Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 613 580
9400613580
ZEXEL
101401-0830
1014010830
ISUZU
8943287690
8943287690
Rating:
Service parts 101401-0830 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
11.
Nozzle and Holder
8-94447-686-0
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
21.6(220)
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 613 580
9400613580
ZEXEL
101401-0830
1014010830
ISUZU
8943287690
8943287690
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
101401-0830
9 400 613 580
8943287690 ISUZU
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4BD1 * K
4BD1 * K
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Rack position
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69.9
68.3
71.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9.7
8.4
11
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11)
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69.9
68.9
70.9
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1
Pump speed
r/min
1600
1600
1600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
76.2
73
79.4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1-0.1
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
53.2
50
56.4
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
88.5
88.5
96.5
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1375--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1325
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1575
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
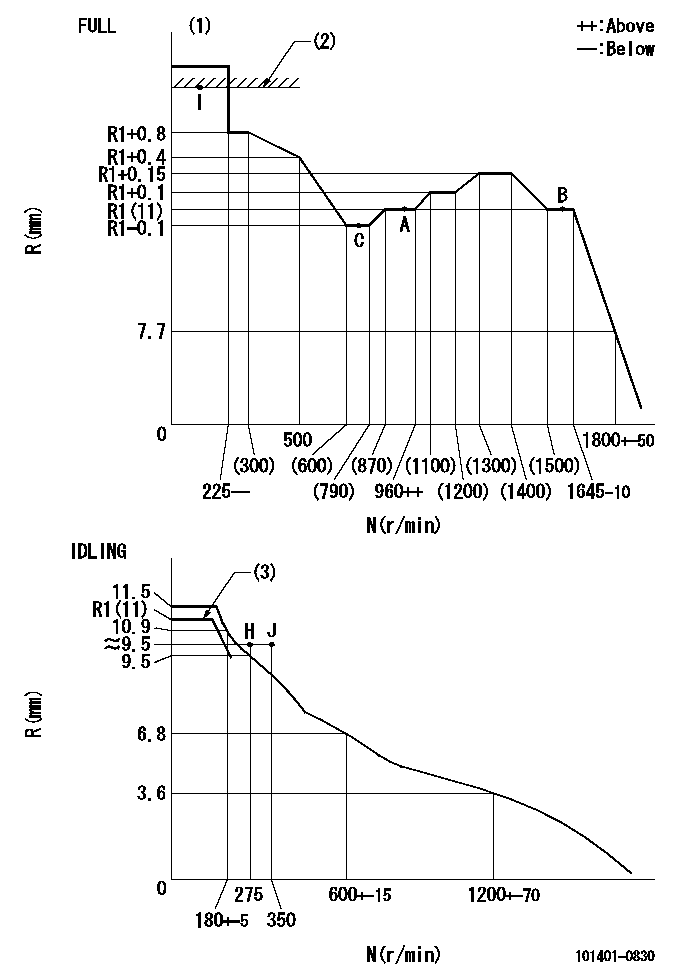
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
(3)At delivery (at R = A, N = N1)
----------
T1=D31 N1=100r/min
----------
----------
T1=D31 N1=100r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
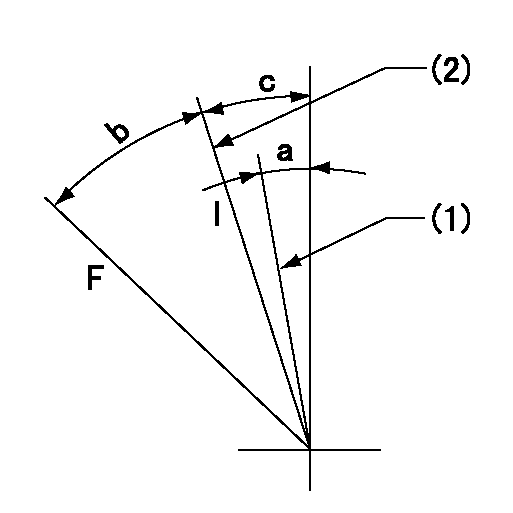
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Set the idle side stopper bolt so that R = aa (at delivery).
(2)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
----------
aa=R1(11)mm
----------
a=(1.5)deg b=42deg+-3deg c=2.5deg+-5deg
----------
aa=R1(11)mm
----------
a=(1.5)deg b=42deg+-3deg c=2.5deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark 'CC' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=14deg
----------
a=(100deg)
----------
aa=14deg
----------
a=(100deg)
Information:
Preparation for Inspection
Perform the following checks prior to inspection.(1) Make sure the engine oil, air cleaner, starter and battery are normal.(2) Make sure the engine is warm.Inspection
(1) Move the control lever to the top position.(2) Remove all glow plugs, then connect Compression Gauge Adapter (ST333060) and compression gauge to the cylinder whose compression is to be checked.
Compression gauge and adapter(3) Crank the engine using the starter until the needle of the compression gauge stops moving, then read the pressure indication.
Measuring compression pressure(4) If the measurement is lower than the specified limit, perform an overhaul.
(a) Measure the compression pressure of every cylinder. Measuring the compression pressure of two or three cylinders and simply assuming the compression pressures of the other cylinders is dangerous.(b) The compression pressure varies with the engine speed, so it is important to take all measurements with the same engine speed.
