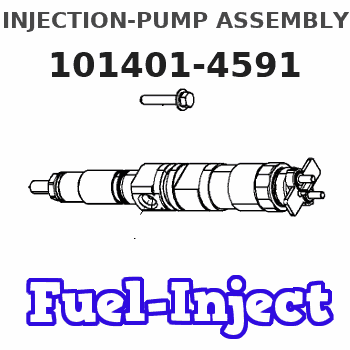
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 613 714
9400613714
ZEXEL
101401-4591
1014014591
ISUZU
8971140080
8971140080
Rating:
Service parts 101401-4591 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
8-97114-017-0
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
18.1{185}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 613 714
9400613714
ZEXEL
101401-4591
1014014591
ISUZU
8971140080
8971140080
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101401-4591
9 400 613 714
8971140080 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4HF1 * K
4HF1 * K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
4.1
4.05
4.15
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
12.6
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
75.4
73.8
77
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
285
285
285
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
15.5
14.2
16.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-10
10
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(12.6)
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
75.4
74.4
76.4
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.2
Pump speed
r/min
1600
1600
1600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
86.3
82.3
90.3
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
80
80
112
Fixing the lever
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1375--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1325
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1500
Advance angle
deg.
3.3
2.8
3.8
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1600--
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
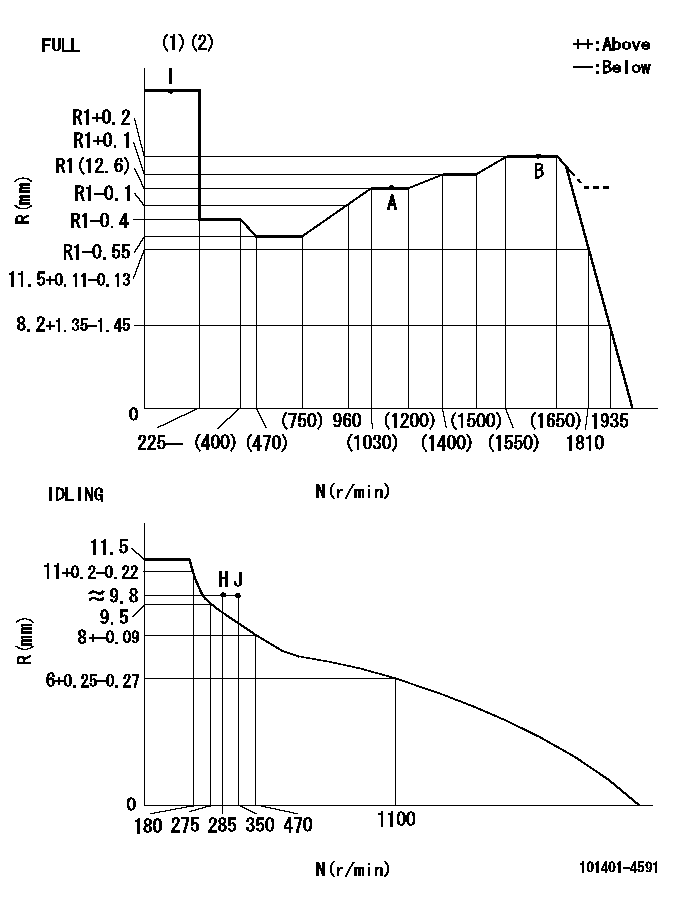
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerances for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
----------
T1=H96
----------
----------
T1=H96
----------
