Information injection-pump assembly
BOSCH
9 400 610 388
9400610388
ZEXEL
101400-9011
1014009011
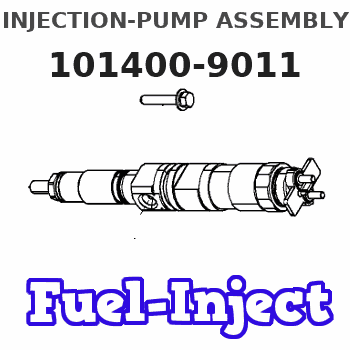
Rating:
Service parts 101400-9011 INJECTION-PUMP ASSEMBLY:
1.
_
4.
SUPPLY PUMP
5.
AUTOM. ADVANCE MECHANIS
6.
COUPLING PLATE
7.
COUPLING PLATE
8.
_
9.
_
10.
NOZZLE AND HOLDER ASSY
11.
Nozzle and Holder
12.
Open Pre:MPa(Kqf/cm2)
13.
NOZZLE-HOLDER
14.
NOZZLE
15.
NOZZLE SET
Cross reference number
BOSCH
9 400 610 388
9400610388
ZEXEL
101400-9011
1014009011
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Calibration Data:
Adjustment conditions
Test oil
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
1404 Test oil ISO4113 or {SAEJ967d}
Test oil temperature
degC
40
40
45
Nozzle and nozzle holder
105780-8140
Bosch type code
EF8511/9A
Nozzle
105780-0000
Bosch type code
DN12SD12T
Nozzle holder
105780-2080
Bosch type code
EF8511/9
Opening pressure
MPa
17.2
Opening pressure
kgf/cm2
175
Injection pipe
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Outer diameter - inner diameter - length (mm) mm 6-2-600
Overflow valve
131424-1520
Overflow valve opening pressure
kPa
157
123
191
Overflow valve opening pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.25
1.95
Tester oil delivery pressure
kPa
157
157
157
Tester oil delivery pressure
kgf/cm2
1.6
1.6
1.6
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection timing adjustment
Direction of rotation (viewed from drive side)
Right R
Right R
Injection order
1-3-4-2
Pre-stroke
mm
3.6
3.55
3.65
Beginning of injection position
Drive side NO.1
Drive side NO.1
Difference between angles 1
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Cal 1-3 deg. 90 89.5 90.5
Difference between angles 2
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Cal 1-4 deg. 180 179.5 180.5
Difference between angles 3
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Cyl.1-2 deg. 270 269.5 270.5
Injection quantity adjustment
Adjusting point
A
Rack position
9.8
Pump speed
r/min
950
950
950
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
64.5
63.5
65.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-2.5
2.5
Basic
*
Fixing the lever
*
Injection quantity adjustment_02
Adjusting point
C
Rack position
6.7+-0.5
Pump speed
r/min
590
590
590
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
10.5
9.5
11.5
Max. variation between cylinders
%
0
-15
15
Fixing the rack
*
Injection quantity adjustment_03
Adjusting point
D
Rack position
-
Pump speed
r/min
100
100
100
Average injection quantity
mm3/st.
70
65
75
Fixing the lever
*
Rack limit
*
Test data Ex:
Governor adjustment
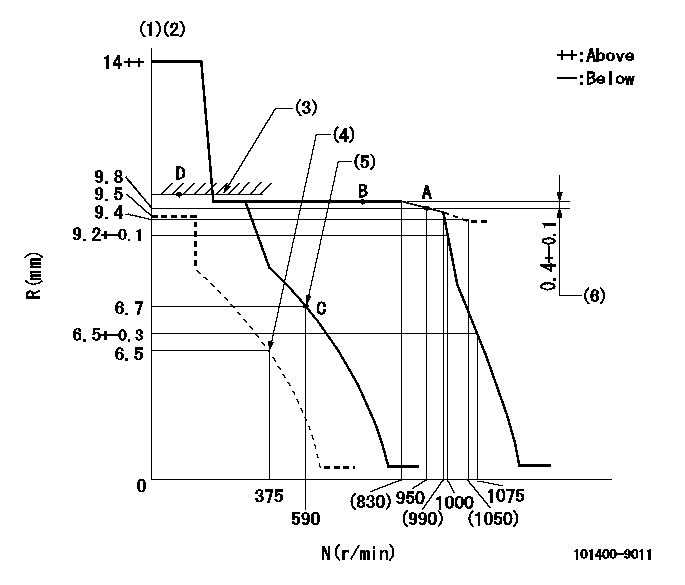
N:Pump speed
R:Rack position (mm)
(1)Target notch: K
(2)Tolerance for racks not indicated: +-0.05mm.
