Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 613 725
9400613725
ZEXEL
101401-4821
1014014821
ISUZU
8971140520
8971140520
Rating:
Service parts 101401-4821 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
18.1(185)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 613 725
9400613725
ZEXEL
101401-4821
1014014821
ISUZU
8971140520
8971140520
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
9 400 613 725
8971140520 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4HF1 * K 14BC PE4A,5A, PE
4HF1 * K 14BC PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
4.1
4.05
4.15
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
12.1
Pump speed
r/min
960
960
960
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
59
57.4
60.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
285
285
285
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15.5
14.2
16.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(12.1)
Pump speed
r/min
960
960
960
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
59
58
60
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.4
Pump speed
r/min
1600
1600
1600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
79
75
83
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
80
80
112
Fixing the lever
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1375--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1325
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
3.3
2.8
3.8
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1600--
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
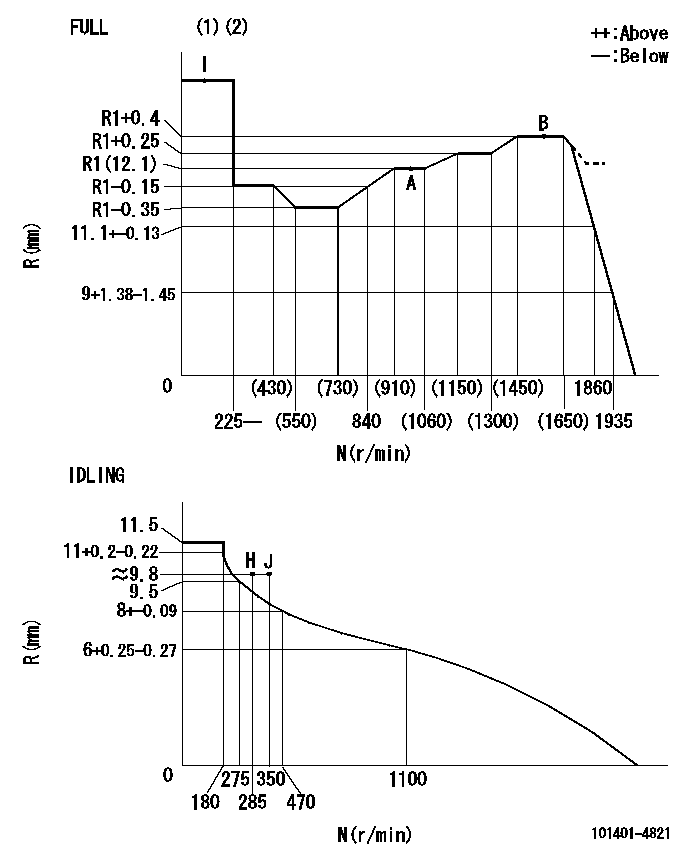
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
----------
T1=J25
----------
----------
T1=J25
----------
Speed control lever angle
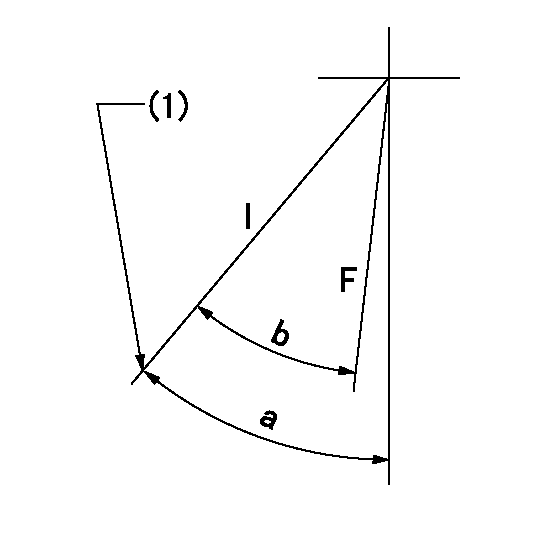
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
