Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 612 486
9400612486
ZEXEL
101401-1853
1014011853
MITSUBISHI
ME217182
me217182
Rating:
Service parts 101401-1853 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
ME016655
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6{220}
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 612 486
9400612486
ZEXEL
101401-1853
1014011853
MITSUBISHI
ME217182
me217182
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101401-1853
9 400 612 486
ME217182 MITSUBISHI
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4D34T K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
4D34T K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4620
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
255
221
289
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.25
2.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
255
255
255
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
2.6
2.6
2.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.5
3.45
3.55
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.8
Pump speed
r/min
1025
1025
1025
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
77.5
76.5
78.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
7.8+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
495
495
495
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
8
6.7
9.3
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Remarks
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Adjust only variation between cylinders; adjust governor according to governor specifications.
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
10.4++
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
115
115
120
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
0
Advance angle
deg.
2.5
2
3
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
-
Advance angle
deg.
2.5
2
3
Remarks
Measure speed (beginning of operation).
Measure speed (beginning of operation).
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
730+-25
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
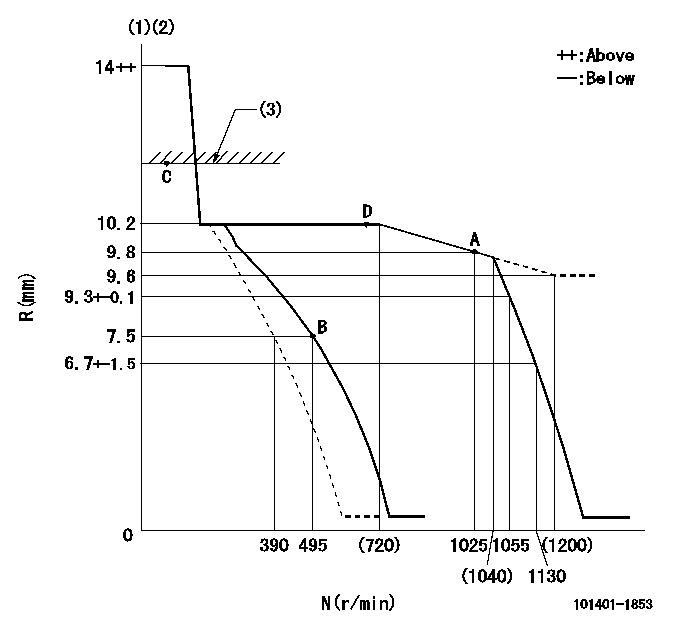
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Notch fixed: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
----------
K=19
----------
----------
K=19
----------
Speed control lever angle
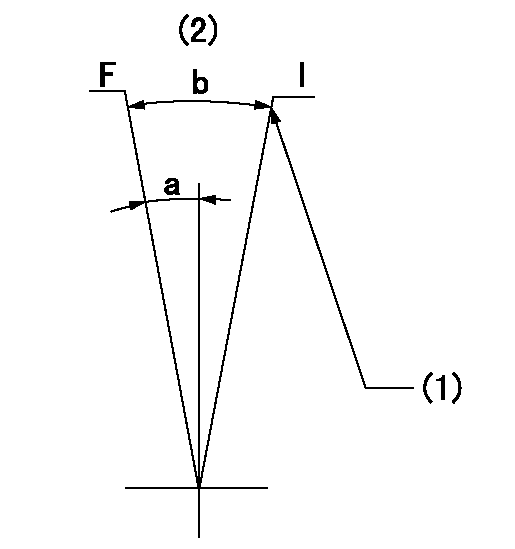
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
(2)Base lever only
----------
----------
a=(10deg)+-5deg b=(20deg)+-5deg
----------
----------
a=(10deg)+-5deg b=(20deg)+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Normal
----------
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=26.5deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark '3' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=12deg
----------
a=(130deg)
----------
aa=12deg
----------
a=(130deg)
Information:
3306 New Scroll Fuel System (NSFS) Hydraulic Actuator
The variable power actuator is mounted to the rear of the governor housing, where the shutoff solenoid is normally mounted. The actuator rod may be in one of two positions -- extended or retracted. The extended position limits the fuel rack travel to the lower power fuel setting. The retracted position allows the fuel rack to travel to the higher power fuel setting. By limiting the travel of the fuel rack, the fuel being injected into the engine is controlled. Fuel being injected into the engine determines the output power of the engine. The position of the actuator rod is determined by the gear engaged in the transmission of the applicable vehicle.High Power Range
Typical Variable Power Arrangement
1. Manifold. 2. Solenoid control valve. 3. Variable power actuator. 4. Governor control lever. 5. Transmission. 6. Switch.An electric switch (6) is mounted in the transmission (5). The transmission (5) is shifted into a gear where the higher power range is allowed. A transmission interlock pin causes the normally open switch (6) to close. When switch (6) is closed, it energizes solenoid control valve (2). The energized solenoid control valve (2) allows engine lube oil (under normal engine lube oil pressure) to flow through manifold (1) and into actuator (3).