(3)RACK LIMIT
(4)Set idle sub-spring
(5)Main spring setting
(6)Rack difference from N = N1
----------
K=14 N1=750r/min
----------
----------
K=14 N1=750r/min
----------
Speed control lever angle

F:Full speed
I:Idle
(1)Stopper bolt setting
----------
----------
a=(6deg)+-5deg b=(16deg)+-5deg
----------
----------
a=(6deg)+-5deg b=(16deg)+-5deg
Stop lever angle
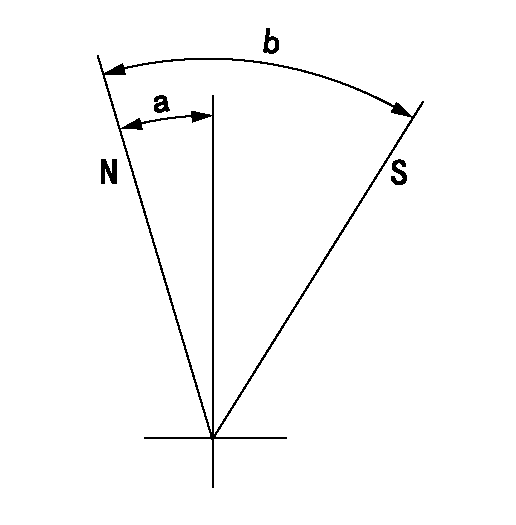
N:Pump normal
S:Stop the pump.
----------
----------
a=7deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
----------
----------
a=7deg+-5deg b=53deg+-5deg
Timing setting
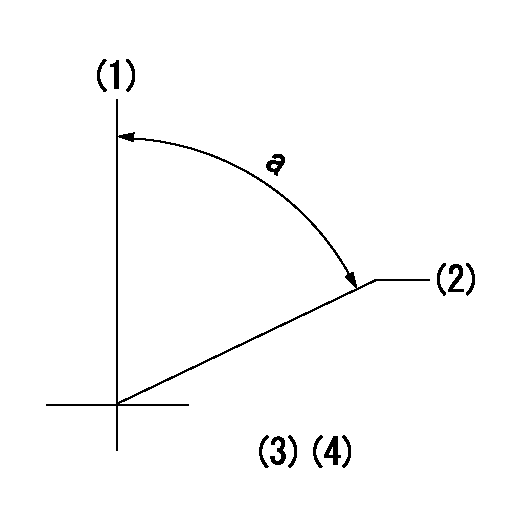
(1)Pump vertical direction
(2)Position of camshaft's key groove at No 1 cylinder's beginning of injection
(3)-
(4)-
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
----------
----------
a=(60deg)
Information:
Engine Serial Numbers
1-1The serial No. is stamped both on the maker's nameplate (Fig. 1-1) and the crankcase.
1-3Engines of the F3/4/5/6L type have the serial number stamped at the back of the oil filler neck, on the flange for mounting the housing of the fuel injection pump.Fig. 1-3Maker's Nameplate
In addition to the engine serial No., the plate indicates the particular engine model and version respectively. Typical example BF6L 913 C:B = Engine with turbochargerF = Automotive or industrial engine6 = Number of cylindersL = Air-cooled9 = Number of series13 = Stroke of piston in cmThe suffix letters of the engine model designation mean:C = With charge air coolerG = Engine for fork-lift truckT = Mildly turbochargedW = Two-stage combustion system (swirl chamber)Further data of the nameplate:Rated power in kW (HP) and speed in rev/min. Letter "A" denotes continuous power (with overload capacity), both according to DIN 6270.De-rated industrial engines have an additional rating plate.The rating for automotive engines refers to DIN 70020.General Notes On Repair
To be successful, every repair job calls for precision workmanship, in clean and neat surroundings.