----------
a=41deg+-5deg b=37deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=41deg+-5deg b=37deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
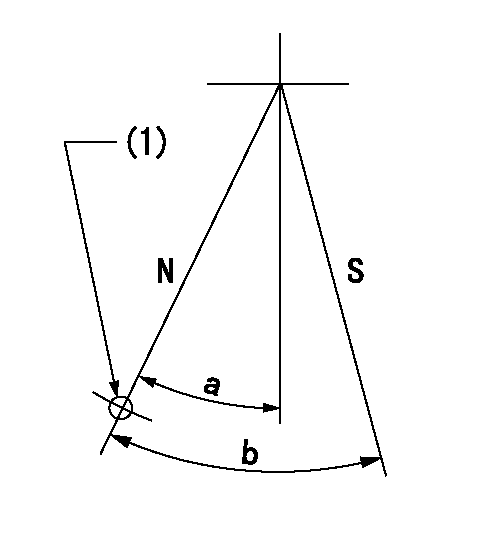
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
----------
aa=64mm
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=29deg+-5deg
----------
aa=64mm
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=29deg+-5deg
0000001501 FICD
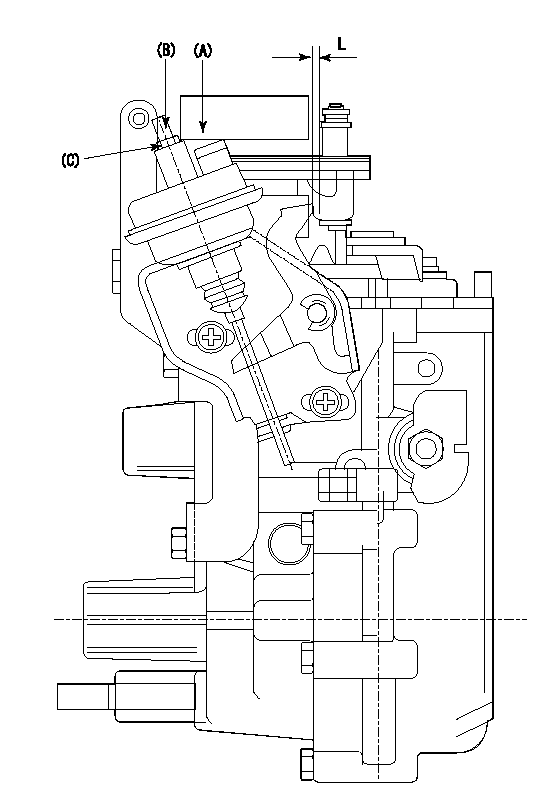
(A) applied negative pressure
(B) Screw
(c) Nut
1. Set the actuator as described below.
(1)Confirm that there is clearance between the actuator lever and the speed lever.
(2)Loosen the nut (C).
(3)Push in the screw (B).
(4)Apply P1 from the actuator (A) part.
(5)Pull out the screw (B) slowly.
(6)Tighten and fix the nut (C) when pump speed is Na and the rack position is Ra.
(7)Torque the nut (C) to T1.
(8)Apply P2 several times.
(9)Confirm that the actuator functions normally.
(10)Confirm that there is a clearance between the actuator lever and the speed lever at that time.
----------
P1=53.3kPa(400mmHg) P2=53.3kPa(400mmHg) Na=440r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm T1=1.2~1.6N-m(0.12~0.16kgf-m)
----------
L=(5)mm
----------
P1=53.3kPa(400mmHg) P2=53.3kPa(400mmHg) Na=440r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm T1=1.2~1.6N-m(0.12~0.16kgf-m)
----------
L=(5)mm
Timing setting
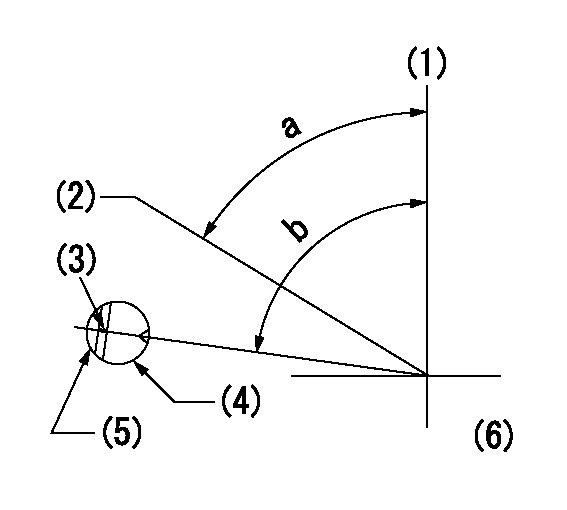
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear's standard threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)Stamping position on the A/T outer rim
(4)Pump bracket check hole position.
(5)At the No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection, align with the projection seen through the bracket's check hole and mark the A/T's bevel C1.
