Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101462-9110
1014629110
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101462-9110
1014629110
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
1.95
1.9
2
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
11.7
Pump speed
r/min
750
750
750
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
55
54
56
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2
2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
7.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
350
350
350
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15
13.5
16.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
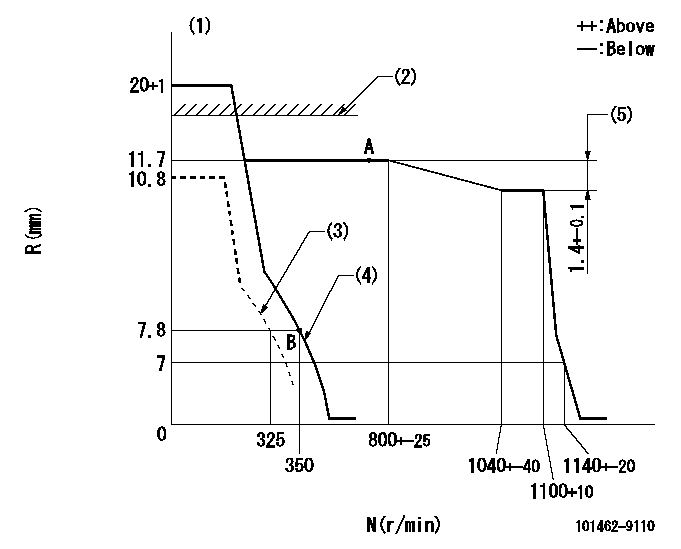
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)RACK CAP: R1
(3)Set idle sub-spring
(4)Main spring setting
(5)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=7 R1=(17.5)mm N1=1100r/min N2=750r/min
----------
----------
K=7 R1=(17.5)mm N1=1100r/min N2=750r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=8deg+-5deg b=27deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=8deg+-5deg b=27deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=(0deg) b=(53deg)
----------
----------
a=(0deg) b=(53deg)
Information:
Locations and Methods for Measuring the Pressures of the Low-Pressure Fuel System
Illustration 1 g03325145
Front View of a typical fuel inlet lines group (A) Fuel inlet port (B) Test port for the fuel supply pressure (C) Fuel transfer pump (D) Test port location for system pressureInlet Fuel Pressure to the Transfer Pump (set at rated speed and load)
Install a 6V-3965 Fitting into Port (B) using a 214-7568 O-Ring Seal Note: The inlet pressure to the fuel transfer pump can affect overall system pressure. All filters or water separators before the transfer pump must be new and clean prior to setting the system pressure at the fuel pressure regulator.
Connect the 6V-7830 Pressure Gauge to the fitting installed in the previous step.
Set the engine to rated speed and load. Record the fuel pressure, and refer to the specifications above.Primary and Secondary Fuel Filter Differential Pressure
Primary and secondary fuel filter differential pressures are determined by the pressures from both sides of the fuel filters. This measurement will monitor fuel filter cleanliness and determine when the fuel filters require changing. Filter replacement will vary depending on fuel quality. Fuel quality can change with each shipment of fuel so monitoring the filter differential is necessary to obtain maximum filter life.Too high of a differential can cause air bubbles in the fuel system and if not corrected will lead to poor performance and injector damage. After the measurements are taken, refer to the specification above for the maximum allowable differential pressure.Primary filters or water separators should be properly sized to meet the flow requirements of the engine or engines as well as fuel being returned to the tank. Reference Table 4 for the flow requirements.
