Information governor
BOSCH
9 420 611 711
9420611711
ZEXEL
105419-2610
1054192610
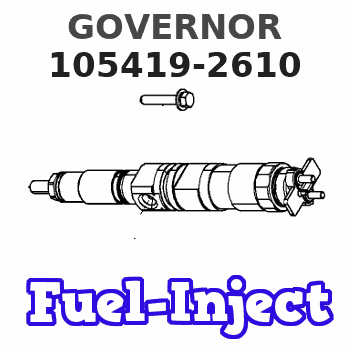
Rating:
Scheme ###:
| 1. | [1] | 154000-6400 | GOVERNOR HOUSING |
| 3. | [1] | 029632-5070 | O-RING |
| 4. | [1] | 154007-2900 | CAPSULE |
| 6. | [1] | 154007-0200 | ADAPTOR |
| 7. | [1] | 020018-1840 | BLEEDER SCREW M8P1.25L18 |
| 9. | [1] | 154350-1900 | PLATE |
| 10. | [6] | 029010-6810 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 12. | [1] | 154010-0100 | FLAT-HEAD SCREW |
| 13. | [2] | 154011-0100 | HEXAGON NUT |
| 13. | [2] | 154011-0100 | HEXAGON NUT |
| 14. | [1] | 154012-1720 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 15. | [1] | 014110-8440 | LOCKING WASHER |
| 35. | [1] | 154500-3020 | GOVERNOR COVER |
| 35/2. | [1] | 154321-0400 | BUSHING |
| 38. | [1] | 154031-0100 | FLAT-HEAD SCREW |
| 39. | [1] | 013020-6020 | UNION NUT M6P1H5 |
| 47. | [2] | 154036-0300 | CAPSULE |
| 47. | [2] | 154036-0300 | CAPSULE |
| 51. | [2] | 020106-5040 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 53. | [1] | 154010-0100 | FLAT-HEAD SCREW |
| 56. | [4] | 020106-3840 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 65. | [1] | 155404-1900 | CAP |
| 80. | [1] | 154063-4600 | COVER |
| 82. | [2] | 029020-6210 | BLEEDER SCREW |
| 83. | [2] | 020006-1640 | BLEEDER SCREW M6P1L16 4T |
| 100. | [1] | 154100-9720 | FLYWEIGHT ASSEMBLY |
| 101. | [1] | 025803-1610 | WOODRUFF KEY |
| 102. | [1] | 029321-2020 | LOCKING WASHER |
| 103. | [1] | 029231-2030 | UNION NUT |
| 117. | [1] | 154123-0120 | SLIDING PIECE |
| 118/1. | [0] | 029311-0010 | SHIM D14&10.1T0.2 |
| 118/1. | [0] | 029311-0180 | SHIM D14&10.1T0.3 |
| 118/1. | [0] | 029311-0190 | SHIM D14&10.1T0.40 |
| 118/1. | [0] | 029311-0210 | SHIM D14&10.1T1 |
| 118/1. | [0] | 139410-0000 | SHIM D14.0&10.1T0.5 |
| 118/1. | [0] | 139410-0100 | SHIM D14.0&10.1T1.5 |
| 118/1. | [0] | 139410-3000 | SHIM D14&10.1T2.0 |
| 118/1. | [0] | 139410-3100 | SHIM D14&10.1T3.0 |
| 118/1. | [0] | 139410-3200 | SHIM D14&10.1T4.0 |
| 130. | [1] | 154150-2700 | GOVERNOR SPRING |
| 132. | [1] | 154154-4200 | COILED SPRING |
| 135. | [1] | 154158-1220 | HEADLESS SCREW |
| 136. | [1] | 154011-1700 | UNION NUT |
| 137. | [2] | 026512-1540 | GASKET D15.4&12.2T1.50 |
| 138. | [1] | 154159-1200 | CAP NUT |
| 140. | [1] | 154177-1520 | HEADLESS SCREW |
| 141. | [1] | 029201-6010 | UNION NUT |
| 150. | [1] | 154200-7220 | SWIVELLING LEVER |
| 151. | [1] | 154204-3000 | BUSHING |
| 152. | [2] | 029631-8020 | O-RING |
| 152. | [2] | 029631-8020 | O-RING |
| 153. | [2] | 016010-1640 | LOCKING WASHER |
| 153. | [2] | 016010-1640 | LOCKING WASHER |
| 154. | [1] | 139611-0000 | PACKING RING |
| 155. | [1] | 139411-0000 | SHIM |
| 156. | [0] | 029311-1070 | SHIM D16&11T0.5 |
| 157. | [1] | 154204-3100 | BUSHING |
| 159. | [1] | 025803-1310 | WOODRUFF KEY |
| 160. | [1] | 154206-2800 | BUSHING |
| 161. | [0] | 154206-0200 | PLAIN WASHER D19.5&11.2T1.0 |
| 170. | [1] | 154210-0820 | FORK LEVER |
| 174. | [1] | 154230-3920 | STRAP |
| 175. | [1] | 016010-0540 | LOCKING WASHER |
| 181. | [1] | 154236-1500 | TENSIONING LEVER |
| 182. | [1] | 154237-0100 | BEARING PIN |
| 190. | [1] | 154395-0920 | CONTROL LEVER |
| 191. | [1] | 154307-4100 | CONTROL LEVER |
| 192. | [1] | 020006-1640 | BLEEDER SCREW M6P1L16 4T |
| 195. | [1] | 154314-0200 | COILED SPRING |
| 201. | [1] | 029631-0030 | O-RING &9.8W2.3 |
| 203. | [1] | 154322-0100 | CAP |
| 207. | [1] | 154326-5120 | CONTROL LEVER |
| 208. | [1] | 154327-7300 | COILED SPRING |
| 211/1. | [0] | 029311-0520 | SHIM D20.8&10.3T0.2 |
| 211/1. | [0] | 029311-0530 | SHIM D20.8&10.3T0.25 |
| 211/1. | [0] | 029311-0540 | SHIM D20.8&10.3T0.3 |
| 211/1. | [0] | 029311-0550 | SHIM D20.8&10.3T0.35 |
| 211/1. | [0] | 029311-0560 | SHIM D20.8&10.3T0.4 |
| 211/1. | [0] | 029311-0570 | SHIM D20.8&10.3T0.5 |
| 236. | [1] | 154390-0000 | GASKET |
| 237. | [1] | 154390-0300 | GASKET |
| 238. | [1] | 029635-2020 | O-RING |
Include in #1:
101441-9830
as GOVERNOR
Cross reference number
Zexel num
Bosch num
Firm num
Name
Information:
Proper operation and maintenance are key factors in obtaining the maximum life and economy of the engine. Following the directions in this manual will lower operating costs.After the engine is started and the cold idle operation is completed, the truck can be operated at low speed and low power. The engine will reach normal operating temperature faster when driven at low speed and low power demand than when idled at no load. Typically the engine should be up to operating temperature by just driving through the yard toward the open road.Engine Operation
