Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101401-4400
1014014400
ISUZU
8970613920
8970613920
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101401-4400
1014014400
ISUZU
8970613920
8970613920
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
134424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Left L
Left L
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.8
3.75
3.85
Rack position
Point A R=A
Point A R=A
Beginning of injection position
Governor side NO.1
Governor side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
13.3
Pump speed
r/min
1200
1200
1200
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
92.5
90.9
94.1
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
Z
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10.5
9.2
11.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(13.3)
Pump speed
r/min
1200
1200
1200
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
92.5
91.5
93.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
50
50
Boost pressure
mmHg
375
375
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.15
Pump speed
r/min
1450
1450
1450
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
94.5
90.5
98.5
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
50
50
Boost pressure
mmHg
375
375
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R2-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
75
71
79
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
55
55
87
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
R2-0.5
Boost pressure
kPa
23.3
22
24.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
175
165
185
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
700
700
700
Rack position
R2[R1-0.
6]
Boost pressure
kPa
40
36.7
43.3
Boost pressure
mmHg
300
275
325
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1250--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1200
Advance angle
deg.
0.5
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1450
Advance angle
deg.
3.8
3.3
4.3
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
-
Advance angle
deg.
4
3.5
4.5
Remarks
Measure the actual speed, stop
Measure the actual speed, stop
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
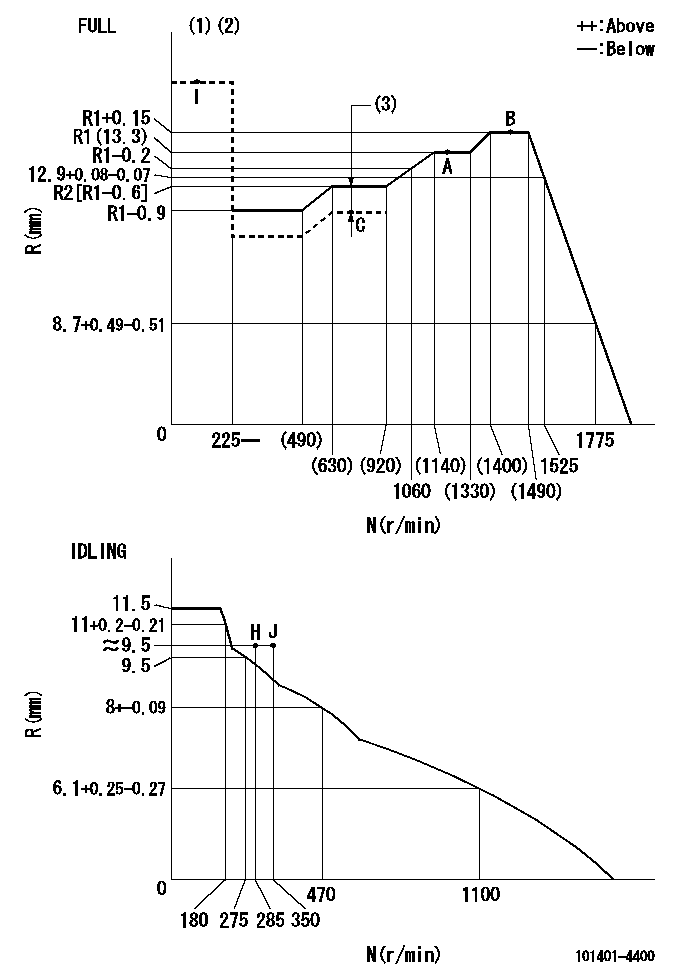
