Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 610 087
9400610087
ZEXEL
101441-9370
1014419370
NISSAN-DIESEL
1670064W01
1670064w01
Rating:
Service parts 101441-9370 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
9.8{100}
14.
NOZZLE
15.
NOZZLE SET
Include in #1:
101441-9370
as INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
Include in #2:
105856-5281
as _
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 610 087
9400610087
ZEXEL
101441-9370
1014419370
NISSAN-DIESEL
1670064W01
1670064w01
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101441-9370
9 400 610 087
1670064W01 NISSAN-DIESEL
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SD25 * K
SD25 * K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
2.3
2.25
2.35
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
12.3
Pump speed
r/min
1000
1000
1000
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
38.3
37.3
39.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
8.7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
300
300
300
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8
6.9
9.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
950--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
900
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1400
Advance angle
deg.
2.1
1.6
2.6
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
2030
Advance angle
deg.
5.6
5.1
6.1
Timer adjustment_05
Pump speed
r/min
-
Advance angle
deg.
6
5.5
6.5
Remarks
Measure the actual speed, stop
Measure the actual speed, stop
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
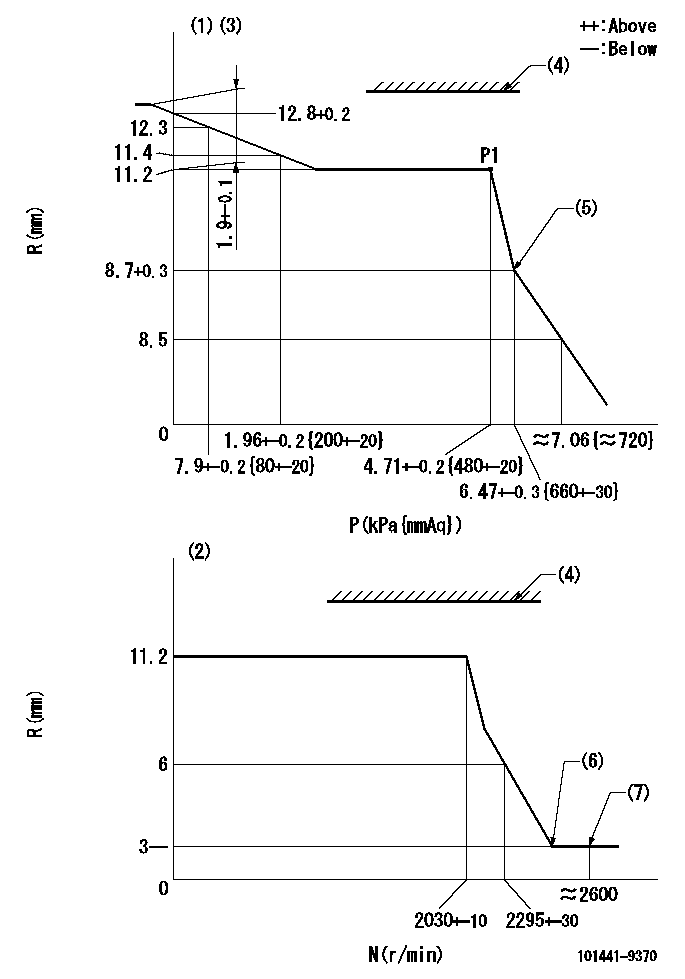
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
P:Negative pressure
(1)Pneumatic governor
(2)Mechanical governor
(3)Acting negative pressure: P1
(4)RACK LIMIT: RAL
(5)Beginning of idle sub spring operation: L1
(6)Without stopper disk
(7)Injection quantity Q = Q1 or less
----------
RAL=14.7-0.3mm L1=8.7+0.3mm Q1=3mm3/st
----------
----------
RAL=14.7-0.3mm L1=8.7+0.3mm Q1=3mm3/st
----------
Speed control lever angle
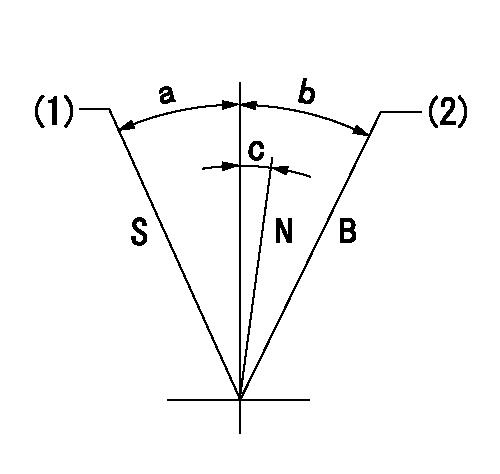
B:When boosted
N:Normal
S:Stop
(1)Rack position = aa
(2)Rack position corresponding to cc
----------
aa=0mm bb=15mm
----------
a=26deg+-3deg b=35deg+-5deg c=1deg+-5deg
----------
aa=0mm bb=15mm
----------
a=26deg+-3deg b=35deg+-5deg c=1deg+-5deg
0000001501 ACS

(N): Speed of the pump
(P): governor's negative pressure
(Pa): aneroid compensator's negative pressure
(A) rubber boot
(B) Nut
(c) Nut
(D) Lever
1. Aneroid compensator installation
(1)Turn nut (C) to adjust gap to L1. (Remove rubber boot at adjustment.)
