Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 610 422
9400610422
ZEXEL
101401-7380
1014017380
ISUZU
8971385790
8971385790
Rating:
Service parts 101401-7380 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
8-94447-686-1
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 610 422
9400610422
ZEXEL
101401-7380
1014017380
ISUZU
8971385790
8971385790
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101401-7380
9 400 610 422
8971385790 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4BD1 * K 14BC PE4A,5A, PE
4BD1 * K 14BC PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Rack position
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.9
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69.2
67.6
70.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9.4
8.1
10.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.9)
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69.2
68.2
70.2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1(11.9)
Pump speed
r/min
1600
1600
1600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
77.9
74.7
81.1
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1-0.2
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
51.3
48.1
54.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
90
90
98
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1375--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1325
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1575
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
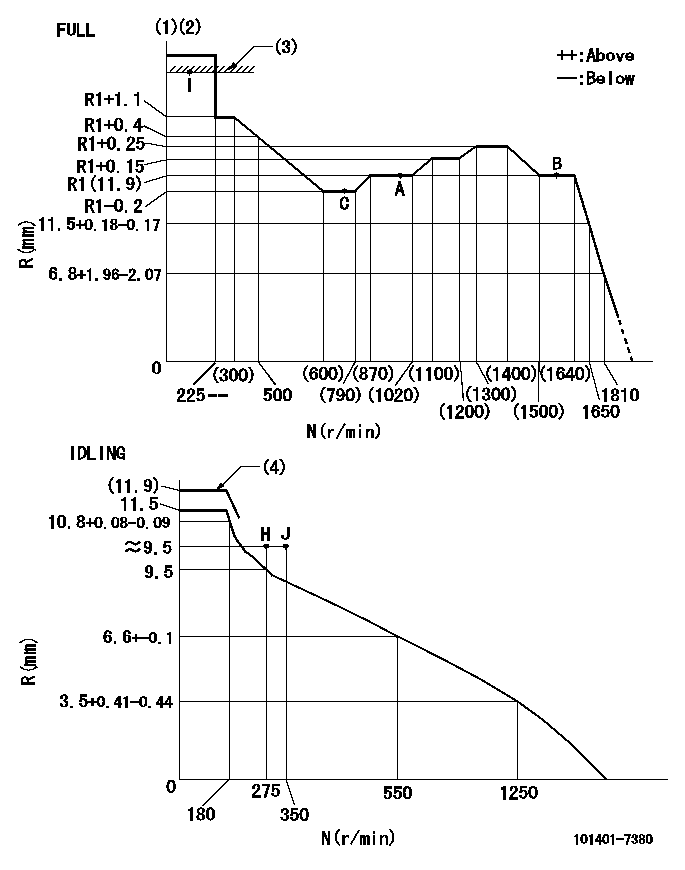
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)At delivery (at R = A, N = N1)
----------
T1=E19 N1=100r/min
----------
----------
T1=E19 N1=100r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
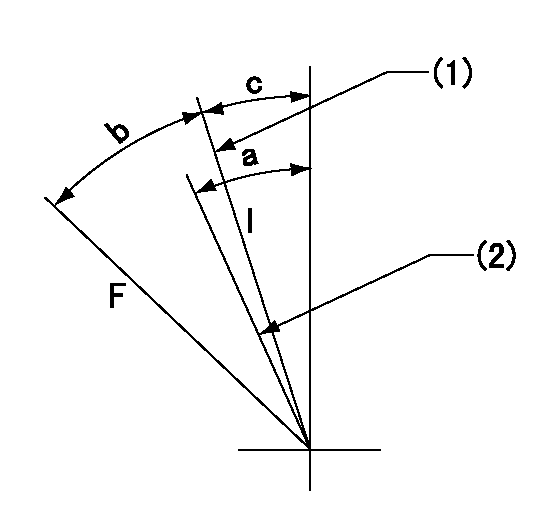
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
(2)Set the idle side stopper bolt at rack position = aa (at delivery).
