Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 611 783
9400611783
ZEXEL
101401-2314
1014012314
HINO
220204501A
220204501a
Rating:
Service parts 101401-2314 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
23600-2601A
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 611 783
9400611783
ZEXEL
101401-2314
1014012314
HINO
220204501A
220204501a
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101401-2314
9 400 611 783
220204501A HINO
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
W04D-T K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
W04D-T K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
101401-2314
9 400 611 783
S220204501 HINO
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
W04D-T A K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
W04D-T A K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
134424-0920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
162
147
177
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.65
1.5
1.8
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.2
3.17
3.23
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.75 90.25
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.75 180.25
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.75 270.25
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
12.8
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
115
113
117
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-3
3
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Boost pressure
kPa
78.6
78.6
Boost pressure
mmHg
590
590
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
9+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
405
405
405
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9
7.5
10.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Boost pressure
kPa
0
0
0
Boost pressure
mmHg
0
0
0
Boost compensator adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Rack position
R1-1.85
Boost pressure
kPa
16
13.3
18.7
Boost pressure
mmHg
120
100
140
Boost compensator adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
900
900
900
Rack position
R1(12.8)
Boost pressure
kPa
65.3
58.6
72
Boost pressure
mmHg
490
440
540
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1275--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Load
1/4
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1225
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Load
1/4
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
-
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Load
4/4
Remarks
Measure speed (beginning of operation).
Measure speed (beginning of operation).
Timer adjustment_04
Pump speed
r/min
1450
Advance angle
deg.
3.25
2.95
3.55
Load
4/4
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
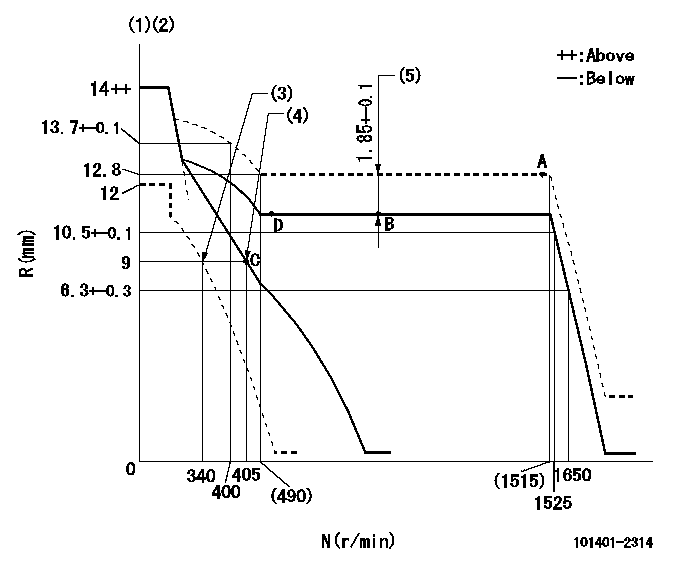
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)Set idle sub-spring
(4)Main spring setting
(5)Boost compensator stroke
----------
K=10
----------
----------
K=10
----------