(2)Lock using nut (B).
(3)After installation, the lever D must move smoothly when the lever D is moved to the excess fuel side, and R = R1 or more.
----------
L1=0.1~0.5mm R1=16mm
----------
N=1000r/min P=2.94kPa(300mmAq) R1=R1(11.2)mm R2=(R1-0.6)mm R3=(R1-0.8)+-0.2mm R4=(R1-1.2)mm Pa1=1.23kPa(125mmHg) Pa2=1.61kPa(164mmHg) Pa3=2.29kPa(234mmHg)
----------
L1=0.1~0.5mm R1=16mm
----------
N=1000r/min P=2.94kPa(300mmAq) R1=R1(11.2)mm R2=(R1-0.6)mm R3=(R1-0.8)+-0.2mm R4=(R1-1.2)mm Pa1=1.23kPa(125mmHg) Pa2=1.61kPa(164mmHg) Pa3=2.29kPa(234mmHg)
Timing setting
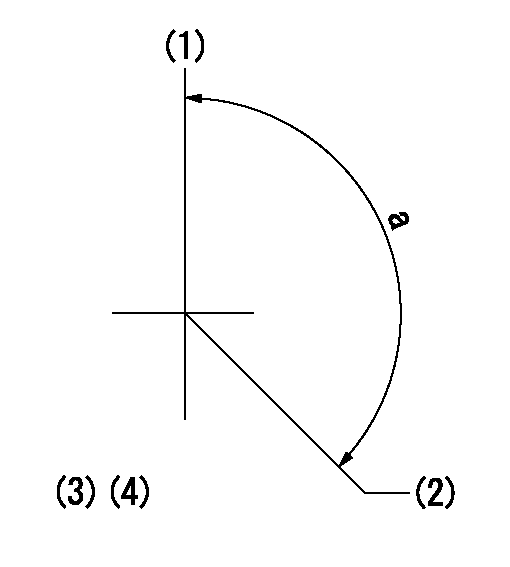
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark 'Y' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=15deg
----------
a=(140deg)
----------
aa=15deg
----------
a=(140deg)
Information:
Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) poses a greater static ignition hazard than earlier diesel formulations, with a higher sulfur content, which may result in a fire or explosion. Consult with your fuel or fuel system supplier for details on proper grounding and bonding practices.
Note: The removal of sulfur and other compounds in Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) fuel decreases the conductivity of ULSD and increases the ability of the fuel to store static charge. Refineries may have treated the fuel with a static dissipating additive. However, there are many factors that can reduce the effectiveness of the additive over time. Static charges can build up in ULSD fuel while the fuel is flowing through fuel delivery systems. Static electricity discharge when combustible vapors are present could result in a fire or explosion. Therefore, ensuring that the entire system used to refuel your machine (fuel supply tank, transfer pump, transfer hose, nozzle, and others) is properly grounded and bonded is important. Consult with your fuel or fuel system supplier to ensure that the delivery system is in compliance with fueling standards for proper grounding and bonding practices.The two basic types of distillate diesel fuel are No. 2 diesel fuel and No. 1 diesel fuel. No. 2 diesel fuel is the most commonly available summer grade diesel fuel. No. 1 diesel fuel is a winter grade diesel fuel. During the winter months fuel suppliers will typically blend No. 1 and No. 2 diesel fuel in various percentages to meet the historical low ambient temperature cold-flow needs for a given area or region. No. 2 diesel fuel is a heavier diesel fuel than No. 1 diesel fuel. In cold weather, heavier fuels can cause problems with fuel filters, fuel lines, fuel tanks, and fuel storage. Heavier diesel fuels such as No. 2 diesel fuel can be used in diesel engines that operate in cold temperatures with an appropriate amount of a well proven pour point depressant additive. For more information on fuels which include blends of No. 1 and No. 2 diesel fuel, consult your fuel supplier.When you use No. 2 diesel fuel or other heavier fuels, some of the fuel characteristics may interfere with successful cold-weather operation. Additional information about the characteristics of diesel fuel is available. This information contains a discussion on the modification to the characteristics of diesel fuel. There are several possible methods that can be used to compensate for the fuel qualities that may interfere with cold-weather operation. These methods include the use of starting aids, engine coolant heaters, fuel heaters, and de-icers. In addition, the manufacturer of the fuel can add cold flow improvers and/or blend No. 1 and No. 2 diesel in various percentages.Not all areas of the world classify diesel fuel using the No. 1 and No. 2 nomenclature described above. But, the basic principles of using additives and/or blending fuels of different densities to help compensate for the fuel qualities that may interfere with cold-weather operation are the same.Starting Aids
The use of
Have questions with 101441-9370?
Group cross 101441-9370 ZEXEL
Nissan-Diesel
101441-9370
9 400 610 087
1670064W01
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
SD25
SD25