----------
aa=11.9mm
----------
a=(3deg) b=44deg+-3deg c=2.5deg+-5deg
----------
aa=11.9mm
----------
a=(3deg) b=44deg+-3deg c=2.5deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark 'CC' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=14deg
----------
a=(100deg)
----------
aa=14deg
----------
a=(100deg)
Information:
White Smoke1. Cold Outside Temperature White smoke is normal in cold temperatures until the engine warms up. There will be less white smoke if No. 1 diesel or blended fuel is used.2. Engine Running Too Cold Check the water temperature gauge in the cab. If the temperature remains below the minimum value of the gauge after a reasonable warm up time, this could indicate an open thermostat. Remove and test the thermostat. See the topic, Testing The Cooling System, in 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine Systems Operation And Testing and Adjusting, Form No. SENR4964.3. Air In Fuel System Disconnect the fuel return line at the tank. Place this end of the line in a container of fuel to see if air bubbles are present when the engine is running. If air bubbles are observed, check for loose fittings or line leaks between the fuel tank and fuel transfer pump. If leaks are found, tighten the connections or replace the lines.To remove air from the engine fuel system: With the engine off, loosen the fuel return line fitting at the fuel manifold. Operate the fuel priming pump until the flow of fuel is free of air. Tighten the return line fitting, fasten the priming pump, and start the engine. If the engine still does not run smooth or produces a lot of white smoke, apply 35 kPa (5 psi) of air pressure to the fuel tank to force fuel through the system.
Do not use more than 55 kPa (8 psi) of air pressure in the fuel tank or damage to the tank may result.
Check the fuel return line for restriction. Replace if plugged.4. Fuel Injection Timing Out Of Calibration Check the fuel injection timing calibration and make necessary adjustments. See the topics, Engine Test Procedure Number P-221 and P-301 in Electronic Troubleshooting, 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine, Form No. SENR5137.5. Valve Adjustment Not Correct Check and make any necessary adjustments. See the topic, Valve Clearance Setting, in 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine Systems Operation And Testing and Adjusting, Form No. SENR4964. Intake valve clearance is 0.38 mm (.015 in), and exhaust valve clearance is 0.64 mm (.025 in).6. Defective Unit Injectors A defective unit injector can be found, by running the engine at the rpm where the problem exists, with the use of the Electronic Control Analyzer and Programmer (ECAP) service tool Interactive Diagnostics feature (single cylinder cutout, see Electronic Troubleshooting, 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine, Form No. SENR5137) to stop the fuel supply to each cylinder in turn. If a cylinder is found where the cutout makes a difference in exhaust smoke, that injector should be removed and tested. Drain the fuel supply manifold and remove the injector(s) (see 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine Disassembly and Assembly, Form No. SENR4965).Testing of the injectors must be done off of the engine. Use the 1U6661 Pop (Injector) Tester Group with a 1U6663 Injector Holding Block, and a 1U6665 Power Supply, to test the injectors. For the test procedure refer to Special Instruction, Form No.
Do not use more than 55 kPa (8 psi) of air pressure in the fuel tank or damage to the tank may result.
Check the fuel return line for restriction. Replace if plugged.4. Fuel Injection Timing Out Of Calibration Check the fuel injection timing calibration and make necessary adjustments. See the topics, Engine Test Procedure Number P-221 and P-301 in Electronic Troubleshooting, 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine, Form No. SENR5137.5. Valve Adjustment Not Correct Check and make any necessary adjustments. See the topic, Valve Clearance Setting, in 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine Systems Operation And Testing and Adjusting, Form No. SENR4964. Intake valve clearance is 0.38 mm (.015 in), and exhaust valve clearance is 0.64 mm (.025 in).6. Defective Unit Injectors A defective unit injector can be found, by running the engine at the rpm where the problem exists, with the use of the Electronic Control Analyzer and Programmer (ECAP) service tool Interactive Diagnostics feature (single cylinder cutout, see Electronic Troubleshooting, 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine, Form No. SENR5137) to stop the fuel supply to each cylinder in turn. If a cylinder is found where the cutout makes a difference in exhaust smoke, that injector should be removed and tested. Drain the fuel supply manifold and remove the injector(s) (see 3176 Vehicular Diesel Engine Disassembly and Assembly, Form No. SENR4965).Testing of the injectors must be done off of the engine. Use the 1U6661 Pop (Injector) Tester Group with a 1U6663 Injector Holding Block, and a 1U6665 Power Supply, to test the injectors. For the test procedure refer to Special Instruction, Form No.
Have questions with 101401-7380?
Group cross 101401-7380 ZEXEL
Isuzu
Nissan
Isuzu
Nissan
Isuzu
Isuzu
Isuzu
Isuzu
Isuzu
Isuzu
Isuzu
Isuzu
101401-7380
9 400 610 422
8971385790
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4BD1
4BD1