Speed control lever angle
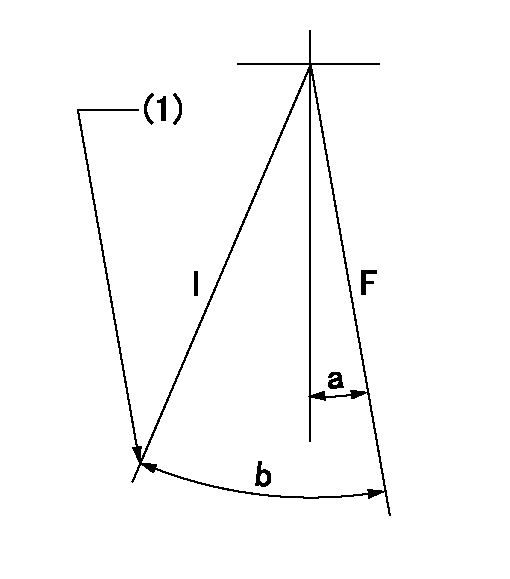
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=10deg+-5deg b=26deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
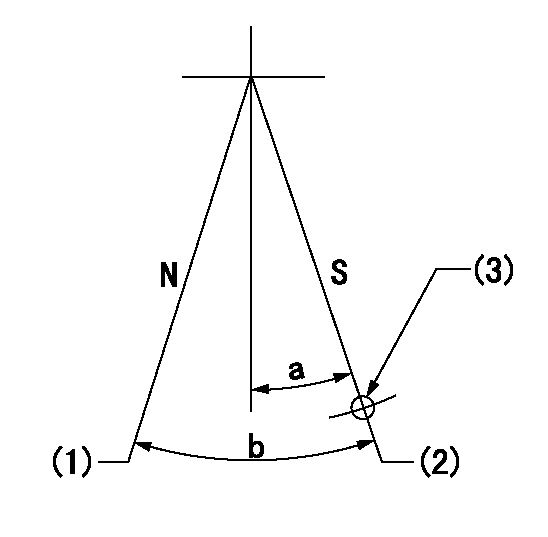
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Normal
(2)Pump speed aa and rack position bb (to be sealed at delivery)
(3)Use the hole above R = cc
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.5mm cc=25mm
----------
a=21deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
----------
aa=0r/min bb=1-0.5mm cc=25mm
----------
a=21deg+-5deg b=(55deg)
Timing setting
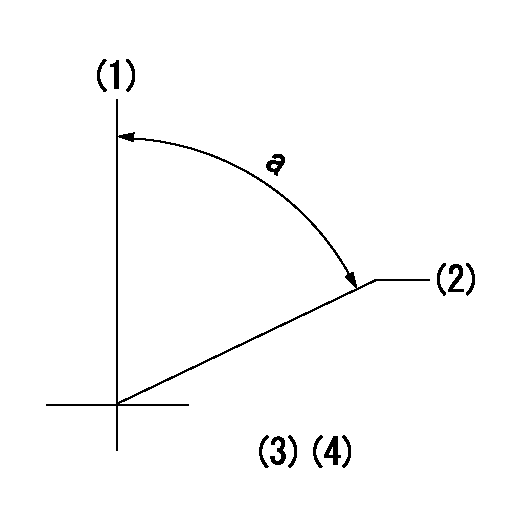
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear's standard threaded hole at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(70deg)
----------
----------
a=(70deg)
Information:
6. Coat the seal of the element with a thin film of clean engine oil or antifreeze. 7. Install the element. Tighten it until the seal contacts the base, then tighten it an additional 3/4 turn. 8. Open the inlet valve and the outlet valve. 9. Maintain the coolant level above the low level plate. 10. Clean and install the radiator cap.11. Start the engine and check for leaks.Brakes
Inspect - Adjust
The machine must be level, the bowl lowered, and the parking brake applied.1. Block the wheels securely.2. Start the engine. 3. When the air pressure reaches the NORMAL range, stop the engine. 4. Release the parking/emergency brake. 5. Measure the distance from the rotochamber to the slack adjuster clevis retaining pin. 6. Apply the service brake and measure the amount of travel of the rod. If the travel is 76 mm (3 inches) or more, adjust the brake.7. Measure the brake rotochamber rod travel of all four wheel brakes. Scraper rotochambers are located inside the push frame.To Adjust
1. Loosen the adjustment locking bolt. 2. Turn the adjusting bolt, as required, until the travel is 41 mm (1.62 inches). 3. Tighten the locking bolt. 4. Apply and release the brakes, watching the rotochamber rod for binding.5. Observe the diaphragm for leaks. 6. Start the engine and allow air pressure to reach 690 kPa (100 psi) or in the green range on the air pressure gauge.7. Apply the parking brake.8. Stop the engine.9. Remove the blocking from the wheels.Check the Air System for Leaks
1. Start the engine and allow air pressure to reach 690 kPa (100 psi) or in the green range on the air pressure gauge. 2. Apply the service brakes and hold them in the applied condition.3. Stop the engine.4. With the brakes applied, watch the air pressure gauge.5. The pressure should drop no more than 35 kPa (5 psi) in 10 minutes.6. If the air pressure loss is greater than 35 kPa (5 psi), inspect the air lines and connections. Make any necessary repairs.To Test Brakes
Be sure the area around the vehicle is clear of personnel and obstructions.Fasten the seat belt before operating the vehicle.Test the brakes on a dry, level surface.