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Boost compensator stroke: BCL
----------
T1=H76 BCL=0.5+-0.1mm
----------
----------
T1=H76 BCL=0.5+-0.1mm
----------
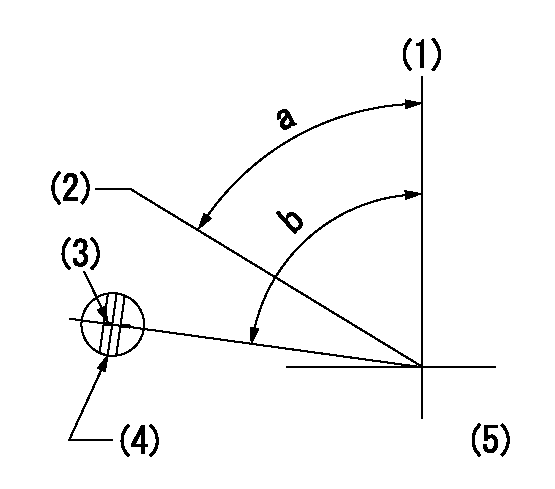
Speed control lever angle
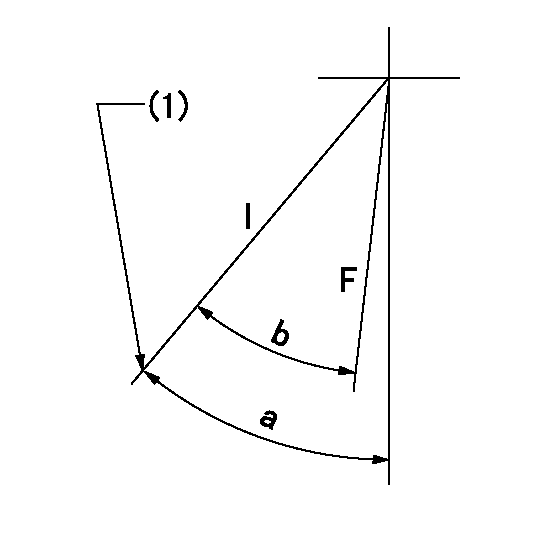
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=43deg+-5deg b=31deg+-3deg
----------
----------
a=43deg+-5deg b=31deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
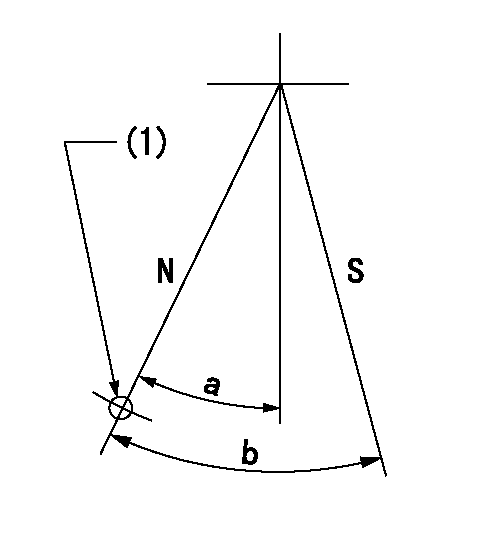
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Use the hole at R = aa
----------
aa=64mm
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=29deg+-5deg
----------
aa=64mm
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=29deg+-5deg
0000001501 MICRO SWITCH
Adjustment of the micro-switch
Adjust the bolt to obtain the following lever position when the micro-switch is ON.
(1)Speed N1
(2)Rack position Ra
----------
N1=1100r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm
----------
----------
N1=1100r/min Ra=9.2+-0.1mm
----------
0000001601 FICD
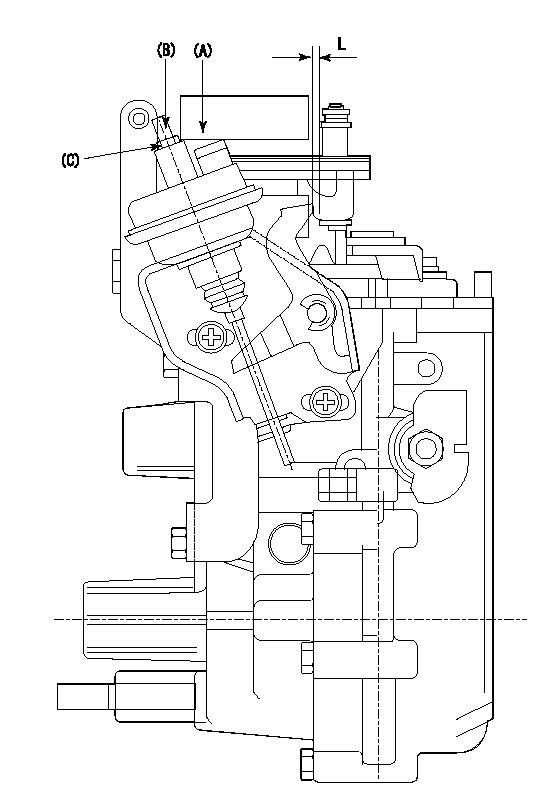
(A) applied negative pressure
(B) Screw
(c) Nut
1. Set the actuator as described below.
(1)Confirm that there is clearance between the actuator lever and the speed lever.
(2)Loosen the nut (C).
(3)Push in the screw (B).
(4)Apply P1 from the actuator (A) part.
(5)Pull out the screw (B) slowly.
(6)Tighten and fix the nut (C) when pump speed is Na and the rack position is Ra.
(7)Torque the nut (C) to T1.
(8)Apply P2 several times.
(9)Confirm that the actuator functions normally.
(10)Confirm that there is a clearance between the actuator lever and the speed lever at that time.
----------
P1=53.3kPa(400mmHg) P2=53.3kPa(400mmHg) Na=475r/min Ra=9.55+-0.1mm T1=1.2~1.6N-m(0.12~0.16kgf-m)
----------
L=(2)mm
----------
P1=53.3kPa(400mmHg) P2=53.3kPa(400mmHg) Na=475r/min Ra=9.55+-0.1mm T1=1.2~1.6N-m(0.12~0.16kgf-m)
----------
L=(2)mm
Timing setting
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear's standard threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)Stamping position on the A/T outer rim
(4)At the No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection, align with the aligning mark seen through the bracket's check hole and mark the A/T's bevel C1.