1-5The "front end" of the engine is understood to be the end opposite the flywheel, and the other engine faces are designated accordingly. Thus: Cylinder No. 1 is at the rear end = at the flywheel end. The cylinder numbers are applied to the crankcase, below the cylinder seating area. The sense of rotation of the engine is anti-clockwise, when facing the flywheel.Fig. 1-5
1-6The parts of the crankshaft assembly, timing gear, cylinders, pistons and cylinder heads should be numbered in sequence, unless they are already marked. The numbering should commence at the flywheel end.Fig. 1-6As the parts are dismantled, place them where they will not get damaged. Components that are subject to wear should be kept apart and should be gauged individually. If the low tolerances are exceeded, the components have to be replaced or rectified. In any case, fit new gaskets, packings and O-seals.The numbers of spare parts should be taken from the part number catalogue for the respective engine type. A good repair job that is to ensure satisfactory engine performance essentially calls for the use of genuine DEUTZ spare parts.Should bearing or pistons be damaged, the crankshaft and connecting rods should be inspected for cracks, if possible by the Magnaflux testing method. It is very important that the cause of the damage is established. Testing, repairs and/or reworking can be undertaken by the manufacturers or their appointed repair shops.
1-8For the repair work to be carried out on the removed engine, mounting on a swivelling assembly stand, special fixture No. 6067, is recommended.Fig. 1-8Tightening Instructions For Bolts And Studs
All bolts and studs tabulated shall first be hand-tightened to approx 30 Nm and then locked down alternately in stages until the specified angle degrees are obtained. Before assembling the bolts and studs, wet the threads and the bearing faces of the heads with motor oil. 1. Preloading
1-9Hold wrench so the thumb touches the end.Fig. 1-9Use a torque wrench for torques
1-1The serial No. is stamped both on the maker's nameplate (Fig. 1-1) and the crankcase.
1-3Engines of the F3/4/5/6L type have the serial number stamped at the back of the oil filler neck, on the flange for mounting the housing of the fuel injection pump.Fig. 1-3Maker's Nameplate
In addition to the engine serial No., the plate indicates the particular engine model and version respectively. Typical example BF6L 913 C:B = Engine with turbochargerF = Automotive or industrial engine6 = Number of cylindersL = Air-cooled9 = Number of series13 = Stroke of piston in cmThe suffix letters of the engine model designation mean:C = With charge air coolerG = Engine for fork-lift truckT = Mildly turbochargedW = Two-stage combustion system (swirl chamber)Further data of the nameplate:Rated power in kW (HP) and speed in rev/min. Letter "A" denotes continuous power (with overload capacity), both according to DIN 6270.De-rated industrial engines have an additional rating plate.The rating for automotive engines refers to DIN 70020.General Notes On Repair
To be successful, every repair job calls for precision workmanship, in clean and neat surroundings.
1-5The "front end" of the engine is understood to be the end opposite the flywheel, and the other engine faces are designated accordingly. Thus: Cylinder No. 1 is at the rear end = at the flywheel end. The cylinder numbers are applied to the crankcase, below the cylinder seating area. The sense of rotation of the engine is anti-clockwise, when facing the flywheel.Fig. 1-5
1-6The parts of the crankshaft assembly, timing gear, cylinders, pistons and cylinder heads should be numbered in sequence, unless they are already marked. The numbering should commence at the flywheel end.Fig. 1-6As the parts are dismantled, place them where they will not get damaged. Components that are subject to wear should be kept apart and should be gauged individually. If the low tolerances are exceeded, the components have to be replaced or rectified. In any case, fit new gaskets, packings and O-seals.The numbers of spare parts should be taken from the part number catalogue for the respective engine type. A good repair job that is to ensure satisfactory engine performance essentially calls for the use of genuine DEUTZ spare parts.Should bearing or pistons be damaged, the crankshaft and connecting rods should be inspected for cracks, if possible by the Magnaflux testing method. It is very important that the cause of the damage is established. Testing, repairs and/or reworking can be undertaken by the manufacturers or their appointed repair shops.
1-8For the repair work to be carried out on the removed engine, mounting on a swivelling assembly stand, special fixture No. 6067, is recommended.Fig. 1-8Tightening Instructions For Bolts And Studs
All bolts and studs tabulated shall first be hand-tightened to approx 30 Nm and then locked down alternately in stages until the specified angle degrees are obtained. Before assembling the bolts and studs, wet the threads and the bearing faces of the heads with motor oil. 1. Preloading
1-9Hold wrench so the thumb touches the end.Fig. 1-9Use a torque wrench for torques