The vehicle must be on a dry, level surface, the bowl lowered and the parking brake applied.The following tests are to determine if the service brake or parking/emergency brake is functional. These tests are not intended to measure maximum brake holding effort.Brake holding effort required to hold a vehicle at a specific engine rpm will vary from vehicle to vehicle due to differences in engine setting, power train efficiency, etc., as well as differences in brake holding ability.Engine rpm at beginning of vehicle movement, with service or parking/emergency brake applied, should be compared against the engine rpm your specific vehicle was able to hold on a prior test, as an indication of system deterioration.Service Brake
1. Start the engine. Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.2. When air pressure registers 690 kPa (100 psi) or
Inspect - Adjust
The machine must be level, the bowl lowered, and the parking brake applied.1. Block the wheels securely.2. Start the engine. 3. When the air pressure reaches the NORMAL range, stop the engine. 4. Release the parking/emergency brake. 5. Measure the distance from the rotochamber to the slack adjuster clevis retaining pin. 6. Apply the service brake and measure the amount of travel of the rod. If the travel is 76 mm (3 inches) or more, adjust the brake.7. Measure the brake rotochamber rod travel of all four wheel brakes. Scraper rotochambers are located inside the push frame.To Adjust
1. Loosen the adjustment locking bolt. 2. Turn the adjusting bolt, as required, until the travel is 41 mm (1.62 inches). 3. Tighten the locking bolt. 4. Apply and release the brakes, watching the rotochamber rod for binding.5. Observe the diaphragm for leaks. 6. Start the engine and allow air pressure to reach 690 kPa (100 psi) or in the green range on the air pressure gauge.7. Apply the parking brake.8. Stop the engine.9. Remove the blocking from the wheels.Check the Air System for Leaks
1. Start the engine and allow air pressure to reach 690 kPa (100 psi) or in the green range on the air pressure gauge. 2. Apply the service brakes and hold them in the applied condition.3. Stop the engine.4. With the brakes applied, watch the air pressure gauge.5. The pressure should drop no more than 35 kPa (5 psi) in 10 minutes.6. If the air pressure loss is greater than 35 kPa (5 psi), inspect the air lines and connections. Make any necessary repairs.To Test Brakes
Be sure the area around the vehicle is clear of personnel and obstructions.Fasten the seat belt before operating the vehicle.Test the brakes on a dry, level surface.
The vehicle must be on a dry, level surface, the bowl lowered and the parking brake applied.The following tests are to determine if the service brake or parking/emergency brake is functional. These tests are not intended to measure maximum brake holding effort.Brake holding effort required to hold a vehicle at a specific engine rpm will vary from vehicle to vehicle due to differences in engine setting, power train efficiency, etc., as well as differences in brake holding ability.Engine rpm at beginning of vehicle movement, with service or parking/emergency brake applied, should be compared against the engine rpm your specific vehicle was able to hold on a prior test, as an indication of system deterioration.Service Brake
1. Start the engine. Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.2. When air pressure registers 690 kPa (100 psi) or
Have questions with 101401-2314?
Group cross 101401-2314 ZEXEL
Hino
Hino
101401-2314
9 400 611 783
220204501A
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
W04D-T
W04D-T
101401-2314
9 400 611 783
S220204501
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
W04D-T
W04D-T