(5)B.T.D.C.: aa
----------
aa=9deg
----------
a=(60deg) b=(85deg)
----------
aa=9deg
----------
a=(60deg) b=(85deg)
Information:
Voltage Regulator and Generator
Clean and Inspect
Before working inside the generator, make sure that the starter motor can not be activated by any automatic or manual signal.When the engine-generator is operating, voltages up to 600V are present in these areas near or on the regulator:1. The regulator terminal strip2. The excitation transformer terminal strip (self-excited generator only).Do not short these terminals to ground with any part of the body or any conductive material. Loss of life or injury could result from electrical shock or injury from molten metal.An electrical shock can be received from the regulator capacitor (C1) when the engine-generator is not in operation. To avoid possible injury, discharge the stored charge using an 100 ohm resistor across C1 terminals.
Electronic components in the regulator can be damaged during generator operation if contact is made between the part and ground.
If Moisture is allowed to remain in contact with an electrical winding, some of the moisture will eventually be absorbed. This will lower the resistance of the winding insulation. The insulation used on the windings of Caterpillar generators is moisture resistant, but constant exposure to moisture will gradually lower the insulation's resistance.Dirt can make the problem worse because it can hold the moisture in contact with the insulation. Salt (from sea air) can also make the problem much worse. This is because salt tends to absorb moisture from the air. When the salt and moisture combine, they make a good electrical conductor.Clean the voltage regulator and generator of dirt and debris. Use a brush to loosen accumulations of dirt and a vacuum system for removal. Use of compressed air is not recommended, because of moisture present in the form of condensate.Carbon tracking on insulators can be caused by dirt or loose connections. These carbon paths must be cleaned or the insulators replaced. Failure to correct a carbon tracking problem will eventually result in a short in the electrical circuit.Visually check for loose or broken wires and connections. Check the wires and connections on the regulator assembly. Check that all circuit boards are fully plugged in their sockets. Check all wires and connections in the generator. Make any necessary repairs to the wiring as required. Refer to the "Electric Set Generator Service Manual" for testing and adjusting or disassembly and assembly procedures.Space Heaters
The SR4 generator can operate in high humidity conditions without problems. However, problems can occur when the generator is idle and the surrounding air is warmer than the generator. Moisture can form on the windings and result in poor performance and even result in damage to the windings. Whenever the generator is not in use, insure that the space heaters are in operation.An external source of either 115 or 230 (200 v at 50 Hz) volts A.C. is required to operate the space heaters. Space Heater Connection to External Source H1, H2, H3, H4. Terminal Strip Terminals If 115 VAC source is available, connect
Clean and Inspect
Before working inside the generator, make sure that the starter motor can not be activated by any automatic or manual signal.When the engine-generator is operating, voltages up to 600V are present in these areas near or on the regulator:1. The regulator terminal strip2. The excitation transformer terminal strip (self-excited generator only).Do not short these terminals to ground with any part of the body or any conductive material. Loss of life or injury could result from electrical shock or injury from molten metal.An electrical shock can be received from the regulator capacitor (C1) when the engine-generator is not in operation. To avoid possible injury, discharge the stored charge using an 100 ohm resistor across C1 terminals.
Electronic components in the regulator can be damaged during generator operation if contact is made between the part and ground.
If Moisture is allowed to remain in contact with an electrical winding, some of the moisture will eventually be absorbed. This will lower the resistance of the winding insulation. The insulation used on the windings of Caterpillar generators is moisture resistant, but constant exposure to moisture will gradually lower the insulation's resistance.Dirt can make the problem worse because it can hold the moisture in contact with the insulation. Salt (from sea air) can also make the problem much worse. This is because salt tends to absorb moisture from the air. When the salt and moisture combine, they make a good electrical conductor.Clean the voltage regulator and generator of dirt and debris. Use a brush to loosen accumulations of dirt and a vacuum system for removal. Use of compressed air is not recommended, because of moisture present in the form of condensate.Carbon tracking on insulators can be caused by dirt or loose connections. These carbon paths must be cleaned or the insulators replaced. Failure to correct a carbon tracking problem will eventually result in a short in the electrical circuit.Visually check for loose or broken wires and connections. Check the wires and connections on the regulator assembly. Check that all circuit boards are fully plugged in their sockets. Check all wires and connections in the generator. Make any necessary repairs to the wiring as required. Refer to the "Electric Set Generator Service Manual" for testing and adjusting or disassembly and assembly procedures.Space Heaters
The SR4 generator can operate in high humidity conditions without problems. However, problems can occur when the generator is idle and the surrounding air is warmer than the generator. Moisture can form on the windings and result in poor performance and even result in damage to the windings. Whenever the generator is not in use, insure that the space heaters are in operation.An external source of either 115 or 230 (200 v at 50 Hz) volts A.C. is required to operate the space heaters. Space Heater Connection to External Source H1, H2, H3, H4. Terminal Strip Terminals If 115 VAC source is available, connect