Governor And Actuator
3. Actuator. 7. Oil inlet/outlet port. 11. Governor servo valve. 12. Lever. 13. Governor control shaft. 14. Actuator rod.The engine oil coming in port (7) compresses spring (15) and moves actuator rod (14) to the RETRACTED position. The RETRACTED actuator rod (14) allows the fuel rack more travel in the FUEL ON direction by a mechanical linkage through the governor servo valve (11) and lever (12). The fuel rack travel is now limited by the fuel setting screw.The actuator rod (14) will remain in the RETRACTED position as long as solenoid control valve (2) is energized. A light on the operator's console indicates when the engine is operating in the higher power range.
Governor And Variable Power Actuator (Retracted Position7. Oil inlet/outlet port.8. Washered adjusting
The variable power actuator is mounted to the rear of the governor housing, where the shutoff solenoid is normally mounted. The actuator rod may be in one of two positions -- extended or retracted. The extended position limits the fuel rack travel to the lower power fuel setting. The retracted position allows the fuel rack to travel to the higher power fuel setting. By limiting the travel of the fuel rack, the fuel being injected into the engine is controlled. Fuel being injected into the engine determines the output power of the engine. The position of the actuator rod is determined by the gear engaged in the transmission of the applicable vehicle.High Power Range
Typical Variable Power Arrangement
1. Manifold. 2. Solenoid control valve. 3. Variable power actuator. 4. Governor control lever. 5. Transmission. 6. Switch.An electric switch (6) is mounted in the transmission (5). The transmission (5) is shifted into a gear where the higher power range is allowed. A transmission interlock pin causes the normally open switch (6) to close. When switch (6) is closed, it energizes solenoid control valve (2). The energized solenoid control valve (2) allows engine lube oil (under normal engine lube oil pressure) to flow through manifold (1) and into actuator (3).
Governor And Actuator
3. Actuator. 7. Oil inlet/outlet port. 11. Governor servo valve. 12. Lever. 13. Governor control shaft. 14. Actuator rod.The engine oil coming in port (7) compresses spring (15) and moves actuator rod (14) to the RETRACTED position. The RETRACTED actuator rod (14) allows the fuel rack more travel in the FUEL ON direction by a mechanical linkage through the governor servo valve (11) and lever (12). The fuel rack travel is now limited by the fuel setting screw.The actuator rod (14) will remain in the RETRACTED position as long as solenoid control valve (2) is energized. A light on the operator's console indicates when the engine is operating in the higher power range.
Governor And Variable Power Actuator (Retracted Position7. Oil inlet/outlet port.8. Washered adjusting
Have questions with 101401-1853?
Group cross 101401-1853 ZEXEL
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
101401-1853
9 400 612 486
ME217182
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4D34T
4D34T
