Information injection-pump assembly
ZEXEL
101401-0705
1014010705
ISUZU
8944471897
8944471897
Rating:
Cross reference number
ZEXEL
101401-0705
1014010705
ISUZU
8944471897
8944471897
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-4920
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
127
107
147
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.3
1.1
1.5
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Rack position
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
After adjusting injection quantity. R=A
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
-
Rack position
11.9
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69.2
67.6
70.8
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-4
4
Basic
*
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
H
Rack position
9.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
275
275
275
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
9.4
8.1
10.7
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-14
14
Fixing the rack
*
Standard for adjustment of the maximum variation between cylinders
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
R1(11.9)
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
69.2
68.2
70.2
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_04
Adjusting point
B
Rack position
R1(11.9)
Pump speed
r/min
1600
1600
1600
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
77.9
74.7
81.1
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_05
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
R1-0.2
Pump speed
r/min
650
650
650
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
51.3
48.1
54.5
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_06
Adjusting point
I
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
150
150
150
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
90
90
98
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Timer adjustment
Pump speed
r/min
1375--
Advance angle
deg.
0
0
0
Remarks
Start
Start
Timer adjustment_02
Pump speed
r/min
1325
Advance angle
deg.
0.3
Timer adjustment_03
Pump speed
r/min
1575
Advance angle
deg.
5
4.5
5.5
Remarks
Finish
Finish
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
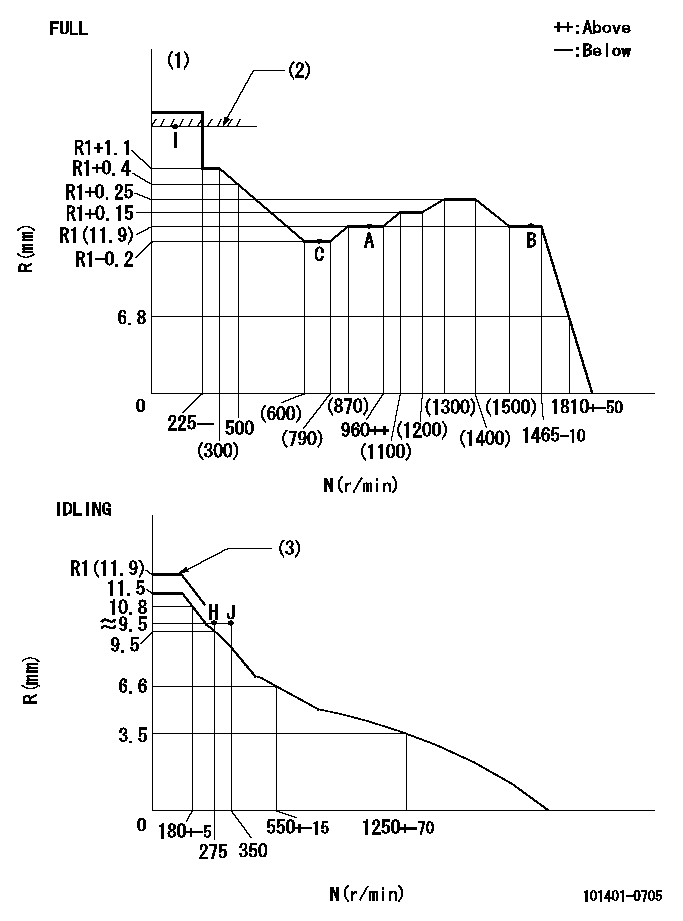
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Torque cam stamping: T1
(2)RACK LIMIT
(3)At delivery (at R = A, N = N1)
----------
T1=C38 N1=100r/min
----------
----------
T1=C38 N1=100r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle
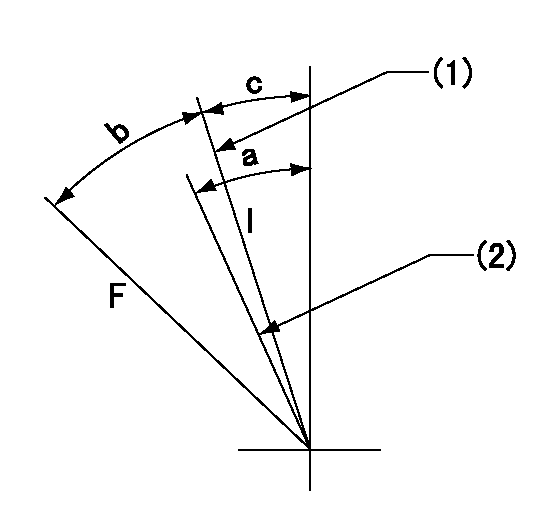
F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt set position 'H'
(2)Set the idle side stopper bolt at rack position = aa (at delivery).
----------
aa=R1(11.9)mm
----------
a=3deg+-5deg b=44deg+-3deg c=2.5deg+-5deg
----------
aa=R1(11.9)mm
----------
a=3deg+-5deg b=44deg+-3deg c=2.5deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle

N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=20deg+-5deg b=40deg+-5deg
Timing setting

(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of gear mark 'CC' at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)B.T.D.C.: aa
(4)-
----------
aa=14deg
----------
a=(100deg)
----------
aa=14deg
----------
a=(100deg)
Information:
COMPRESSION PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
1. Inspection Check to make sure -(1) The crankcase oil level is correct, and the air cleaner, starter and battery are all in normal condition.(2) The engine is at the normal operating temperature.2. Measurement (1) Move the control lever to a position for shutting off fuel supply.(2) Remove all glow plugs from the engine. Install the compression gauge and adapter (ST332270) combination to a cylinder on which the compression pressure is to be measured.
