Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 818
9400611818
ZEXEL
101402-9970
1014029970

Rating:
Service parts 101402-9970 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
10.
NOZZLE AND HOLDER ASSY
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
13.
NOZZLE-HOLDER
14.
NOZZLE
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 818
9400611818
ZEXEL
101402-9970
1014029970
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-1520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.3
3.25
3.35
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
10.7
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
73.5
72.5
74.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
7.6+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
550
550
550
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13
12
14
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
100
95
105
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
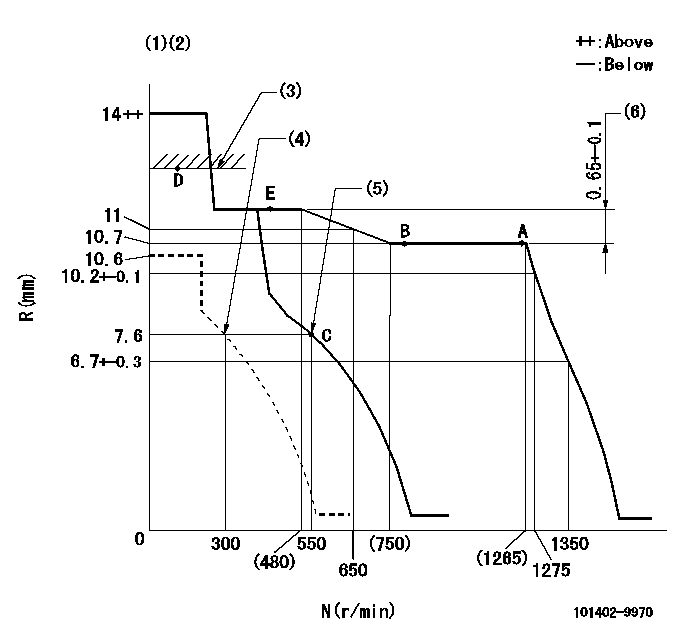
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Set idle sub-spring
(5)Main spring setting
(6)Rack difference between N = N1 and N = N2
----------
K=12 N1=1250r/min N2=400r/min
----------
----------
K=12 N1=1250r/min N2=400r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
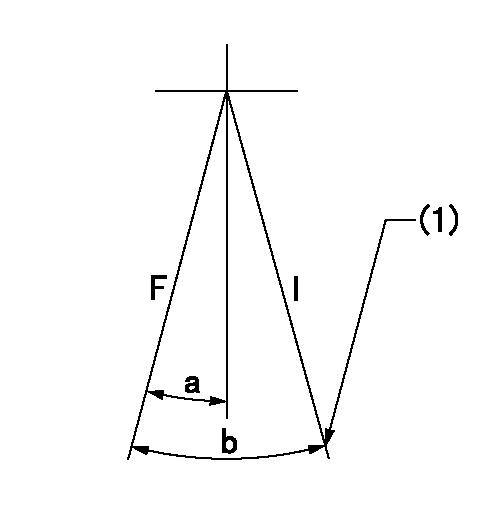
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=17deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=17deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
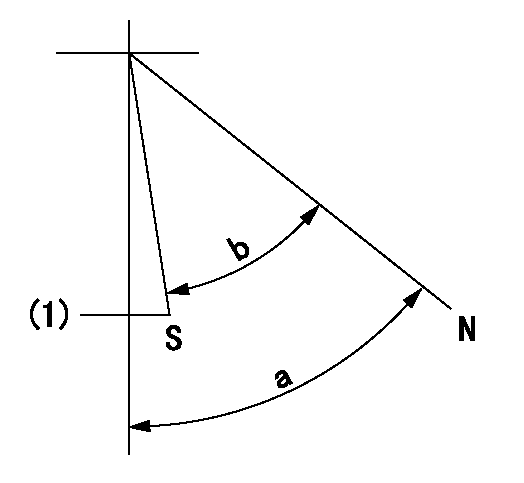
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)At delivery
----------
----------
a=58deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=58deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting
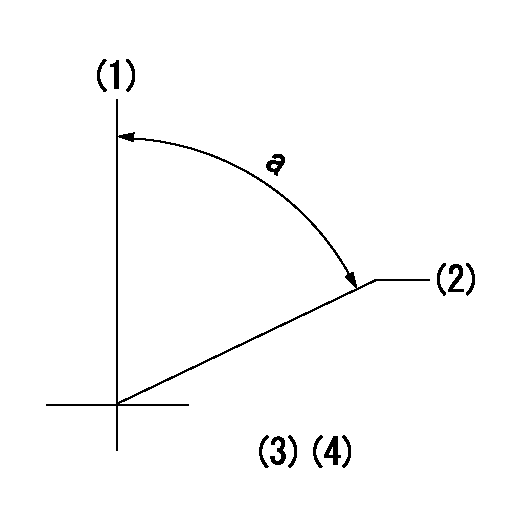
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of camshaft's key groove at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
Information:
Proper operation and maintenance are key factors in determining the useful life and economy of a truck engine. Follow the directions in this guide for trouble-free, economical truck engine operation. After the engine starts, reduce engine RPM to low idle with no load.(1674 and 1693: Before normal oil pressure is reached the governor control linkage travel is limited to below half engine speed by an oil pressure actuated stop inside the governor.) Do not attempt to force the governor control linkage past the stop. When normal oil pressure is reached, operate the engine at low load for 5 minutes before applying full load.Select the lowest gear for a smooth, easy start without slipping the clutch. Rapid engine acceleration causes heavy exhaust smoke and high fuel consumption with no increase in vehicle performance. For best performance, do not skip gears when loaded.Caterpillar engines have good lugging characteristics; however, avoid operating in a lug condition for extended periods of time as it causes exhaust temperatures to rise and results in high fuel consumption. A lug condition exists when an increase in engine speed cannot be achieved with an increase in accelerator pedal position, or when engine speed decreases with the accelerator pedal in its maximum position. A lug condition can exist at any engine speed below full load speed.Continue to upshift until cruising speed is reached. Cruising speed should be between three-fourths and full governed RPM. (The governor will maintain a constant speed without accelerator pedal correction.)On upgrade, begin downshifting if engine starts to labor. Downshift until a gear is reached in which the engine will pull the load without lugging. For best performance, downshift before engine RPM falls below peak torque RPM (see page 2).On downgrade, do not coast or put transmission in neutral. Select the correct gear to keep engine speed below idle and retard the vehicle. A simple rule to follow is to select the same gear that would be used to go up the grade. Do not allow engine speed to exceed high idle.Before stopping the engine, operate at low load for 5 minutes, then at low idle for 30 seconds. (This procedure allows hot areas in the engine to cool gradually, extending the engine life.) To stop the engine, use one of the methods listed. TO STOP THE ENGINE, DO ONE OF THE FOLLOWING, DEPENDING ON TRUCK ARRANGEMENT1. Turn the key to the spring-loaded position and hold until engine stops, then release key, or2. Pull out the manual shutoff control, or3. Push in and hold stop button until engine stops, then release button, or4. Pull up on the accelerator.