Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101401-0790
1014010790
ISUZU
8944574770
8944574770
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101401-0790
1014010790
ISUZU
8944574770
8944574770
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.4
3.35
3.45
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.6
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
72.1
70.5
73.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
325
325
325
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
12.1
10.8
13.4
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.6)
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
72.1
71.1
73.1
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1+0.2
Pump speed
r/min
1500
1500
1500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
82.6
79.4
85.8
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1+0.1
Pump speed
r/min
500
500
500
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
53.6
49.6
57.6
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
(R1+0.1)
Pump speed
r/min
1100
1100
1100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
76.1
72.9
79.3
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_07
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
116
116
124
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1000+-50
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1600
Advance angle
deg.
2
1.5
2.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
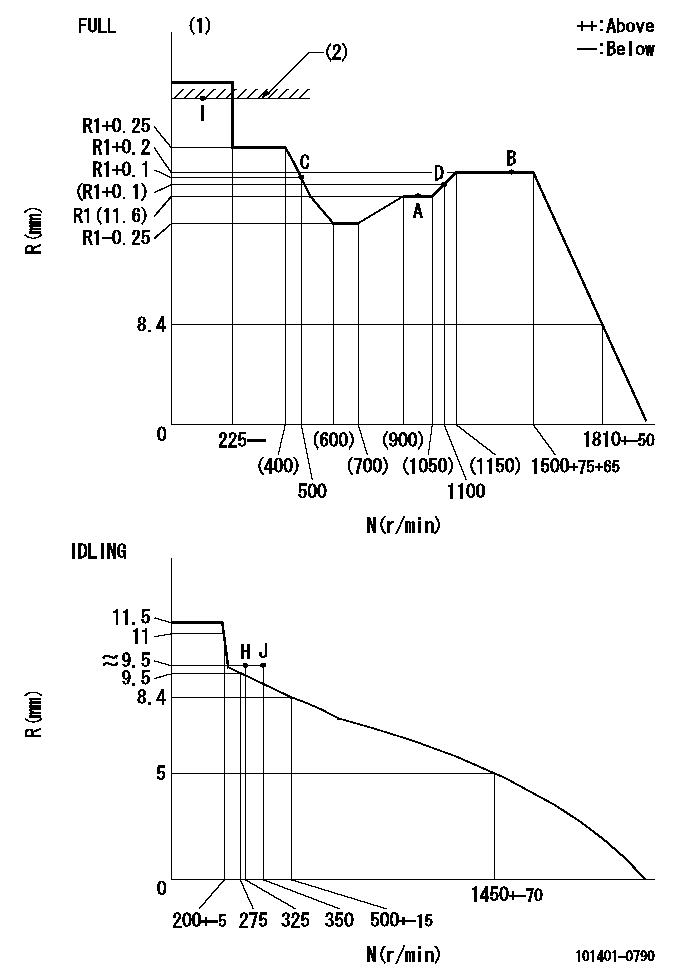
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
----------
T1=C52
----------
----------
T1=C52
----------
Speed control lever angle
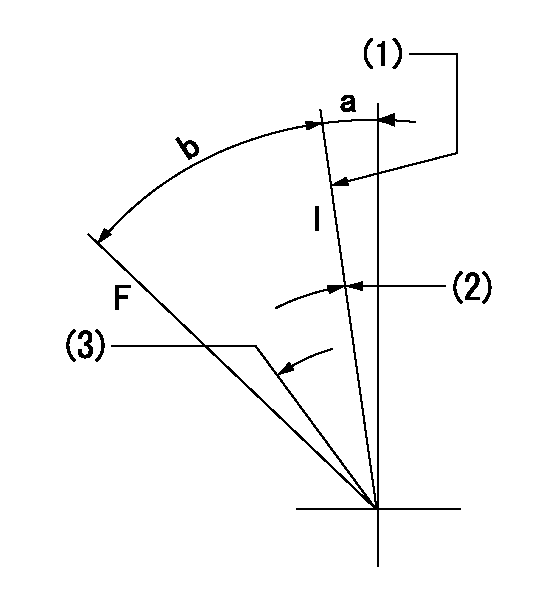
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
(2)The microswitch must turn ON when moved from the full side to contact the idle side stopper bolt.
(3)Confirm that the microswitch turns OFF at rack position = aa and speed = bb.