2Unit: MPa {kgf/cm} (psi) Take measurements with an engine speed of 240 min-1.
(a) It is important to measure compression pressures regularly and to keep track of changes in them.(b) During the engine's run-in period and after an overhaul, the compression pressures will increase slightly as the piston rings, valve seats, and other parts fit snugly in position. The Pressures will then decrease as parts wear.
Troubleshooting
Overview
Diesel-engine fault symptoms tend to have multiple causes, which influence each other. Consequently, it is often difficult to locate a fault based on the symptoms. Particular care is required when diagnosing faults related to the injection pump, injectors, and compression pressures since such faults may produce the same symptoms.For the above-mentioned reasons, the inspection sequences in the troubleshooting charts on the following pages start with items where the likelihood of a fault is greatest or with items that are easiest to inspect.Owing to their structure and combustion method, diesel engines exhibit the characteristics listed below. Familiarize yourself with these characteristics before performing troubleshooting operations.* Distinctive combustion noise (diesel knock) is emitted during normal operation.* Some black smoke is emitted during high-load operation.* Torque vibration is significant owing to the high compression pressure and high torque.* Slight hunting occurs during rapid deceleration.* Some white smoke is emitted immediately after startup when the engine is cold.
(a) The injection pump cannot be adjusted without a pump tester. Do not attempt to adjust or disassemble the injection pump during troubleshooting operations.(b) To check the combustion conditions in each cylinder, undo the cylinder's injection pipes one at a time (undoing an injection pipe stops injection in that cylinder) and compare the resulting decreases in engine speed. Retighten each injection pipe before undoing the next one.
Difficult Starting
(1) Items to Check
Before performing inspections, check for the following problems:* Clogged air cleaner element* Coagulation of engine oil* Inferior fuel* Low cranking speed(2) Inspection
Knocking
Diesel engines emit a distinctive knocking sound owing to their combustion method. This sound is normal unless it is excessive(1) Items to Check
Before performing inspections, check for the following problems:* Clogged air cleaner element* Inferior fuel(2) Inspection
Overheating
(1) Items to Check
Before performing inspections, check for the following problems:* Low
Perform the following checks prior to inspection.(1) Make sure the engine oil, air cleaner, starter and battery are normal.(2) Make sure the engine is warm.Inspection
(1) Move the control lever to the top position.(2) Remove all glow plugs, then connect Compression Gauge Adapter (ST333060) and compression gauge to the cylinder whose compression is to be checked.
Compression gauge and adapter(3) Crank the engine using the starter until the needle of the compression gauge stops moving, then read the pressure indication.
Measuring compression pressure(4) If the measurement is lower than the specified limit, perform an overhaul.
(a) Measure the compression pressure of every cylinder. Measuring the compression pressure of two or three cylinders and simply assuming the compression pressures of the other cylinders is dangerous.(b) The compression pressure varies with the engine speed, so it is important to take all measurements with the same engine speed.
2Unit: MPa {kgf/cm} (psi) Take measurements with an engine speed of 240 min-1.
(a) It is important to measure compression pressures regularly and to keep track of changes in them.(b) During the engine's run-in period and after an overhaul, the compression pressures will increase slightly as the piston rings, valve seats, and other parts fit snugly in position. The Pressures will then decrease as parts wear.
Troubleshooting
Overview
Diesel-engine fault symptoms tend to have multiple causes, which influence each other. Consequently, it is often difficult to locate a fault based on the symptoms. Particular care is required when diagnosing faults related to the injection pump, injectors, and compression pressures since such faults may produce the same symptoms.For the above-mentioned reasons, the inspection sequences in the troubleshooting charts on the following pages start with items where the likelihood of a fault is greatest or with items that are easiest to inspect.Owing to their structure and combustion method, diesel engines exhibit the characteristics listed below. Familiarize yourself with these characteristics before performing troubleshooting operations.* Distinctive combustion noise (diesel knock) is emitted during normal operation.* Some black smoke is emitted during high-load operation.* Torque vibration is significant owing to the high compression pressure and high torque.* Slight hunting occurs during rapid deceleration.* Some white smoke is emitted immediately after startup when the engine is cold.
(a) The injection pump cannot be adjusted without a pump tester. Do not attempt to adjust or disassemble the injection pump during troubleshooting operations.(b) To check the combustion conditions in each cylinder, undo the cylinder's injection pipes one at a time (undoing an injection pipe stops injection in that cylinder) and compare the resulting decreases in engine speed. Retighten each injection pipe before undoing the next one.
Difficult Starting
(1) Items to Check
Before performing inspections, check for the following problems:* Clogged air cleaner element* Coagulation of engine oil* Inferior fuel* Low cranking speed(2) Inspection
Knocking
Diesel engines emit a distinctive knocking sound owing to their combustion method. This sound is normal unless it is excessive(1) Items to Check
Before performing inspections, check for the following problems:* Clogged air cleaner element* Inferior fuel(2) Inspection
Overheating
(1) Items to Check
Before performing inspections, check for the following problems:* Low
Have questions with 101401-0830?
Group cross 101401-0830 ZEXEL
Isuzu
101401-0830
9 400 613 580
8943287690
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4BD1
4BD1
