuel system reconditioning. 3 The chart that follows gives the part number of the governor spring (1) that is already installed in each Service Pump Group. Make reference to the FUEL SETTING INFORMATION, to find the part number of the governor spring needed for the fuel system reconditioning. If the governor spring must be changed, the chart for governor spring identification gives a method to find the correct governor spring. See the Service Manual for the procedure needed to change the governor spring. 4 The chart that follows gives the part number of the detent spring that is installed in the governor control of each service group. Look at the Parts Book for the specific engine or machine, to find which detent spring is needed for the fuel system reconditioning. If it is necessary to change detent spring (2), see the Service Manual for the procedure to install the detent spring. The illustrations with steps 4 and 5 show a 4 cylinder engine fuel system only; the procedure is the same for a 6 cylinder engine fuel system. 5 Make a comparison of side cover (3) on the new pump housing in the service group and the side cover on the old pump housing. If the side covers are different, they must be exchanged. The new pump housing must have the same type of side cover that is installed on the old pump housing. Use new gaskets when the side cover is exchanged. 6 Remove cover (4) from the new service group and the similar cover from the old fuel system. If the torque control groups are different, they must be exchanged. The torque control group on the new pump housing must be the same as the torque control group on the old pump housing. 7 The new service group has one bolt (5) and a stud (6) with nut (7) to fasten the torque control group in position. For those earlier fuel systems that had two bolts, similar to bolt (5), and did not have stud (6) and nut (7), use only the one bolt (5) and stud (6) with nut
When any replacement parts are put in the fuel system, the low idle, high idle and fuel setting must be checked and adjustments made as necessary. Only a mechanic with training in fuel system maintenance must be permitted to make these adjustments. The correct low idle and high idle rpm, and fuel setting are given in the FUEL SETTING INFORMATION.
2 Find and write down the serial number of the machine, the serial number of the engine and the engine arrangement number. All of these numbers are needed to find which parts to use for the fuel system reconditioning. 3 The chart that follows gives the part number of the governor spring (1) that is already installed in each Service Pump Group. Make reference to the FUEL SETTING INFORMATION, to find the part number of the governor spring needed for the fuel system reconditioning. If the governor spring must be changed, the chart for governor spring identification gives a method to find the correct governor spring. See the Service Manual for the procedure needed to change the governor spring. 4 The chart that follows gives the part number of the detent spring that is installed in the governor control of each service group. Look at the Parts Book for the specific engine or machine, to find which detent spring is needed for the fuel system reconditioning. If it is necessary to change detent spring (2), see the Service Manual for the procedure to install the detent spring. The illustrations with steps 4 and 5 show a 4 cylinder engine fuel system only; the procedure is the same for a 6 cylinder engine fuel system. 5 Make a comparison of side cover (3) on the new pump housing in the service group and the side cover on the old pump housing. If the side covers are different, they must be exchanged. The new pump housing must have the same type of side cover that is installed on the old pump housing. Use new gaskets when the side cover is exchanged. 6 Remove cover (4) from the new service group and the similar cover from the old fuel system. If the torque control groups are different, they must be exchanged. The torque control group on the new pump housing must be the same as the torque control group on the old pump housing. 7 The new service group has one bolt (5) and a stud (6) with nut (7) to fasten the torque control group in position. For those earlier fuel systems that had two bolts, similar to bolt (5), and did not have stud (6) and nut (7), use only the one bolt (5) and stud (6) with nut