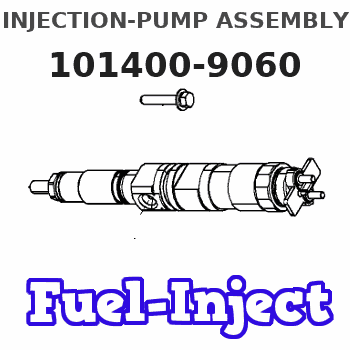
Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 612 485
9400612485
ZEXEL
101400-9060
1014009060
YANMAR
12995651020
12995651020
Rating:
Service parts 101400-9060 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
4.
SUPPLY PUMP
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
10.
NOZZLE AND HOLDER ASSY
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
13.
NOZZLE-HOLDER
14.
NOZZLE
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 612 485
9400612485
ZEXEL
101400-9060
1014009060
YANMAR
12995651020
12995651020
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
9 400 612 485
12995651020 YANMAR
INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY
4TNE98 K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
4TNE98 K 14BC INJECTION PUMP ASSY PE4A,5A, PE
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-1520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.3
Pump speed
r/min
1250
1250
1250
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
42.6
41.6
43.6
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
7.5+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
460
460
460
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
13
12
14
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
10.1++
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
85
80
90
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
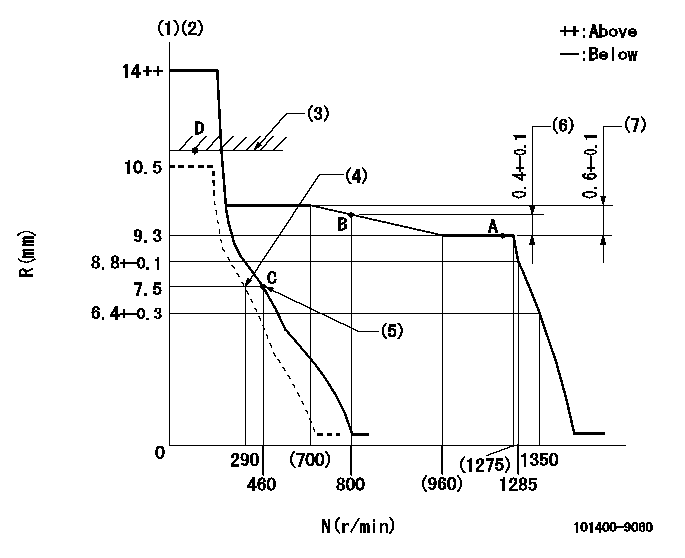
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Set idle sub-spring
(5)Main spring setting
(6)Rack difference from N = N1
(7)Rack difference between N = N2 and N = N3
----------
K=17 N1=1250r/min N2=1250r/min N3=450r/min
----------
----------
K=17 N1=1250r/min N2=1250r/min N3=450r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=18deg+-5deg b=28deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=18deg+-5deg b=28deg+-5deg
Stop lever angle
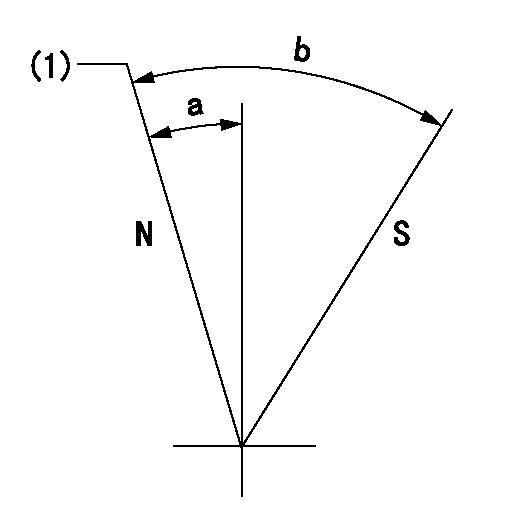
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
(1)Normal
----------
----------
a=7deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=7deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting
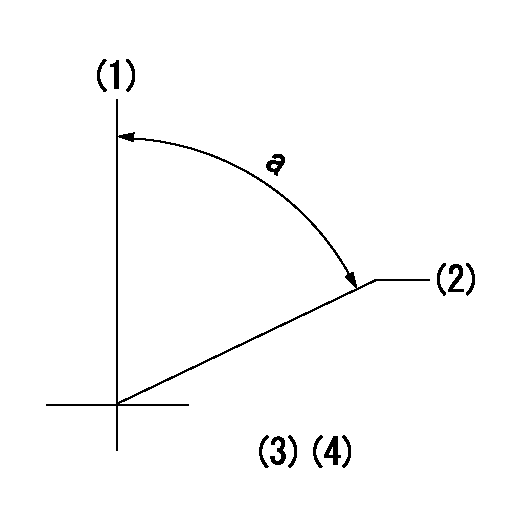
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of camshaft's key groove at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
Information:
Fault Finding Chart
Key to Fault Finding Chart
1. Battery capacity low.2. Bad electrical connections.3. Faulty starter motor.4. Incorrect grade of lubricating oil.5. Low cranking speed.6. Fuel tank empty.7. Faulty stop control operation.8. Blocked fuel feed pipe.9. Faulty fuel lift pump.10. Choked fuel filter.11. Restriction in air cleaner or induction system.12. Air in fuel system.13. Faulty fuel injection pump.14. Faulty atomisers or incorrect type.15. Incorrect use of cold start equipment.16. Faulty cold starting equipment.17. Broken fuel injection pump drive.18. Incorrect fuel pump timing.19. Incorrect valve timing.20. Poor compression.21. Blocked fuel tank vent.22. Incorrect type or grade of fuel.23. Sticking throttle or restricted movement.24. Exhaust pipe restriction.25. Cylinder head gasket