Table 4
3600 Engine Fuel Flow
Engine Model Rated Speed (rpm) Fuel Flow to Engine Fuel Flow from Engine Fuel Heat Rejection
3606 1000
41.5 L/min (11 US gpm)
32.4 L/min (8.6 US gpm)
12.5 kW (712 Btu/min)
900
38 L/min (10 US gpm)
30.0 L/min (7.9 US gpm)
11.0 kW (626 Btu/min)
750
31.5 L/min (8.3 US gpm)
24.5 L/min (6.5 US gpm)
10.5 kW (598 Btu/min)
720
30 L/min (7.9 US gpm)
23.6 L/min (6.2 US gpm)
10.0 kW (567 Btu/min)
3608 1000
41.5 L/min (11 US gpm)
30.0 L/min (7.9 US gpm)
16.7 kW (951 Btu/min)
900
38 L/min (10 US gpm)
27.6 L/min (7.3 US gpm)
14.6 kW (831 Btu/min)
750
31.5 L/min (8.3 US gpm)
22.6 L/min (6.0 US gpm)
14.0 kW (797 Btu/min)
720
30 L/min (7.9 US gpm)
21.4 L/min (5.6 US gpm)
13.3 kW (757 Btu/min)
3612 1000
78.5 L/min (20.7 US gpm)
60.1 L/min (15.9 US gpm)
25.0 kW (1423 Btu/min)
900
72 L/min (19 US gpm)
55.4 L/min (14.6 US gpm)
22.0 kW (1252 Btu/min)
750
61.2 L/min (16.2 US gpm)
47.3
Illustration 1 g03325145
Front View of a typical fuel inlet lines group (A) Fuel inlet port (B) Test port for the fuel supply pressure (C) Fuel transfer pump (D) Test port location for system pressureInlet Fuel Pressure to the Transfer Pump (set at rated speed and load)
Install a 6V-3965 Fitting into Port (B) using a 214-7568 O-Ring Seal Note: The inlet pressure to the fuel transfer pump can affect overall system pressure. All filters or water separators before the transfer pump must be new and clean prior to setting the system pressure at the fuel pressure regulator.
Connect the 6V-7830 Pressure Gauge to the fitting installed in the previous step.
Set the engine to rated speed and load. Record the fuel pressure, and refer to the specifications above.Primary and Secondary Fuel Filter Differential Pressure
Primary and secondary fuel filter differential pressures are determined by the pressures from both sides of the fuel filters. This measurement will monitor fuel filter cleanliness and determine when the fuel filters require changing. Filter replacement will vary depending on fuel quality. Fuel quality can change with each shipment of fuel so monitoring the filter differential is necessary to obtain maximum filter life.Too high of a differential can cause air bubbles in the fuel system and if not corrected will lead to poor performance and injector damage. After the measurements are taken, refer to the specification above for the maximum allowable differential pressure.Primary filters or water separators should be properly sized to meet the flow requirements of the engine or engines as well as fuel being returned to the tank. Reference Table 4 for the flow requirements.
Table 4
3600 Engine Fuel Flow
Engine Model Rated Speed (rpm) Fuel Flow to Engine Fuel Flow from Engine Fuel Heat Rejection
3606 1000
41.5 L/min (11 US gpm)
32.4 L/min (8.6 US gpm)
12.5 kW (712 Btu/min)
900
38 L/min (10 US gpm)
30.0 L/min (7.9 US gpm)
11.0 kW (626 Btu/min)
750
31.5 L/min (8.3 US gpm)
24.5 L/min (6.5 US gpm)
10.5 kW (598 Btu/min)
720
30 L/min (7.9 US gpm)
23.6 L/min (6.2 US gpm)
10.0 kW (567 Btu/min)
3608 1000
41.5 L/min (11 US gpm)
30.0 L/min (7.9 US gpm)
16.7 kW (951 Btu/min)
900
38 L/min (10 US gpm)
27.6 L/min (7.3 US gpm)
14.6 kW (831 Btu/min)
750
31.5 L/min (8.3 US gpm)
22.6 L/min (6.0 US gpm)
14.0 kW (797 Btu/min)
720
30 L/min (7.9 US gpm)
21.4 L/min (5.6 US gpm)
13.3 kW (757 Btu/min)
3612 1000
78.5 L/min (20.7 US gpm)
60.1 L/min (15.9 US gpm)
25.0 kW (1423 Btu/min)
900
72 L/min (19 US gpm)
55.4 L/min (14.6 US gpm)
22.0 kW (1252 Btu/min)
750
61.2 L/min (16.2 US gpm)
47.3