Speed control lever angle
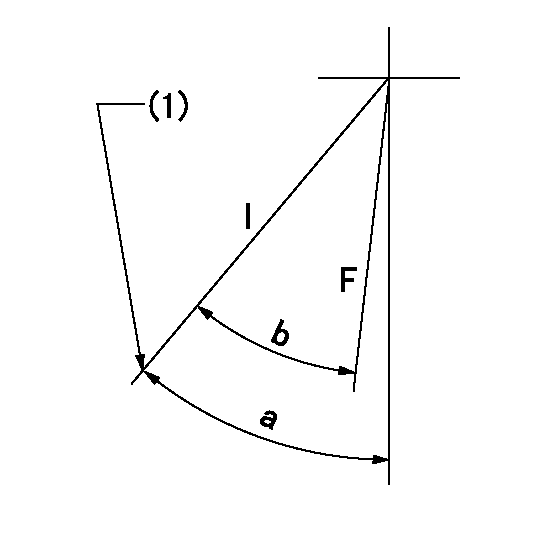
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
----------
a=41deg+-5deg b=35deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=41deg+-5deg b=35deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
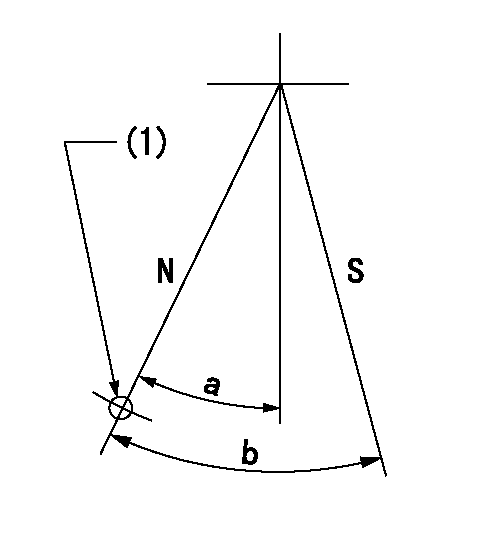
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
----------
aa=64mm
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=29deg+-5deg
----------
aa=64mm
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=29deg+-5deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=1100r/min Ra=8.9+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=1100r/min Ra=8.9+-0.1mm
----------
0000001601 FICD
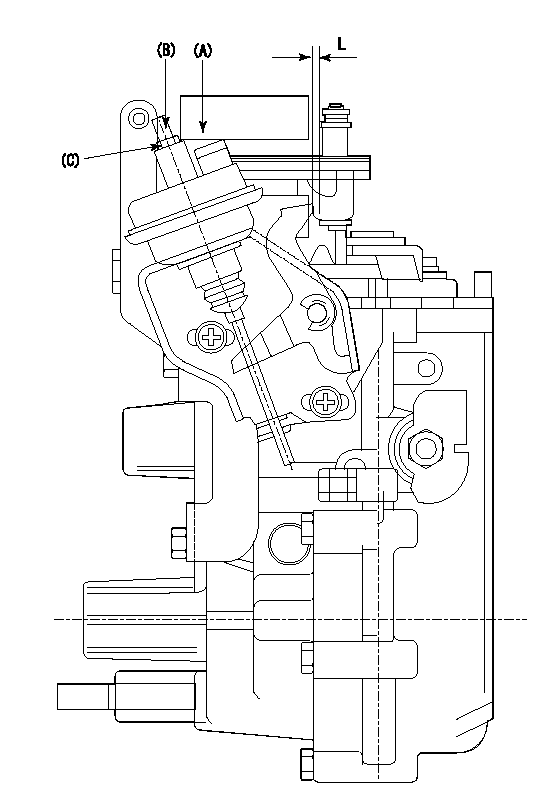
(A) applied negative pressure
(B) Screw
(c) Nut
1. Set the actuator as described below.
(1)Confirm that there is clearance between the actuator lever and the speed lever.
(2)Loosen the nut (C).
(3)Push in the screw (B).
(4)Apply P1 from the actuator (A) part.
(5)Pull out the screw (B) slowly.
(6)Tighten and fix the nut (C) when pump speed is Na and the rack position is Ra.
(7)Torque the nut (C) to T1.
(8)Apply P2 several times.
(9)Confirm that the actuator functions normally.
(10)Confirm that there is a clearance between the actuator lever and the speed lever at that time.
----------
P1=53.3kPa(400mmHg) P2=53.3kPa(400mmHg) Na=440r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm T1=1.2~1.6N-m(0.12~0.16kgf-m)
----------
L=(5)mm
----------
P1=53.3kPa(400mmHg) P2=53.3kPa(400mmHg) Na=440r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm T1=1.2~1.6N-m(0.12~0.16kgf-m)
----------
L=(5)mm
Timing setting
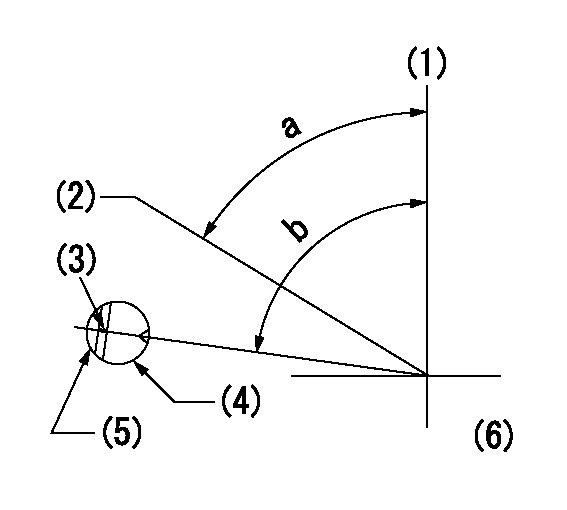
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear's standard threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)Stamping position on the A/T outer rim
(4)Pump bracket check hole position.