(6)B.T.D.C.: aa
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(60deg) b=(85deg)
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(60deg) b=(85deg)
Information:
The cylinder head is either water-cooled or air-cooled by fins in order to prevent overheating by the compression heat of the air compressor.The water-cooled type has coolant led from the oil cooler to cool cylinder head valves. Coolant is then returned to the rear end of the engine cylinder head.1.2 Pressure Governor
The pressure governor controls compressor operation to keep the air tank pressure within specified limits.To the high pressure valve of the diaphragm, the same air pressure as in the air tank acts always through the filter, thereby balancing with the adjusting spring force. When the pressure in the air tank increases to exceed that opening pressure of the high pressure valve, the air forces up the high pressure valve seat of the diaphragm. This causes increase of acting area so that the diaphragm moves up quickly to close the seat of the low pressure valve.When the low pressure valve is closed, air now flows through the valve body to force down the unloader valve of the air compressor, thereby stopping air supply to the air tank.As the air pressure in the air tank gradually drops, the diaphragm is forced down by the adjusting spring and the low pressure valve opens and the high pressure one closes. As a result, the air on the unloader side is exhausted through the exhaust hole and air supply to the air tank is resumed.2. Specifications
3. Service Standards
3.1 Service Standards Table
(1) Air Compressor (2) Pressure Governor 3.2 Tightening Torque Table
(1) Air compressor (2) Pressure governor 4. Special Tool
5. Service Procedure
5.1 Air Compressor
Removal and installation
The removal and installation procedures of the air compressor are same as those of the pump drive case. See Group 13 Fuel and Engine Control.Disassembly
Disassembly(1) Removal of suction valve holder Using special tool, Air Compressor Suction Valve Tool, remove the suction valve holder.(2) Removal of delivery valve holder (Air-cooled type only) Using special tool, Air Compressor Delivery Valve Tool, remove the delivery valve holder.(3) Removal of piston ring Using special tool, Piston Ring Tool, remove the piston ring.Inspection
Inspection(1) Piston to cylinder liner clearance Calculate the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the piston or cylinder liner.(2) Piston ring to ring groove clearance Measure the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the piston ring or piston. Measure over entire circumference of the piston.(3) Piston ring open end gap Fit the piston ring to a new cylinder liner or gauge and measure the open end gap. If the gap exceeds the limit, replace the ring. Push in the piston ring flat by the piston and measure.(4) Piston to piston pin clearance Calculate the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the piston or piston pin.(5) Piston to connecting rod clearance Calculate the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the piston pin or connecting rod.(6) Crankshaft pin to connecting rod bearing clearance Calculate the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the bearing.(7) Connecting rod end play If the end play exceeds the limit,
The pressure governor controls compressor operation to keep the air tank pressure within specified limits.To the high pressure valve of the diaphragm, the same air pressure as in the air tank acts always through the filter, thereby balancing with the adjusting spring force. When the pressure in the air tank increases to exceed that opening pressure of the high pressure valve, the air forces up the high pressure valve seat of the diaphragm. This causes increase of acting area so that the diaphragm moves up quickly to close the seat of the low pressure valve.When the low pressure valve is closed, air now flows through the valve body to force down the unloader valve of the air compressor, thereby stopping air supply to the air tank.As the air pressure in the air tank gradually drops, the diaphragm is forced down by the adjusting spring and the low pressure valve opens and the high pressure one closes. As a result, the air on the unloader side is exhausted through the exhaust hole and air supply to the air tank is resumed.2. Specifications
3. Service Standards
3.1 Service Standards Table
(1) Air Compressor (2) Pressure Governor 3.2 Tightening Torque Table
(1) Air compressor (2) Pressure governor 4. Special Tool
5. Service Procedure
5.1 Air Compressor
Removal and installation
The removal and installation procedures of the air compressor are same as those of the pump drive case. See Group 13 Fuel and Engine Control.Disassembly
Disassembly(1) Removal of suction valve holder Using special tool, Air Compressor Suction Valve Tool, remove the suction valve holder.(2) Removal of delivery valve holder (Air-cooled type only) Using special tool, Air Compressor Delivery Valve Tool, remove the delivery valve holder.(3) Removal of piston ring Using special tool, Piston Ring Tool, remove the piston ring.Inspection
Inspection(1) Piston to cylinder liner clearance Calculate the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the piston or cylinder liner.(2) Piston ring to ring groove clearance Measure the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the piston ring or piston. Measure over entire circumference of the piston.(3) Piston ring open end gap Fit the piston ring to a new cylinder liner or gauge and measure the open end gap. If the gap exceeds the limit, replace the ring. Push in the piston ring flat by the piston and measure.(4) Piston to piston pin clearance Calculate the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the piston or piston pin.(5) Piston to connecting rod clearance Calculate the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the piston pin or connecting rod.(6) Crankshaft pin to connecting rod bearing clearance Calculate the clearance and if it exceeds the limit, replace the bearing.(7) Connecting rod end play If the end play exceeds the limit,