* Begin operating the engine at low load. After normal oil pressure is reached and the temperature gauge begins to move, the engine may be operated at full load.* To get the vehicle in motion, use a gear that will result in a smooth, easy start without increasing engine speed above low idle or slipping the clutch. Engage the clutch smoothly. Abrupt or jerky starts put stress on the drive train and waste fuel.* Use progressive shifting to reduce fuel consumption. Progressive shifting is using only the rpm required to make an upshift into the next gear. The amount of rpm required to make an upshift increases as the truck speed increases unless upshifts are made on upgrades. Experience with your truck will show you how much rpm is required to make upshifts under various conditions.* If the truck can be operated in a higher gear after the desired speed is reached, select the highest gear available that will pull the load. By following this recommendation, you will lower your fuel costs, since your engine will be operating at the lowest rpm required to pull the load.Uphill Operation
On upgrades, begin downshifting when the engine rpm starts to approach peak torque (1100-1200 rpm) speed. Fuel economy will be best if you let the engine lug back to around this speed before you downshift. Downshift until a gear is reached in which the engine will pull the load. Allowing the engine to lug below peak torque is permissible if the truck is cresting the top of a hill without downshifting.However, note that extended operation in a lug condition will raise exhaust temperature and cylinder pressure and can lead to reduced engine life.Downhill Operation
Do NOT allow the engine rpm to exceed 2300 rpm, engine damage can result. If equipped with an exhaust brake, do not exceed 2100 rpm.
* When operating the vehicle downhill, do not coast or put the transmission in NEUTRAL.* Select the correct gear that does not allow the engine speed (rpm) to exceed the limits above and use the engine retarder and/or brakes to limit the speed of the truck.* A simple rule to follow is to select the same gear that would be required to go up the grade. However, DO NOT allow the engine to overspeed.For more information on economical operation of this engine, refer to form LEDT5092, Driving Techniques for Maximum Fuel Economy.
* Begin operating the engine at low load. After normal oil pressure is reached and the temperature gauge begins to move, the engine may be operated at full load.* To get the vehicle in motion, use a gear that will result in a smooth, easy start without increasing engine speed above low idle or slipping the clutch. Engage the clutch smoothly. Abrupt or jerky starts put stress on the drive train and waste fuel.* Use progressive shifting to reduce fuel consumption. Progressive shifting is using only the rpm required to make an upshift into the next gear. The amount of rpm required to make an upshift increases as the truck speed increases unless upshifts are made on upgrades. Experience with your truck will show you how much rpm is required to make upshifts under various conditions.* If the truck can be operated in a higher gear after the desired speed is reached, select the highest gear available that will pull the load. By following this recommendation, you will lower your fuel costs, since your engine will be operating at the lowest rpm required to pull the load.Uphill Operation
On upgrades, begin downshifting when the engine rpm starts to approach peak torque (1100-1200 rpm) speed. Fuel economy will be best if you let the engine lug back to around this speed before you downshift. Downshift until a gear is reached in which the engine will pull the load. Allowing the engine to lug below peak torque is permissible if the truck is cresting the top of a hill without downshifting.However, note that extended operation in a lug condition will raise exhaust temperature and cylinder pressure and can lead to reduced engine life.Downhill Operation
Do NOT allow the engine rpm to exceed 2300 rpm, engine damage can result. If equipped with an exhaust brake, do not exceed 2100 rpm.
* When operating the vehicle downhill, do not coast or put the transmission in NEUTRAL.* Select the correct gear that does not allow the engine speed (rpm) to exceed the limits above and use the engine retarder and/or brakes to limit the speed of the truck.* A simple rule to follow is to select the same gear that would be required to go up the grade. However, DO NOT allow the engine to overspeed.For more information on economical operation of this engine, refer to form LEDT5092, Driving Techniques for Maximum Fuel Economy.