leaking.26. Overheating.27. Cold running.28. Incorrect tappet adjustment.29. Sticking valves.30. Incorrect high pressure pipes.31. Worn cylinder bores.32. Pitted valves and seats.33. Broken, worn or sticking piston ring/s.34. Worn valve stems and guides.35. Overfull air cleaner or use of incorrect grade of oil.36. Worn or damaged bearings.37. Insufficient oil in sump.38. Inaccurate gauge.39. Oil pump worn.40. Pressure relief valve sticking open.41. Pressure relief valve sticking closed.42. Broken relief valve spring.43. Faulty suction pipe.44. Choked oil filter.45. Piston seizure/pick up.46. Incorrect piston height.47. Damaged fan.48. Faulty engine mounting (Housing).49. Incorrect aligned flywheel housing, or flywheel.50. Faulty thermostat.51. Restriction in water jacket.52. Loose fan belt.53. Choked radiator.54. Faulty water pump.55. Choked breather pipe.56. Damaged valve stem oil deflectors (if fitted).57. Coolant level too low.58. Blocked sump strainer.59. Broken valve spring.60. Fault in exhauster or vacuum pipe leaks.61. Turbocharger impeller damaged or dirty.62. Turbocharger lubricating oil seal leaks.63. Induction system leaks (turbocharged engines).
Key to Fault Finding Chart
1. Battery capacity low.2. Bad electrical connections.3. Faulty starter motor.4. Incorrect grade of lubricating oil.5. Low cranking speed.6. Fuel tank empty.7. Faulty stop control operation.8. Blocked fuel feed pipe.9. Faulty fuel lift pump.10. Choked fuel filter.11. Restriction in air cleaner or induction system.12. Air in fuel system.13. Faulty fuel injection pump.14. Faulty atomisers or incorrect type.15. Incorrect use of cold start equipment.16. Faulty cold starting equipment.17. Broken fuel injection pump drive.18. Incorrect fuel pump timing.19. Incorrect valve timing.20. Poor compression.21. Blocked fuel tank vent.22. Incorrect type or grade of fuel.23. Sticking throttle or restricted movement.24. Exhaust pipe restriction.25. Cylinder head gasket leaking.26. Overheating.27. Cold running.28. Incorrect tappet adjustment.29. Sticking valves.30. Incorrect high pressure pipes.31. Worn cylinder bores.32. Pitted valves and seats.33. Broken, worn or sticking piston ring/s.34. Worn valve stems and guides.35. Overfull air cleaner or use of incorrect grade of oil.36. Worn or damaged bearings.37. Insufficient oil in sump.38. Inaccurate gauge.39. Oil pump worn.40. Pressure relief valve sticking open.41. Pressure relief valve sticking closed.42. Broken relief valve spring.43. Faulty suction pipe.44. Choked oil filter.45. Piston seizure/pick up.46. Incorrect piston height.47. Damaged fan.48. Faulty engine mounting (Housing).49. Incorrect aligned flywheel housing, or flywheel.50. Faulty thermostat.51. Restriction in water jacket.52. Loose fan belt.53. Choked radiator.54. Faulty water pump.55. Choked breather pipe.56. Damaged valve stem oil deflectors (if fitted).57. Coolant level too low.58. Blocked sump strainer.59. Broken valve spring.60. Fault in exhauster or vacuum pipe leaks.61. Turbocharger impeller damaged or dirty.62. Turbocharger lubricating oil seal leaks.63. Induction system leaks (turbocharged engines).