Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 614 139
9400614139
ZEXEL
101441-9610
1014419610
NISSAN-DIESEL
1670090074
1670090074
Rating:
Service parts 101441-9610 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
16600-43G02
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
9.8{100}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101441-9610
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
105856-7800
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 614 139
9400614139
ZEXEL
101441-9610
1014419610
NISSAN-DIESEL
1670090074
1670090074
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
2.3
2.25
2.35
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
12.5
Pump speed
r/min
1400
1400
1400
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
41.4
40.4
42.4
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
9+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
600
600
600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10
8.9
11.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
550--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
500
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
3
2.5
3.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
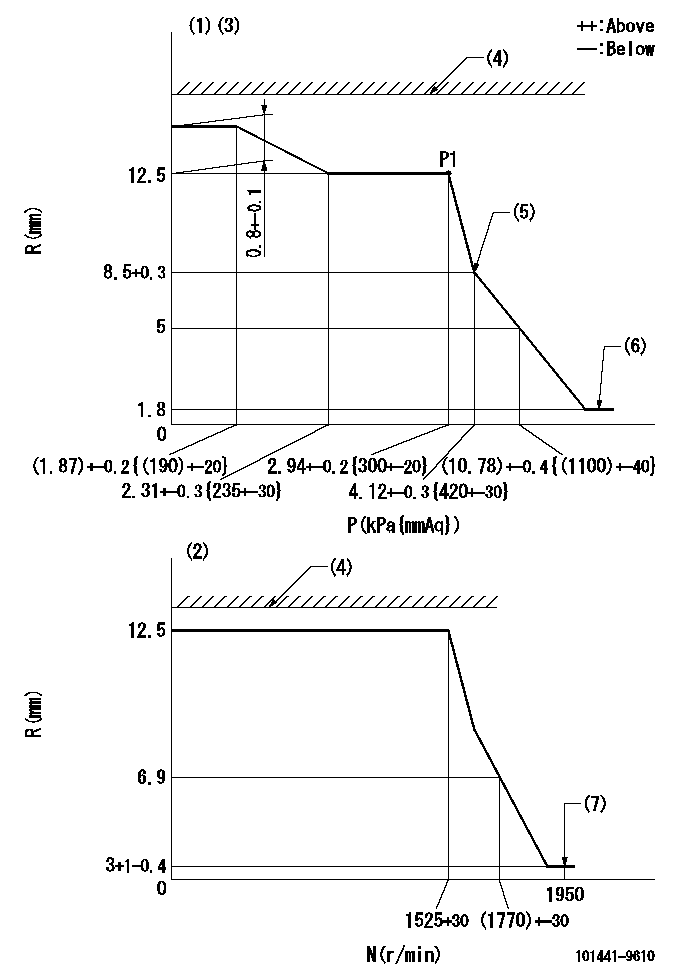
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
P:Negative pressure
(1)Pneumatic governor
(2)Mechanical governor
(3)Acting negative pressure: P1
(4)RACK LIMIT: RAL
(5)Beginning of idle sub spring operation: L1
(6)With stopper disk.
(7)Injection quantity Q = Q1 or less
----------
RAL=14.7-0.3mm L1=8.5+0.3mm Q1=3mm3/st
----------
----------
RAL=14.7-0.3mm L1=8.5+0.3mm Q1=3mm3/st
----------
0000001101
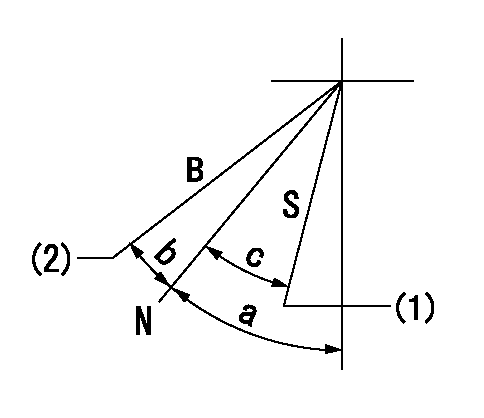
N:Normal
B:When boosted
S:Stop
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Rack position corresponding to bb
----------
aa=(1.8)mm bb=(15)mm
----------
a=31deg+-5deg b=3.5deg+-5deg c=23deg+-3deg
----------
aa=(1.8)mm bb=(15)mm
----------
a=31deg+-5deg b=3.5deg+-5deg c=23deg+-3deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark 'ZZ' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=18deg
----------
a=(100deg)
----------
aa=18deg
----------
a=(100deg)
Information:
Input Modules
The following modules are input modules:
Thermocouple Module
RTD Input Module
Digital Modules
Analog ModulesWhen you apply a voltage to the channel, the relay is energized. An energized input will close all of the contacts that are normally open. An energized input will open all of the contacts that are normally closed. Digital modules are used to determine whether a circuit is ON/OFF. A number of modules are available. The MMS modules have sixteen channels. Discrete Output Modules
The programmable logic controller discrete output modules consist of analog modules and digital modules. Control of Voltage is provided by the output modules. A module provides power for the following list of functions: energizing the lamps, energizing the relays, energizing the fuel shutoff solenoid and energizing the air shutoff solenoid.Replacing a Module
Disconnect the power supply.
To avoid damage to electronic components, do not remove the processor from the SLC 5/04 Chassis until all power is removed from the power supply.Do not expose memory modules to surfaces or areas that may typically hold an electrostatic charge.
Press the retaining clips at the top of the module and press the retaining clips at the bottom of the module.
Remove the module from the chassis.
To avoid potential damage to the processor, handle all modules by the ends of the carrier or edges of the plastic housing. Skin oil or dirt can corrode metallic surfaces, inhibiting electrical contact.
Align the module and the guides in the chassis.
Gently slide the module in the chassis. Secure the top retainer clips and secure the bottom retainer clips.
Install a wire tie in order to secure the wiring.
Illustration 1 g00563310
Cover any unused slots. This protects the chassis.
Verify that the new module corrects the problem.
The following modules are input modules:
Thermocouple Module
RTD Input Module
Digital Modules
Analog ModulesWhen you apply a voltage to the channel, the relay is energized. An energized input will close all of the contacts that are normally open. An energized input will open all of the contacts that are normally closed. Digital modules are used to determine whether a circuit is ON/OFF. A number of modules are available. The MMS modules have sixteen channels. Discrete Output Modules
The programmable logic controller discrete output modules consist of analog modules and digital modules. Control of Voltage is provided by the output modules. A module provides power for the following list of functions: energizing the lamps, energizing the relays, energizing the fuel shutoff solenoid and energizing the air shutoff solenoid.Replacing a Module
Disconnect the power supply.
To avoid damage to electronic components, do not remove the processor from the SLC 5/04 Chassis until all power is removed from the power supply.Do not expose memory modules to surfaces or areas that may typically hold an electrostatic charge.
Press the retaining clips at the top of the module and press the retaining clips at the bottom of the module.
Remove the module from the chassis.
To avoid potential damage to the processor, handle all modules by the ends of the carrier or edges of the plastic housing. Skin oil or dirt can corrode metallic surfaces, inhibiting electrical contact.
Align the module and the guides in the chassis.
Gently slide the module in the chassis. Secure the top retainer clips and secure the bottom retainer clips.
Install a wire tie in order to secure the wiring.
Illustration 1 g00563310
Cover any unused slots. This protects the chassis.
Verify that the new module corrects the problem.