Compression gauge and adaptor
Measuring compression pressure(3) Turn the engine with the starter and read the gauge pressure at the instant the gauge pointer comes to stop.(4) If the gauge reading is below the limit, overhaul the engine.
a) Be sure to measure the compression pressure on all cylinders.b) The compression pressure varies with change of engine rpm. This makes it necessary to check engine rpm at the time of measuring the compression pressure.
a) It is important to measure the compression pressure at regular intervals to obtain the data on the gradual change of the compression pressure.b) The compression pressure would be slightly higher than the standard in a new or overhauled engine owing to break-in of the piston rings, valve seats, etc. It drops as the engine components wear down.
TROUBLESHOOTING
1. GeneralThe diagnosis of troubles, especially those caused by a faulty fuel injection pump or injection nozzles, or low compression pressure, can be difficult. It requires a careful inspection to determine not which item is the cause, but how many causes are contributing to the cause. Several causes may be contributing to a single trouble.On the following pages, there are troubleshooting charts on which engine troubles can be traced to their causes. Each chart has items to be verified ahead and suggested inspection procedure.Diesel engines exhibit some marked characteristics during operation. Knowing these characteristics will help minimize time lost in tracing engine troubles to their source. Following are the characteristics of diesel engines you should know about for diagnosis:* Combustion know (diesel knock)* Some black exhaust smoke (when the engine picks up load)* Vibration (due to high compression pressure and high torque)* Hunting (when the engine speed is quickly decreased)* Some white exhaust smoke (when the engine is cold, or shortly after the engine has been started) 2. Engine troubleshooting Problem 1: Hard starting(1) Items to be checked for ahead* Clogged air cleaner* Wrong oil grade for weather conditions * Poor quality fuel* Low cranking speed(2) Inspection procedure Problem 2: Fuel knockMore or less fuel knock occurs in diesel engines. This may be caused either by an excessively large delay period or by a too fast rate of fuel injection.(1) Items to be checked for ahead* Clogged air cleaner* Poor quality fuel(2) Inspection procedure Problem 3: Overheating(1) Items to be checked for aheadOverheating might also be caused by abnormal operating conditions. If the engine is overheating but its cooling system is not contributing to this trouble, it is necessary to check the difference between the ambient temperature and coolant temperature when the engine is in
1. Inspection Check to make sure -(1) The crankcase oil level is correct, and the air cleaner, starter and battery are all in normal condition.(2) The engine is at the normal operating temperature.2. Measurement (1) Move the control lever to a position for shutting off fuel supply.(2) Remove all glow plugs from the engine. Install the compression gauge and adapter (ST332270) combination to a cylinder on which the compression pressure is to be measured.
Compression gauge and adaptor
Measuring compression pressure(3) Turn the engine with the starter and read the gauge pressure at the instant the gauge pointer comes to stop.(4) If the gauge reading is below the limit, overhaul the engine.
a) Be sure to measure the compression pressure on all cylinders.b) The compression pressure varies with change of engine rpm. This makes it necessary to check engine rpm at the time of measuring the compression pressure.
a) It is important to measure the compression pressure at regular intervals to obtain the data on the gradual change of the compression pressure.b) The compression pressure would be slightly higher than the standard in a new or overhauled engine owing to break-in of the piston rings, valve seats, etc. It drops as the engine components wear down.
TROUBLESHOOTING
1. GeneralThe diagnosis of troubles, especially those caused by a faulty fuel injection pump or injection nozzles, or low compression pressure, can be difficult. It requires a careful inspection to determine not which item is the cause, but how many causes are contributing to the cause. Several causes may be contributing to a single trouble.On the following pages, there are troubleshooting charts on which engine troubles can be traced to their causes. Each chart has items to be verified ahead and suggested inspection procedure.Diesel engines exhibit some marked characteristics during operation. Knowing these characteristics will help minimize time lost in tracing engine troubles to their source. Following are the characteristics of diesel engines you should know about for diagnosis:* Combustion know (diesel knock)* Some black exhaust smoke (when the engine picks up load)* Vibration (due to high compression pressure and high torque)* Hunting (when the engine speed is quickly decreased)* Some white exhaust smoke (when the engine is cold, or shortly after the engine has been started) 2. Engine troubleshooting Problem 1: Hard starting(1) Items to be checked for ahead* Clogged air cleaner* Wrong oil grade for weather conditions * Poor quality fuel* Low cranking speed(2) Inspection procedure Problem 2: Fuel knockMore or less fuel knock occurs in diesel engines. This may be caused either by an excessively large delay period or by a too fast rate of fuel injection.(1) Items to be checked for ahead* Clogged air cleaner* Poor quality fuel(2) Inspection procedure Problem 3: Overheating(1) Items to be checked for aheadOverheating might also be caused by abnormal operating conditions. If the engine is overheating but its cooling system is not contributing to this trouble, it is necessary to check the difference between the ambient temperature and coolant temperature when the engine is in