Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 612 523
9400612523
ZEXEL
101402-9673
1014029673
YANMAR
12991551020
12991551020
Rating:
Service parts 101402-9673 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
10.
NOZZLE AND HOLDER ASSY
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
13.
NOZZLE-HOLDER
14.
NOZZLE
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 612 523
9400612523
ZEXEL
101402-9673
1014029673
YANMAR
12991551020
12991551020
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
9 400 612 523
12991551020 YANMAR
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4TNE94 * K 14BC PE4A,5A, PE
4TNE94 * K 14BC PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-1520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.7
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
62.5
61.5
63.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
790
790
790
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9.5
8.5
10.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
9.9++
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
90
85
95
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
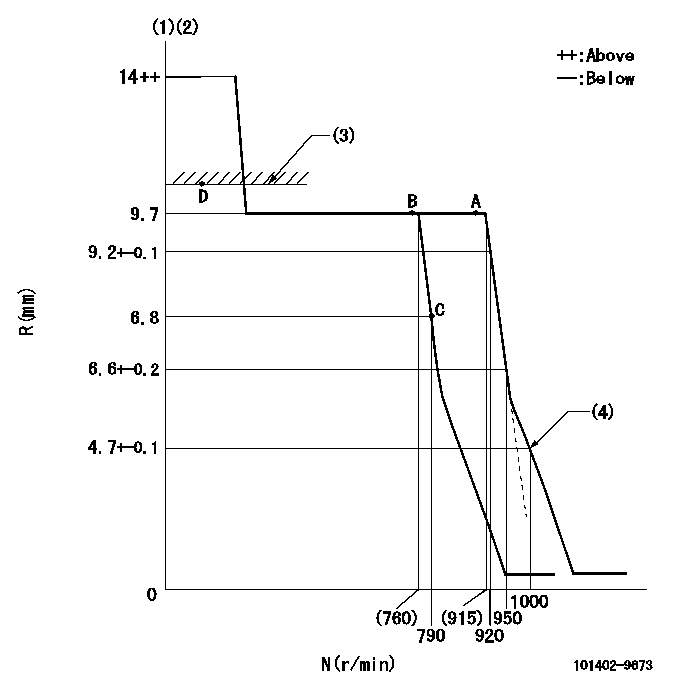
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Set idle sub-spring
----------
K=7
----------
----------
K=7
----------
Speed control lever angle
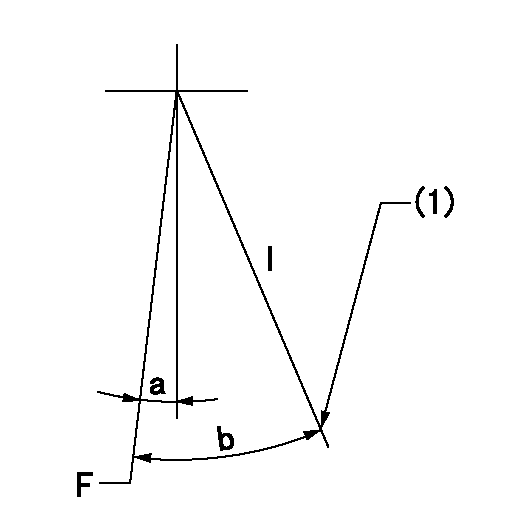
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=1deg+-5deg b=5deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=1deg+-5deg b=5deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
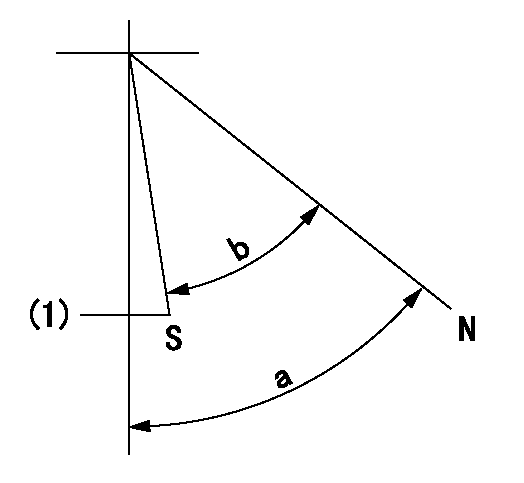
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Normal stop
----------
----------
a=58deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=58deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting
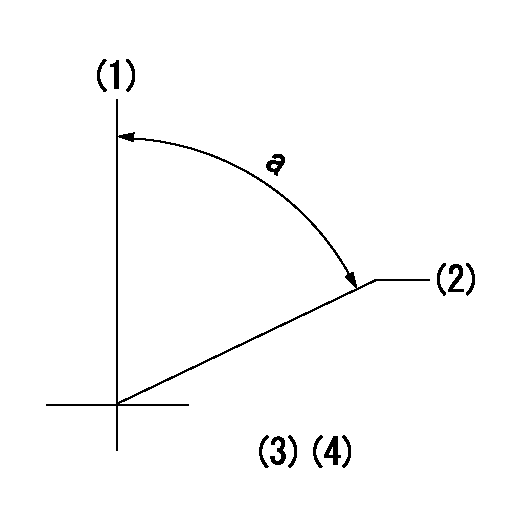
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of camshaft's key groove at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
Information:
This engine may be equipped with a 12 or 24 volt starting system. Use only equal voltage for boost starting. The use of a welder or higher voltage will damage the electrical system.
Charging System Components
Alternator
The alternator is driven by belts from the crankshaft pulley. This alternator is a three phase, self-rectifying charging unit, and the regulator is part of the alternator.The alternator design has no need for slip rings or brushes, and the only part that has movement is the rotor assembly. All conductors that carry current are stationary. The conductors are: the field winding, stator windings, six rectifying diodes, and the regulator circuit components.The rotor assembly has many magnetic poles like fingers with air space between each opposite pole. The poles have residual magnetism (like permanent magnets) that produce a small amount of magnet-like lines of force (magnetic field) between the poles. As the rotor assembly begins to turn between the field winding and the stator windings, a small amount of alternating current (AC) is produced in the stator windings from the small magnetic lines of force made by the residual magnetism of the poles. This AC current is changed to direct current (DC) when it passes through the diodes of the rectifier bridge. Most of this current goes to charge the battery and to supply the low amperage circuit, and the remainder is sent on to the field windings. The DC current flow through the field windings (wires around an iron core) now increases the strength of the magnetic lines of force. These stronger lines of force now increase the amount of AC current produced in the stator windings. The increased speed of the rotor assembly also increases the current and voltage output of the alternator.The voltage regulator is a solid state (transistor, stationary parts) electronic switch. It feels the voltage in the system and switches on and off many times a second to control the field current (DC current to the field windings) for the alternator to make the needed voltage output.
Never operate the alternator without the battery in the circuit. Making or breaking an alternator connection with heavy load on the circuit can cause damage to the regulator.
Alternator Components
(1) Regulator. (2) Roller bearing. (3) Stator winding. (4) Ball bearing. (5) Rectifier bridge. (6) Field winding. (7) Rotor assembly. (8) Fan.Starting System Components
Solenoid
Typical Solenoid SchematicA solenoid is a magnetic switch that does two basic operations.a. Closes the high current starter motor circuit with a low current start switch circuit.b. Engages the starter motor pinion with the ring gear.The solenoid switch is made of an electromagnet (one to two sets of windings) around a hollow cylinder. There is a plunger (core) with a spring load inside the cylinder that can move forward and backward. When the start switch is closed and electricity is sent through the windings, a magnetic field is made that pulls the plunger forward in the cylinder. This moves the shift lever (connected to the rear of the plunger) to engage the pinion