----------
aa=10.1mm bb=275r/min
----------
a=3.5deg+-5deg b=27deg+-3deg
----------
aa=10.1mm bb=275r/min
----------
a=3.5deg+-5deg b=27deg+-3deg
Stop lever angle
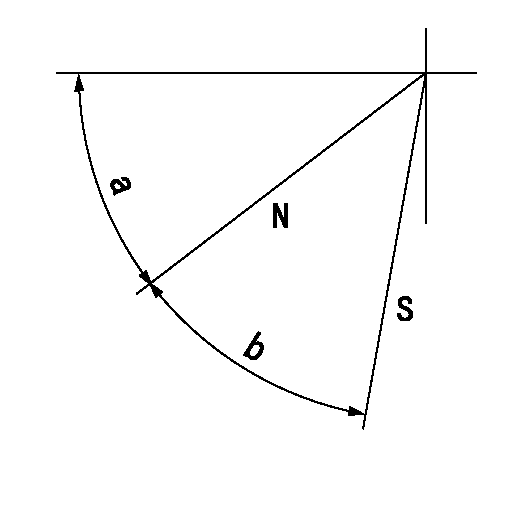
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=45deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=45deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
0000001501 ACS
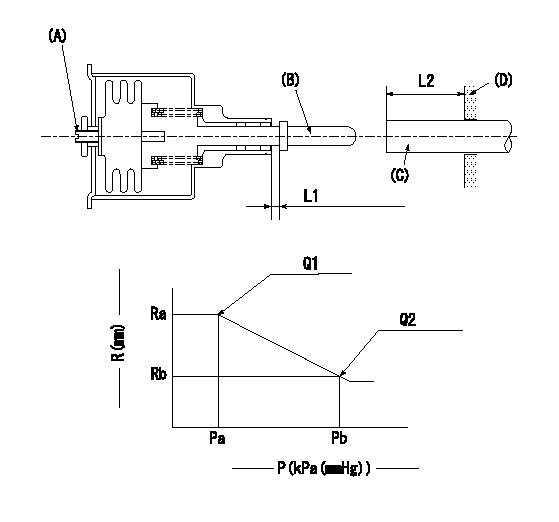
(A) Set screw
(B) Push rod 1
(C) Push rod 2
(D) Cover
1. Aneroid compensator unit adjustment
(1)Select the push rod 2 to obtain L2.
(2)Screw in (A) to obtain L1.
2. Adjustment when mounting the governor.
(1)Set the speed of the pump to N1 r/min and fix the control lever at the full set position.
(2)Screw in the aneroid compensator to obtain the performance shown in the graph above.
(3)As there is hysterisis, measure when the absolute pressure drops.
(4)Hysterisis must not exceed rack position = h1.
----------
N1=950r/min L1=(1.5)mm L2=11+-0.5mm h1=0.15mm
----------
Ra=R1(11.6)mm Rb=(R1-0.15)mm Pa=79.4+-2.7kPa(596+-20mmHg) Pb=70.1+-0.7kPa(526+-5mmHg) Q1=72.1+-1cm3/1000st Q2=69.8+-1.6cm3/1000st
----------
N1=950r/min L1=(1.5)mm L2=11+-0.5mm h1=0.15mm
----------
Ra=R1(11.6)mm Rb=(R1-0.15)mm Pa=79.4+-2.7kPa(596+-20mmHg) Pb=70.1+-0.7kPa(526+-5mmHg) Q1=72.1+-1cm3/1000st Q2=69.8+-1.6cm3/1000st
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark 'CC' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=13deg
----------
a=(100deg)
----------
aa=13deg
----------
a=(100deg)
Information:
Injection timing adjustment shim
Adjusting injection timing(3) Alternative Adjustment/Inspection ProcedureThe injection timing adjustment/inspection procedure in which the delivery valve is removed allows the flow of fuel to be verified clearly, but removing the delivery valve can allow dirt to enter the fuel system. With the procedure described below, it is possible to check the injection timing without removing the delivery valve.(a) Disconnect injection pipe No. 1 from the nozzle holder.
Disconnecting injection pipe No. 1(b) Slowly turn the crankshaft clockwise, and note the position of the IT mark at the point in time when fuel emerges from the end of the pipe. The timing indicated by the IT mark is retarded by approximately 1° relative to the actual injection timing, so this 1° difference must be taken into account in the shim selection. Air-bleed the fuel system before turning the crankshaft. 4. Injectors
4.1 Removal
Removing and installing injectors1 Fuel injection pipe2 Injector holder3 Injector4 Gasket
The fuel injection pipe nut should be tightened to the specified torque using a tool specially designed for the purpose.
4.2 Inspection and AdjustmentCheck each injector for the following points. If the result is not satisfactory, either repair or replace it according to conditions.(1) Injector Valve Opening Pressure(a) Install an injector on an injector tester. Move the handle up and down repeatedly to remove air from the injector.(b) While observing the pressure gauge, operate the handle at a rate of approximately one stroke per second. Record the reading.
Testing injector valve opening pressure The needle of the gauge moves slowly toward the higher pressure side and then wobbles while injection is taking place. Injector valve opening pressure corresponds to a pressure at which the gauge needle starts wobbling.(c) If the reading on the gauge does not correspond to the specified injector valve opening pressure of 21.6+10 MPa {220+100kgf/cm2} (3130+1420 psi), disassemble the injector and replace the washer with one of proper thickness.(d) A change of 0.1 mm (0.004 in.) in the washer thickness yields a change of 1.5 MPa {15 kgf/cm2} (213 psi).
Never expose any part of your body to the spray of fuel injected from the injector.
Adjusting injector valve opening pressure(2) Spray Condition(a) Operate the injector tester handle at a rate of approximately one stroke per second.(b) The spray pattern A in the drawing on the right is normal while all the other patterns are abnormal. The spray may be coarse and narrow, and some fuel may remain on the nozzle hole after injection. However, these conditions are typically observed during tests on a tester and thus do not indicate abnormal operation of the injector.(c) Operate the tester handle at a rate of approximately four to six strokes per second. The injector can be considered normal if fuel is injected evenly and at correct angles (see drawing) from all the four nozzle holes and fine atomization of fuel is observed in all sprays.
Inspecting spray condition(3) Leakage from InjectorsUse the injector tester to maintain a pressure 1-2 MPa {10-20 kgf/cm2} (142-285 psi) lower than the specified injector valve opening