(5)At the No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection, align with the projection seen through the bracket's check hole and mark the A/T's bevel C1.
(6)B.T.D.C.: aa
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(60deg) b=(85deg)
----------
aa=10deg
----------
a=(60deg) b=(85deg)
Information:
Coolant is essential to control engine operating temperatures and make components last longer. Poorly maintained coolant can actually shorten component life by causing a chain reaction of heat problems. Excessive heat can cause: * Hot spots that crack steel, notably in cylinder heads* Bubble pockets that form on cylinder surfaces and result in liner pitting* Oil to degrade, leading to component damage* Lacquer and shellac build up on precision hydraulic parts* Oil additives to break down and transmission clutches to slipS O S Coolant Analysis is the best way to monitor the condition of your coolant and your cooling system. The two level program, based on samples you submit, shows the condition of coolant and the cooling system.Level I: Basic Coolant Maintenance Check
Checks for correct chemical balance for proper heat and corrosion control. Tests for: * glycol* SCA concentrations* pH* conductivityS O S Coolant Analysis reports results and makes recommendations, usually within 24 hours.The concentration of SCA should be checked regularly for overconcentration or underconcentration. This should be done with test kits, or S O S Coolant Analysis (Level I) at the Every 250 Service Hours interval.Further coolant analysis is recommended at twice a year or after every 1000 service hours.For example, suppose considerable deposits are found in the water jacket areas on the external cooling system, yet coolant additive concentrations were carefully maintained. Chances are that the coolant water had minerals which deposited on the engine over time.One way to verify the water condition, or to be sure of new water at fill time, is to have a coolant analysis conducted. Full water analysis can sometimes be obtained locally by contacting your local water utility company or an agricultural agent. Private laboratories are also available.Caterpillar recommends S O S Level II Coolant Analysis.Level II: Comprehensive Cooling System Analysis
Completely analyzes coolant and coolant effects on the cooling system. Level II Analysis provides: * full Level I analysis* visual properties inspection* metal corrosion and contaminant identification* identification of built up impurities that point to corrosion and scaling problems BEFORE they lead to costly repairs.Level II Analysis provides a simple, clear report of results, and makes recommendations for the lowest cost corrective options.For more information of coolant analysis and how it can help manage your equipment, see your Caterpillar dealer. Consult your Caterpillar dealer for complete information and assistance in establishing an S O S analysis program for your engine(s).
Checks for correct chemical balance for proper heat and corrosion control. Tests for: * glycol* SCA concentrations* pH* conductivityS O S Coolant Analysis reports results and makes recommendations, usually within 24 hours.The concentration of SCA should be checked regularly for overconcentration or underconcentration. This should be done with test kits, or S O S Coolant Analysis (Level I) at the Every 250 Service Hours interval.Further coolant analysis is recommended at twice a year or after every 1000 service hours.For example, suppose considerable deposits are found in the water jacket areas on the external cooling system, yet coolant additive concentrations were carefully maintained. Chances are that the coolant water had minerals which deposited on the engine over time.One way to verify the water condition, or to be sure of new water at fill time, is to have a coolant analysis conducted. Full water analysis can sometimes be obtained locally by contacting your local water utility company or an agricultural agent. Private laboratories are also available.Caterpillar recommends S O S Level II Coolant Analysis.Level II: Comprehensive Cooling System Analysis
Completely analyzes coolant and coolant effects on the cooling system. Level II Analysis provides: * full Level I analysis* visual properties inspection* metal corrosion and contaminant identification* identification of built up impurities that point to corrosion and scaling problems BEFORE they lead to costly repairs.Level II Analysis provides a simple, clear report of results, and makes recommendations for the lowest cost corrective options.For more information of coolant analysis and how it can help manage your equipment, see your Caterpillar dealer. Consult your Caterpillar dealer for complete information and assistance in establishing an S O S analysis program for your engine(s).
Have questions with 101401-4591?
Group cross 101401-4591 ZEXEL
Isuzu
101401-4591
9 400 613 714
8971140080
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4HF1
4HF1
